前面的章节我们学会了如何解析语言、构建AST,如何访问重写AST,有了这些基础,我们可以开始进行“语义分析”了。
在分析语义的一个基本方面是要追踪“符号”,符号是语句定义的变量、函数,我们通过建立一种叫做“符号表”的基础结构来完成此项工作。
有两种模式的符号表:
- Pattern 16, Symbol Table for Monolithic Scope,所有的符号存在于单一的作用域内,早期的BASIC使用这种模式;
- Pattern 17, Symbol Table for Nested Scopes,符号存在于多个作用域,”作用域“之间可以嵌套,C语言使用这种模式;
收集语言实体信息
先看一段C++代码:
class T { ... }; // define class T
T f() { ... } // define function f returning type T
int x; // define variable x of type int
这个段代码实际上定义了3个符号,在一个语言处理程序里面,可能以下面的方式来收集信息:
Type c = new ClassSymbol("T");
MethodSymbol m = new MethodSymbol("f", c);
Type intType = new BuiltInTypeSymbol("int");
VariableSymbol v = new VariableSymbol("x", intType);
每个符号都包含了以下几项信息:
- 名字:一般是一个标记符,也有可能是一个操作符;
- 类别:类、函数、变量;
- 类型:类型允许语言程序判定表达式的有效性,静态类型的语言在编译时做类型检查,动态类型的语言延迟到运行时。
符号表实现用一个class来表示一个”类别“,包含”名字“和”类型“字段:
public class Symbol {
public String name; // All symbols at least have a name public
Type type; // Symbols have types
}
public class VariableSymbol extends Symbol {
public VariableSymbol(String name, Type type) { super(name, type); }
}
出于一致性考虑,Class和Struct类别的符号也从Symbol集成,为了区别于其他类别的符号,我们通过一个Type接口来给符号打个标签:
public class BuiltInTypeSymbol extends Symbol implements Type {
public BuiltInTypeSymbol(String name) { super(name);
}
public interface Type { public String getName(); }
}
Type接口本身并不包含任何有意义的内容,它仅仅是一个标签来说明这个Symbol能承担某种角色。
符号作用域
一个作用域是一个代码有明确范围的代码区域,对符号定义进行分组。比如类作用域将成员定义分成一个组;函数作用域将参数变量、局部变脸分成一个组。
作用域一般与某些特定token重合,比如括号;这样的作用域叫做词法作用域;或许”静态作用域“的叫法更好,因为光看代码就可以确定作用域了。
下面列出了作用域的一些特征,对不同的语言有不同的值:
- 静态VS动态, 大部分语言都是静态作用域,少数(LISP和PostScript)有动态作用域;
- 具名作用域,类、函数作用域有名字,其他一些作用域,比如全局作用域、局部作用域,没有名字;
- 嵌套,语言一般都允许作用域嵌套,一般对嵌套层数有限制;
- 内容,有些作用域只允许变量定义,有些则只允许其他语句,比如C struct的作用域只允许变量定义;
- 可见性,一个作用域的符号对其他代码段可见或不可见;
与上面类似,我们通过接口来标记一个Class、Function是一个作用域:
public interface Scope {
public String getScopeName(); //do I have a name
public Scope getEnclosingScope(); //am I nested in another scope
public void define(Symbol sym); //define sym in this scope
public Symbol resolve(String name); // look up name in scope
}
scope并不追踪对应的代码区域,反过来,代码区域的AST指向所述的scope;这个设计是很有意义的,因为访问AST的时候需要经常查找遇到的符号。
单一作用域
早期的Basic拥有单一的作用域,而现在只有配置文件这种及其简单的语言才有单一的作用域。
追踪符号只需要一个符号集合,遇到重复的符号定义要么覆盖之前的定义,要么被认为是一个错误;遇到新的符号定义则加入集合。
一个<符号名:符号对象>的map可以很好地承担这个职责。
嵌套作用域
多个作用域允许我们用同一名字来代表不同的语法实体。编程语言一般用上下文来区分相同的名字,”上下文”对应某个作用域以及外围嵌套的作用域;作用域嵌套就像一个栈一样,遇到一个新的scope,我们push进栈,栈顶的scope被成为当前scope,当从一个scope退出时,我们执行pop操作。
看一段c代码:
// start of global scope
int x; // define variable x in global scope
void f() { // define function f in global scope
int y; // define variable y in local scope of f
{ int i; } // define variable i in nested local scope
{ int j; } // define variable j in another nested local scope
}
void g() { // define function g in global scope
int i; // define variable i in local scope of g
}
包含的scope如下图:
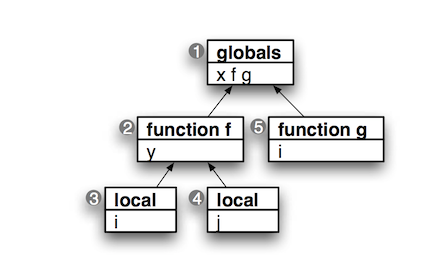
值得注意的是,这个树形图的节点之间的指针方向,是从子节点指向父节点,这是符号的搜寻方向。
于是,scope栈的操作过程,恰好定义了上面的scope树:
<b>//push</b>
currentScope = new LocalScope(currentScope);
<b>//pop</b>
currentScope = currentScope.getEnclosingScope();
<b>//def</b>
Symbol s = 《some-new-symbol》;
currentScope.define(s);
因此对于上面的c代码,Parser会执行以下的scope操作序列(暂时不去考虑如何引发这些操作):
1. push global scope .
2. def variable x in current scope, .
3. def method f in scope and push scope
4. def variable y.
5. push local scope.
6. def variable i.
...
解析符号引用
当代码里面遇到一个符号,需要解析它所引用的对象。对于单一的作用域,这个操作很简单:`myOnlyScope.resolve(《symbol-name》)。
当存在多个作用域的时候,符号引用的对象取决于它所处的位置;符号引用的scope栈是引用所处的scope到scope tree根节点的路径,这个栈称之为语义上下文(semantic context)。于是,解析一个符号引用,就是在它的语义上下文寻找他,从当前的scope开始一直到栈顶scope。
public Symbol resolve(String name) {
Symbol s = members.get(name); // look in this scope
if ( s!=null ) return s; // return it if in this scope
if ( enclosingScope != null ) { // have an enclosing scope?
return enclosingScope.resolve(name); // check enclosing scope
}
return null; // not found in this scope or there's no scope above
}
从代码可以看出,scope树的巧妙设计,让这个过程变得简单直观。
Pattern 16 Symbol Table for Monolithic Scope
单一层次的符号表,适合简单的语言(没有函数),比如配置文件、小型图形语言或小型DSL。
下面的表格展示了,基于语言输入构建scope的操作:
| Upon | Actions |
| Start of file | push a GlobalScope. def BuiltInType objects for any built-in types such as int and float. |
| Declaration x | ref x’s type (if any). def x in the current scope. |
| Reference x | ref x starting in the current scope. |
| End of file | pop the GlobalScope. |
Pattern 17 Symbol Tale for Nested Scope
该模式构建一棵scope tree,包含多个、嵌套的scope
看下面一段代码:
// start of global scope
int i = 9;
float f(int x, float y) {
float i;
{ float z = x+y; i = z; }
{ float z = i+1; i = z; }
return i;
}
void g() {
f(i,2);
}
对应的scope tree如下:

函数定义的对应的MethodScope包含了参数符号,里面嵌套一个LocalScope包含所有的局部变量。
同样用一个表格来描述Parse过程中的Scope构建操作:
| Upon | Actions |
| Start of file | push a GlobalScope. def BuiltInType objects for any built-in types such as int and float. |
| Declaration x | ref x’s type (if any). def x in the current scope. |
| Method declaration f | ref f’s return type. def f in the current scope and push it as the current scope. |
| { | push a LocalScope as the new current scope. |
| } | pop, revealing previous scope as current scope. |
| End of method | pop the MethodSymbol scope (the parameters). |
| Reference x | ref x starting in the current scope. If not found, look in the immediately enclosing scope (if any). |
| End of file | pop the GlobalScope. |
具体实现上,应用AST Tree Pattern Matcher可以方便地构建出符号表。