Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree.
Note:
You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree.
利用中序和后序遍历构造二叉树,要注意到后序遍历的最后一个元素是二叉树的根节点,而中序遍历中,根节点前面为左子树节点后面为右子树的节点。例如二叉树:{1,2,3,4,5,6,#}的后序遍历为4->5->2->6->3->1;中序遍历为:4->2->5->1->6->3。
故,递归的整体思路是,找到根节点,然后遍历左右子树。这里有一个很重要的条件是:树中没有重复元素。
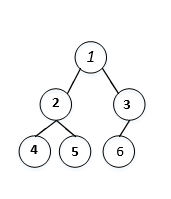
方法一:递归
值得注意的是:递归过程中,起始点的选取。Grandyang对下标的选取有较为详细的说明。至于这个递归过程,(个人愚见,欢迎大神给出更好递归过程)可以在脑海想,构造顺序为4->5->2构建好左子树,接上1,然后6->3构建好右子树,最后接上1,完成。
1 /** 2 * Definition for binary tree 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 TreeNode *buildTree(vector<int> &inorder, vector<int> &postorder) 13 { 14 int len=inorder.size(); 15 return build(inorder,0,len-1,postorder,0,len-1); 16 } 17 TreeNode *build(vector<int> &inorder,int inBeg,int inEnd,vector<int> &postorder,int postBeg,int postEnd) 18 { 19 if(inBeg>inEnd||postBeg>postEnd) return NULL; 20 TreeNode *root=new TreeNode(postorder[postEnd]); 21 22 for(int i=0;i<inorder.size();++i) 23 { 24 if(inorder[i]==postorder[postEnd]) 25 { 26 root->left=build(inorder,inBeg,i-1,postorder,postBeg,postBeg+i-1-inBeg); 27 root->right=build(inorder,i+1,inEnd,postorder,postBeg+i-inBeg,postEnd-1); 28 } 29 } 30 return root; 31 } 32 };
方法二:
利用栈。这个方法是以前看到出处也尴尬的忘了,分析过程等我再次看懂了再补上。这种方法改变了数组。

1 /** 2 * Definition for binary tree 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 TreeNode *buildTree(vector<int> &inorder, vector<int> &postorder) 13 { 14 if(inorder.size()==0) return NULL; 15 TreeNode* p; 16 TreeNode* root; 17 stack<TreeNode*> stn; 18 19 root=new TreeNode(postorder.back()); 20 stn.push(root); 21 postorder.pop_back(); 22 23 while(true) 24 { 25 if(inorder.back()==stn.top()->val) 26 { 27 p=stn.top(); 28 stn.pop(); 29 inorder.pop_back(); 30 31 if(inorder.size()==0) break; 32 if(stn.size()&&inorder.back()==stn.top()->val) 33 continue; 34 35 p->left=new TreeNode(postorder.back()); 36 postorder.pop_back(); 37 stn.push(p->left); 38 } 39 else 40 { 41 p=new TreeNode(postorder.back()); 42 postorder.pop_back(); 43 stn.top()->right=p; 44 stn.push(p); 45 } 46 } 47 return root; 48 } 49 };
