1:静态数据在程序开始时即获得空间,直到程序结束后才被收回。静态数据可以声明在函数体内,也可以声明在函数体外。
类中的静态成员与非静态成员有很大区别。从使用上来将,调用静态成员不需要实例化对象,而是以如下形式调用:
类名::静态成员
从类的设计思想来看,静态成员应该是类共用的。若想在静态函数中使用某些成员变量,可以在形参列表中实例化本类的对象,这样就可以在函数中使用该对象的成员。
2:实例代码如下:
(1)human.h

#include <string> using std::string; class human{ public: string m_name; human(); human(string name); static int nTheEarth;//静态变量,以数量表示环境的好坏 static void GetFeel(human h);//人类对环境的感觉 void Protect();// void Destroy(); };
(2)human.cpp

#include "stdafx.h" #include "human.h" #include <iostream> using std::endl; using std::cout; int human::nTheEarth = 101; //静态变量初始化!!! human::human() { m_name = "佚名"; } human::human(string name) { m_name = name; } void human::Destroy() { human::nTheEarth-=20; cout<<m_name<<"破坏了环境"<<endl; } void human::Protect() { human::nTheEarth+=6; cout<<m_name<<"劲微薄之力保护了环境"<<endl; } void human::GetFeel(human h) { cout<<"环境现在的情况:"; if(nTheEarth>100) cout<<"世界真美好"<<endl; else if(nTheEarth>80) cout<<"空气还算新鲜,但总觉得还是差了一些"<<endl; else if (nTheEarth>60) cout<<"天不蓝,水不清,勉强可以忍受"<<endl; else if(nTheEarth>40) cout<<"树木稀少,黄沙漫天"<<endl; else if (nTheEarth>20) cout<<"呼吸困难,水源稀缺"<<endl; else if (nTheEarth>0) cout<<"难道世界末日到了么?"<<endl; if(nTheEarth<50) { cout<<"感到环境变的很糟糕,"; h.Protect(); } }
(3)main.cpp

// 7.4.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include "human.h" using std::cout; using std::endl; int main() { human h1("雷锋"); human h2("某工厂老板"); human h3("小明"); human::GetFeel(h3);//静态变量要用这种双冒号的表示方法 for(int day = 0;day<4;day++) { h1.Protect(); h2.Destroy(); if(day%2 == 0) h3.Destroy(); else h3.Protect(); } cout<<"现在的环境指数:"<<human::nTheEarth<<",看来人类需要行动起来了..."<<endl; for(int day = 0;day<3;day++) { h1.Protect(); human::GetFeel(h2); h3.Protect(); } cout<<"现在的环境指数:"<<human::nTheEarth<<endl; return 0; }
运行结果:
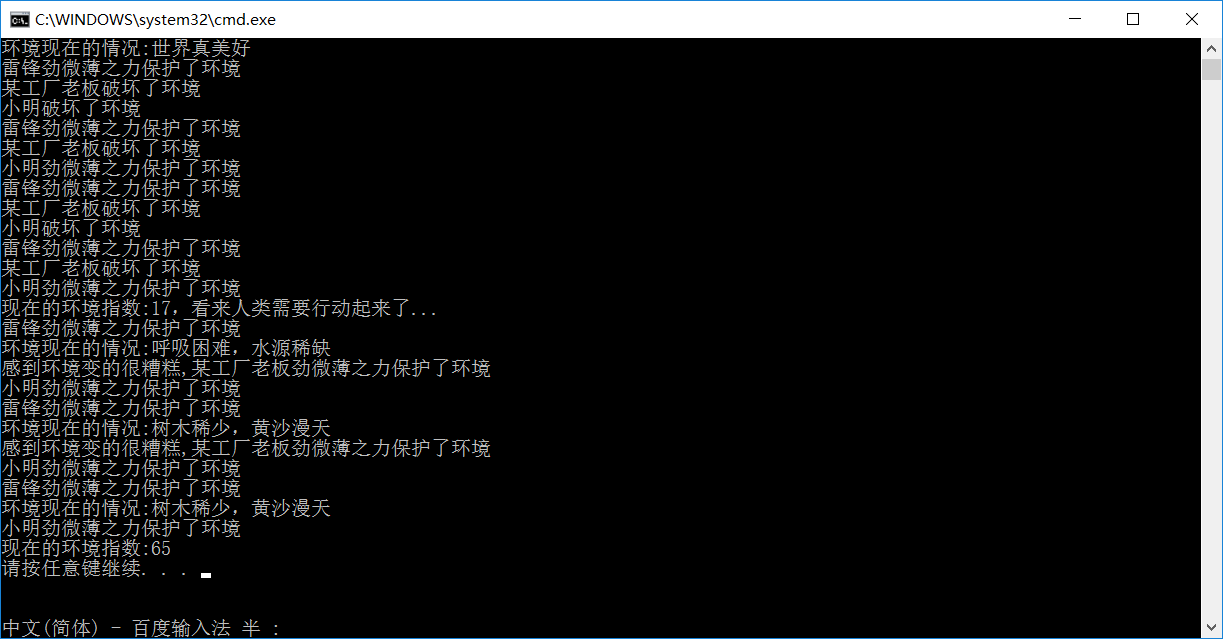
程序中,Protect和Destroy方法都对静态成员nTheEarth进行了操作。可以看出,每个human实例执行两个函数后,静态成员nTheEarth都会变化,这个值是所有对象所共用的。主函数使用区域符调用了human类的静态方法GetFeel()。
