在做ACM题的时候我们常常会遇到一类题:动态规划。
初学者常常觉得动态规划难以理解,并且用到动态规划的题往往能用递归解决,但我们知道,递归往往用时较长,而且动态规划的思想很值得我们借鉴学习,所以,动态规划还是很有必要了解学习的。
和以前一样,我将尝试用一种通俗易懂的方式解释动态规划的思想。
一、递归
在解释动态规划之前,有必要先了解递归。
试看这么一道题:
Leetcode #62. Unique Paths
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?

分析这道题,就会得到某一点的路径数量 f[x][y]=f[x-1][y]+f[x][y-1],也就是说我们在(x,y)点只能有两种选择,一种是向右走,一种是向下走,分别是 f[x-1][y] 和f[x][y-1]。
很明显,我们可以用dfs深搜递归得到答案。
/* 深搜 runtime exceeded */ class Solution { public: int dfs(int m,int n){ if(m<1||n<1) return 0; if(m==1&&n==1) return 1; return dfs(m-1,n)+dfs(m,n-1); } int uniquePaths(int m, int n) { return dfs(m,n); } };
但很可惜,只用这样的递归的话在leetcode上面提交是会“runtime exceeded"的,我们需要优化一下,如何优化呢?认真分析我们会发现在递归的过程中有很多是重复的过程。
比如说 向右走一步(x-1)再向下走一步(y-1) 和 向下走一步(y-1)再向右走一步(x-1) 走到的位置是相同的,但是我们在两个过程中仍然重复的去求了 f[x-1][y-1]的路径数。
这时候我们再想:如果有一个”备忘录“能记住我们曾经求得的路径数就好了,这样便避免了重复过程。
/* 深搜+备忘录(用一个cache作缓存) 0ms 28.59% */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> cache; int dfs(int m,int n){ if(m<0||n<0) return 0; if(m==0||n==0) return 1; if(cache[m][n]>0) return cache[m][n]; return cache[m][n]=dfs(m-1,n)+dfs(m,n-1); } int uniquePaths(int m, int n) { cache=vector<vector<int>>(m,vector<int>(n,0)); cache[0][0]=1; return dfs(m-1,n-1); } };
这里用了一个cache二维数组当作“备忘录”,leetcode上AC。
二、动态规划
既然我们可以自顶向下的递归得到答案,自然我们也可以自底向上的用动态规划得到答案。
根据前面的公式,f[x][y]=f[x-1]f[y]+f[x]+f[y-1],说明某一位置的路径数与它下面一位的路径数和右边一位的路径数有关,所以在最下一行的路径数全为1,因为最下一行的下面没有路可走。
如图所示:
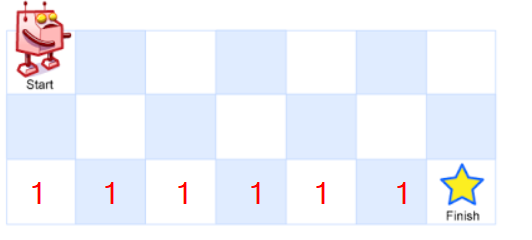
而且finish的上面一格路径也为1(只有一条路,就是向下)。
这样对于第二行来说,路径数就能确定了(因为路径数=右边的+下面的)。
如图:
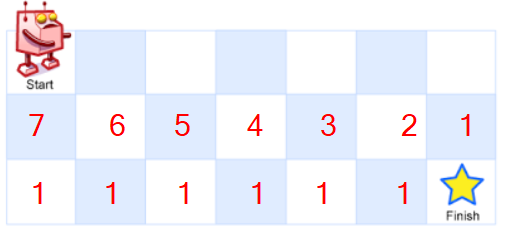
第二行确定了,第一行也就自然确定了。
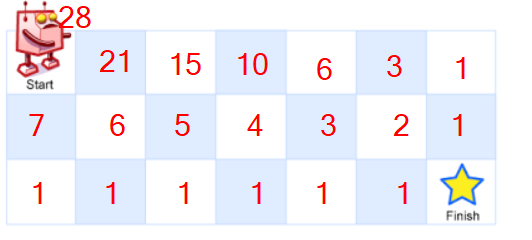
所以start位置的路径数也就确定了,这就是动态规划解决此题的整个过程。
并且,在实际写代码的过程中,我们不必用一个二维数组来存放数据,只需用一个滚动数组每次更新数据即可。
即 f[j]=f[j]+f[j+1]
代码如下:
class Solution { public: //动态规划 int uniquePaths(int m, int n) { vector<int> nums(n,0); nums[0]=1; while(m--){ for(int cnt=1;cnt<n;cnt++) nums[cnt]+=nums[cnt-1]; } return nums[n-1]; } };
三、总结
如此我们便得到用动态规划解题的一般过程:
1. 确定状态转换方程,在这题里,方程是:f[x][y]=f[x-1]f[y]+f[x]+f[y-1]。
2.确定初始状态的值。 最下面一行全部初始化为1。
3.解题
四、其它例题
leetcode# 64. Minimum Path Sum
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example 1:
[[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]]
Given the above grid map, return 7. Because the path 1→3→1→1→1 minimizes the sum.
/*Solution 1:dfs+备忘录 9ms 20.82% 1.注意到这里定义了两个函数dfs 和getOrUpdate,参考前面的例题,这里因为每一步都有权重的关系,仅用一个函数是做不出来的。 2.注意到备忘录的初始化与前面不同,初始化每个都为-1,也是因为权重的关系,权重可能为0 3.if(m<0||n<0) 注意返回的是INT_MAX而不是0 */ class Solution { public: //dfs+备忘录 vector<vector<int>> cache; int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid,int m,int n){ if(m<0||n<0) return INT_MAX; if(m==0&&n==0) return grid[m][n]; return min(getOrUpdate(grid,m-1,n),getOrUpdate(grid,m,n-1))+grid[m][n]; } int min(int m,int n){ return m<n?m:n; } int getOrUpdate(vector<vector<int>>&grid,int m,int n){ if(m<0||n<0) return INT_MAX; if(m==0&&n==0) return grid[m][n]; if(cache[m][n]>=0) return cache[m][n]; return cache[m][n]=dfs(grid,m,n); } int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int m=grid.size(); if(m<=0) return 0; int n=grid[0].size(); cache=vector<vector<int>>(m,vector<int>(n,-1)); return dfs(grid,m-1,n-1); } }; /* Solution 2: 动态规划 9ms 20.82% */ class Solution { public: //动态规划 // ans[i][j]=min(ans[i][j-1],ans[i-1][j])+grid[i][j] int min(int m,int n){ return m<n?m:n; } int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int m=grid.size(); if(m<=0) return 0; int n=grid[0].size(); vector<int> ans(n,0); ans=grid[m-1]; for(int cnt=n-2;cnt>=0;cnt--){ ans[cnt]+=ans[cnt+1]; } int i=m; for(int i=m-2;i>=0;i--){ ans[n-1]+=grid[i][n-1]; for(int j=n-2;j>=0;j--){ ans[j]=min(ans[j],ans[j+1])+grid[i][j]; } } return ans[0]; } };