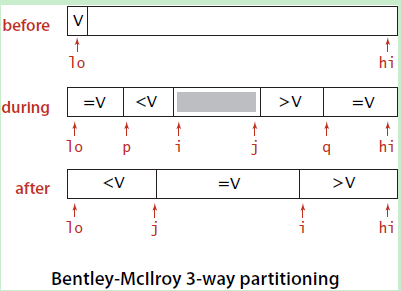
2.3.22快速三向切分。(J.Bently,D.McIlroy)用将重复元素放置于子数组两端的方式实现一个信息量最优的排序算法。使用两个索引p和q,使得a[lo..p-1]和a[q+1..hi]的元素都和a[lo]相等。使用另外两个索引i和j,使用a[p..i-1]小于a[lo],a[j+1..q]大于a[lo]。在内循环中加入代码,在a[i]和v相当时将其与a[p]交换(并将p加1),在a[j]和v相等且a[i]和a[j]尚未和v进行比较之前将其与a[q]交换。添加在切分循环结束后将和v相等的元素交换到正确位置的代码,如图2.3.6所示。请注意:这里实现的代码和正文中给出的代码是等价的,因为这里额外的交换用于和切分元素相等的元素,而正文中的代码将额外的交换用于和切分元素不等的元素。
英文版问题:
2.3.22 Fast 3-way partitioning. ( J. Bentley and D. McIlroy) Implement an entropyoptimal
sort based on keeping item's with equal keys at both the left and right ends
of the subarray. Maintain indices p and q such that
a[lo..p-1] and a[q+1..hi] are all equal to a[lo],
an index i such that a[p..i-1] are all less than a[lo],
and an index j such that a[j+1..q] are all greater than
a[lo]. Add to the inner partitioning loop code to swap
a[i] with a[p] (and increment p) if it is equal to v and
to swap a[j] with a[q] (and decrement q) if it is equal
to v before the usual comparisons of a[i] and a[j]
with v. After the partitioning loop has terminated, add
code to swap the items with equal keys into position.
Note : This code complements the code given in the
text, in the sense that it does extra swaps for keys equal to the partitioning item’s key,
while the code in the text does extra swaps for keys that are not equal to the partitioning
item’s key.
实现:
public class E2d3d22v1
{
public static void sort(Comparable[] a)
{
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
sort(a,0,a.length-1);
}
private static void sort(Comparable[] a,int lo,int hi)
{
//数组少于2个元素时不处理
if (hi<=lo) return;
//p的初值为lo+1,满足lo~p-1的元素=v
//i的初值为lo+1,p~i-1为0长,满足p~i-1的元素<v
//q的初值为hi,q+1~hi为0长,满足q+1~hi的元素=v
//j的初值为hi,j+1~q为0长,满足q+1~hi的元素>v
int p=lo+1,i=lo+1,q=hi,j=hi;
// StdOut.printf("lo=%d,i=%d,j=%d,hi=%d ",lo,i,j,hi);
Comparable v=a[lo];
while(i<=j)
{
//当i<j时一定需要i位置元素与v对比,当出现数组只有两个元素v,<v时,i=j,此时如果不进行对比排序后的结果就无序的,所以i=j时也需要对比。
//由于i=j时还需要对比,那么可能会出现i越过j形成i>=j的情况。
while(i<=j)
{
int cmp=a[i].compareTo(v);
//StdOut.printf("ToRight i=%d,j=%d,cmp=%d,a[i]=%f,v=%f ",i,j,cmp,a[i],v);
//当i位置元素<v时,i向右移动一个位置,此时p~i-1的元素<v
if (cmp<0) i++;
//当i位置元素=v时,交换i,p位置的元素,i,p指针向右移动一个位置,此时lo~p-1的元素=v,p~i-1的元素<v
else if (cmp==0) exch(a,i++,p++);
//当位置i的元素>v时,i指针暂停右移
else if(cmp>0) break;
}
//当i<j时一定需要j位置元素与v对比,
//当出现数组只有两个元素v,>v时,i=j,由于在上一个while中i位置元素已与v进行过对比,如果j位置元素再与v进行一次对比就多比较一次了,所以j位置元素与v的比较必要性不强。
//所以i=j时可以不进行对比了,那么意味着j向左移动时不可能会越过i位置形成i>j的情况,最多只可能是形成i=j的情况。
while(i<j)
{
int cmp=a[j].compareTo(v);
// StdOut.printf("ToRight i=%d,j=%d,cmp=%d,a[i]=%f,v=%f ",i,j,cmp,a[i],v);
//当j位置元素<v时,j指针暂停左移
if (cmp<0) break;
//当j位置元素=v时,交换j,q位置的元素,j,q指针向左移动一个位置,此时q+1~hi的元素=v,j+1~q的元素>v
else if(cmp==0) exch(a,j--,q--);
//当j位置元素>v时,j向左移动一个位置,此时j+1~q的元素>v
else if(cmp>0)j-- ;
}
//i,j指针相遇或i越过j时形成i>=j的几种具体排列
//1)v,<v 此情况时i>j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//2)v,v,此情况时i>j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//3)v,>v,此情况时i=j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//4)v,>v,<v此情况时i<j需要交换i,j位置元素,并将i,j向前移动一位,此时i>j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//5)v,<v,>v此情况时i=j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//当i,j 指针相遇或越过时,结束本轮比较
if (i>=j) break;
//StdOut.printf("Exch i=%d,j=%d ",i,j);
//上述第4点。
exch(a,i,j);
i++;
j--;
}
//依据上述5点的结论,得出位置i和i右边的元素>=v,保存i到j
j=i;
//左端=v元素与<v的元素段的右边交换。具体
//从左端向右将所有=v的元素与i-1位置到左边的元素交换,
//lo~i-1段,p无论是靠左或靠右或均分此段时,这种交换都将得到<v,=v的排列。
i--;
for (int k = lo; k < p; k++) exch(a, k, i--);
//右端=v端元素与>v的元素段的左端进行交换。
//从右端向左将所有=v的元素与j位置到右边的元素交换,
//j~hi段,q无论是靠左或靠右或均分此段时,这种交负都将得到=v,>v的排列。
for (int k = hi; k > q; k--) exch(a, k, j++);
// StdOut.printf("Move lo=%d,i-1=%d,j+1=%d,hi=%d ",lo,i-1,j+1,hi);
// StdOut.println("Left Sort");
//对<v的左子数组再排序,此时i处在最右边的<v的位置上。
sort(a, lo, i);
//StdOut.println("Right Sort");
//对>v的右子数组再排序,此时j处在最左边的>v的位置上。
sort(a, j, hi);
}
private static boolean less(Comparable v,Comparable w)
{ return v.compareTo(w)<0;}
private static void exch(Comparable[] a,int i,int j)
{
Comparable t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
private static void show(Comparable[] a)
{
for (int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
StdOut.print(a[i]+" ");
StdOut.println();
}
public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a)
{
for (int i=1;i<a.length;i++)
if(less(a[i],a[i-1])) return false;
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
Double[] a=new Double[N];
StdOut.println(a.length);
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
a[k]=StdRandom.random();
sort(a);
StdOut.println("isSorted=" +isSorted(a));
// show(a);
}
}
摘自网络的另一种实现:
public class E2d3d22v2
{
public static void sort(Comparable[] a)
{
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
sort(a,0,a.length-1);
}
private static void sort(Comparable[] a,int lo,int hi)
{
if (hi <= lo) return;
int i = lo, j = hi + 1;
int p = lo, q = hi + 1;
Comparable v = a[lo];
while (true)
{
while (less(a[++i], v))
if (i == hi) break;
while (less(v, a[--j]))
if (j == lo) break;
// pointers cross
if (i == j && equal(a[i], v))
exch(a, ++p, i);
if (i >= j) break;
exch(a, i, j);
if (equal(a[i], v)) exch(a, ++p, i);
if (equal(a[j], v)) exch(a, --q, j);
}
//将相等的元素交换到中间
i = j + 1;
for (int k = lo; k <= p; k++) exch(a, k, j--);
for (int k = hi; k >= q; k--) exch(a, k, i++);
sort(a, lo, j);
sort(a, i, hi);
}
private static boolean less(Comparable v,Comparable w)
{ return v.compareTo(w)<0;}
private static boolean equal(Comparable v,Comparable w)
{ return v.compareTo(w)==0;}
private static void exch(Comparable[] a,int i,int j)
{
Comparable t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
private static void show(Comparable[] a)
{
for (int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
StdOut.print(a[i]+" ");
StdOut.println();
}
public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a)
{
for (int i=1;i<a.length;i++)
if(less(a[i],a[i-1])) return false;
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
Double[] a=new Double[N];
StdOut.println(a.length);
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
a[k]=StdRandom.random();
sort(a);
StdOut.println("isSorted=" +isSorted(a));
// show(a);
}
}
J.Bently,D.McIlroy 发表的文章下载地址:https://cs.fit.edu/~pkc/classes/writing/papers/bentley93engineering.pdf
摘自其中的C语言实现
void iqsort2(int *x, int n)
{
int a, b, c, d, l, h, s, v;
if (n <= 1) return;
v = x[rand() % n];
a = b = 0;
c = d = n-1;
for (;;) {
while (b <= c && x[b] <= v) {
if (x[b] == v) iswap(a++, b, x);
b++;
}
while (c >= b && x[c] >= v) {
if (x[c] == v) iswap(d--, c, x);
c--;
}
if (b > c) break;
iswap(b++, c--, x);
}
s = min(a, b-a);
for(l = 0, h = b-s; s; s--) iswap(l++, h++, x);
s = min(d-c, n-1-d);
for(l = b, h = n-s; s; s--) iswap(l++, h++, x);
iqsort2(x, b-a);
iqsort2(x + n-(d-c), d-c);
}
英文版问题:
2.3.22 Fast 3-way partitioning. ( J. Bentley and D. McIlroy) Implement an entropyoptimal
sort based on keeping item's with equal keys at both the left and right ends
of the subarray. Maintain indices p and q such that
a[lo..p-1] and a[q+1..hi] are all equal to a[lo],
an index i such that a[p..i-1] are all less than a[lo],
and an index j such that a[j+1..q] are all greater than
a[lo]. Add to the inner partitioning loop code to swap
a[i] with a[p] (and increment p) if it is equal to v and
to swap a[j] with a[q] (and decrement q) if it is equal
to v before the usual comparisons of a[i] and a[j]
with v. After the partitioning loop has terminated, add
code to swap the items with equal keys into position.
Note : This code complements the code given in the
text, in the sense that it does extra swaps for keys equal to the partitioning item’s key,
while the code in the text does extra swaps for keys that are not equal to the partitioning
item’s key.
实现:
public class E2d3d22v1
{
public static void sort(Comparable[] a)
{
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
sort(a,0,a.length-1);
}
private static void sort(Comparable[] a,int lo,int hi)
{
//数组少于2个元素时不处理
if (hi<=lo) return;
//p的初值为lo+1,满足lo~p-1的元素=v
//i的初值为lo+1,p~i-1为0长,满足p~i-1的元素<v
//q的初值为hi,q+1~hi为0长,满足q+1~hi的元素=v
//j的初值为hi,j+1~q为0长,满足q+1~hi的元素>v
int p=lo+1,i=lo+1,q=hi,j=hi;
// StdOut.printf("lo=%d,i=%d,j=%d,hi=%d ",lo,i,j,hi);
Comparable v=a[lo];
while(i<=j)
{
//当i<j时一定需要i位置元素与v对比,当出现数组只有两个元素v,<v时,i=j,此时如果不进行对比排序后的结果就无序的,所以i=j时也需要对比。
//由于i=j时还需要对比,那么可能会出现i越过j形成i>=j的情况。
while(i<=j)
{
int cmp=a[i].compareTo(v);
//StdOut.printf("ToRight i=%d,j=%d,cmp=%d,a[i]=%f,v=%f ",i,j,cmp,a[i],v);
//当i位置元素<v时,i向右移动一个位置,此时p~i-1的元素<v
if (cmp<0) i++;
//当i位置元素=v时,交换i,p位置的元素,i,p指针向右移动一个位置,此时lo~p-1的元素=v,p~i-1的元素<v
else if (cmp==0) exch(a,i++,p++);
//当位置i的元素>v时,i指针暂停右移
else if(cmp>0) break;
}
//当i<j时一定需要j位置元素与v对比,
//当出现数组只有两个元素v,>v时,i=j,由于在上一个while中i位置元素已与v进行过对比,如果j位置元素再与v进行一次对比就多比较一次了,所以j位置元素与v的比较必要性不强。
//所以i=j时可以不进行对比了,那么意味着j向左移动时不可能会越过i位置形成i>j的情况,最多只可能是形成i=j的情况。
while(i<j)
{
int cmp=a[j].compareTo(v);
// StdOut.printf("ToRight i=%d,j=%d,cmp=%d,a[i]=%f,v=%f ",i,j,cmp,a[i],v);
//当j位置元素<v时,j指针暂停左移
if (cmp<0) break;
//当j位置元素=v时,交换j,q位置的元素,j,q指针向左移动一个位置,此时q+1~hi的元素=v,j+1~q的元素>v
else if(cmp==0) exch(a,j--,q--);
//当j位置元素>v时,j向左移动一个位置,此时j+1~q的元素>v
else if(cmp>0)j-- ;
}
//i,j指针相遇或i越过j时形成i>=j的几种具体排列
//1)v,<v 此情况时i>j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//2)v,v,此情况时i>j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//3)v,>v,此情况时i=j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//4)v,>v,<v此情况时i<j需要交换i,j位置元素,并将i,j向前移动一位,此时i>j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//5)v,<v,>v此情况时i=j,i-1位置(含i-1)左边的元素<=v,右边的元素>=v。
//当i,j 指针相遇或越过时,结束本轮比较
if (i>=j) break;
//StdOut.printf("Exch i=%d,j=%d ",i,j);
//上述第4点。
exch(a,i,j);
i++;
j--;
}
//依据上述5点的结论,得出位置i和i右边的元素>=v,保存i到j
j=i;
//左端=v元素与<v的元素段的右边交换。具体
//从左端向右将所有=v的元素与i-1位置到左边的元素交换,
//lo~i-1段,p无论是靠左或靠右或均分此段时,这种交换都将得到<v,=v的排列。
i--;
for (int k = lo; k < p; k++) exch(a, k, i--);
//右端=v端元素与>v的元素段的左端进行交换。
//从右端向左将所有=v的元素与j位置到右边的元素交换,
//j~hi段,q无论是靠左或靠右或均分此段时,这种交负都将得到=v,>v的排列。
for (int k = hi; k > q; k--) exch(a, k, j++);
// StdOut.printf("Move lo=%d,i-1=%d,j+1=%d,hi=%d ",lo,i-1,j+1,hi);
// StdOut.println("Left Sort");
//对<v的左子数组再排序,此时i处在最右边的<v的位置上。
sort(a, lo, i);
//StdOut.println("Right Sort");
//对>v的右子数组再排序,此时j处在最左边的>v的位置上。
sort(a, j, hi);
}
private static boolean less(Comparable v,Comparable w)
{ return v.compareTo(w)<0;}
private static void exch(Comparable[] a,int i,int j)
{
Comparable t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
private static void show(Comparable[] a)
{
for (int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
StdOut.print(a[i]+" ");
StdOut.println();
}
public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a)
{
for (int i=1;i<a.length;i++)
if(less(a[i],a[i-1])) return false;
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
Double[] a=new Double[N];
StdOut.println(a.length);
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
a[k]=StdRandom.random();
sort(a);
StdOut.println("isSorted=" +isSorted(a));
// show(a);
}
}
摘自网络的另一种实现:
public class E2d3d22v2
{
public static void sort(Comparable[] a)
{
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
sort(a,0,a.length-1);
}
private static void sort(Comparable[] a,int lo,int hi)
{
if (hi <= lo) return;
int i = lo, j = hi + 1;
int p = lo, q = hi + 1;
Comparable v = a[lo];
while (true)
{
while (less(a[++i], v))
if (i == hi) break;
while (less(v, a[--j]))
if (j == lo) break;
// pointers cross
if (i == j && equal(a[i], v))
exch(a, ++p, i);
if (i >= j) break;
exch(a, i, j);
if (equal(a[i], v)) exch(a, ++p, i);
if (equal(a[j], v)) exch(a, --q, j);
}
//将相等的元素交换到中间
i = j + 1;
for (int k = lo; k <= p; k++) exch(a, k, j--);
for (int k = hi; k >= q; k--) exch(a, k, i++);
sort(a, lo, j);
sort(a, i, hi);
}
private static boolean less(Comparable v,Comparable w)
{ return v.compareTo(w)<0;}
private static boolean equal(Comparable v,Comparable w)
{ return v.compareTo(w)==0;}
private static void exch(Comparable[] a,int i,int j)
{
Comparable t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
private static void show(Comparable[] a)
{
for (int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
StdOut.print(a[i]+" ");
StdOut.println();
}
public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a)
{
for (int i=1;i<a.length;i++)
if(less(a[i],a[i-1])) return false;
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
Double[] a=new Double[N];
StdOut.println(a.length);
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
a[k]=StdRandom.random();
sort(a);
StdOut.println("isSorted=" +isSorted(a));
// show(a);
}
}
J.Bently,D.McIlroy 发表的文章下载地址:https://cs.fit.edu/~pkc/classes/writing/papers/bentley93engineering.pdf
摘自其中的C语言实现
void iqsort2(int *x, int n)
{
int a, b, c, d, l, h, s, v;
if (n <= 1) return;
v = x[rand() % n];
a = b = 0;
c = d = n-1;
for (;;) {
while (b <= c && x[b] <= v) {
if (x[b] == v) iswap(a++, b, x);
b++;
}
while (c >= b && x[c] >= v) {
if (x[c] == v) iswap(d--, c, x);
c--;
}
if (b > c) break;
iswap(b++, c--, x);
}
s = min(a, b-a);
for(l = 0, h = b-s; s; s--) iswap(l++, h++, x);
s = min(d-c, n-1-d);
for(l = b, h = n-s; s; s--) iswap(l++, h++, x);
iqsort2(x, b-a);
iqsort2(x + n-(d-c), d-c);
}