字符串排序
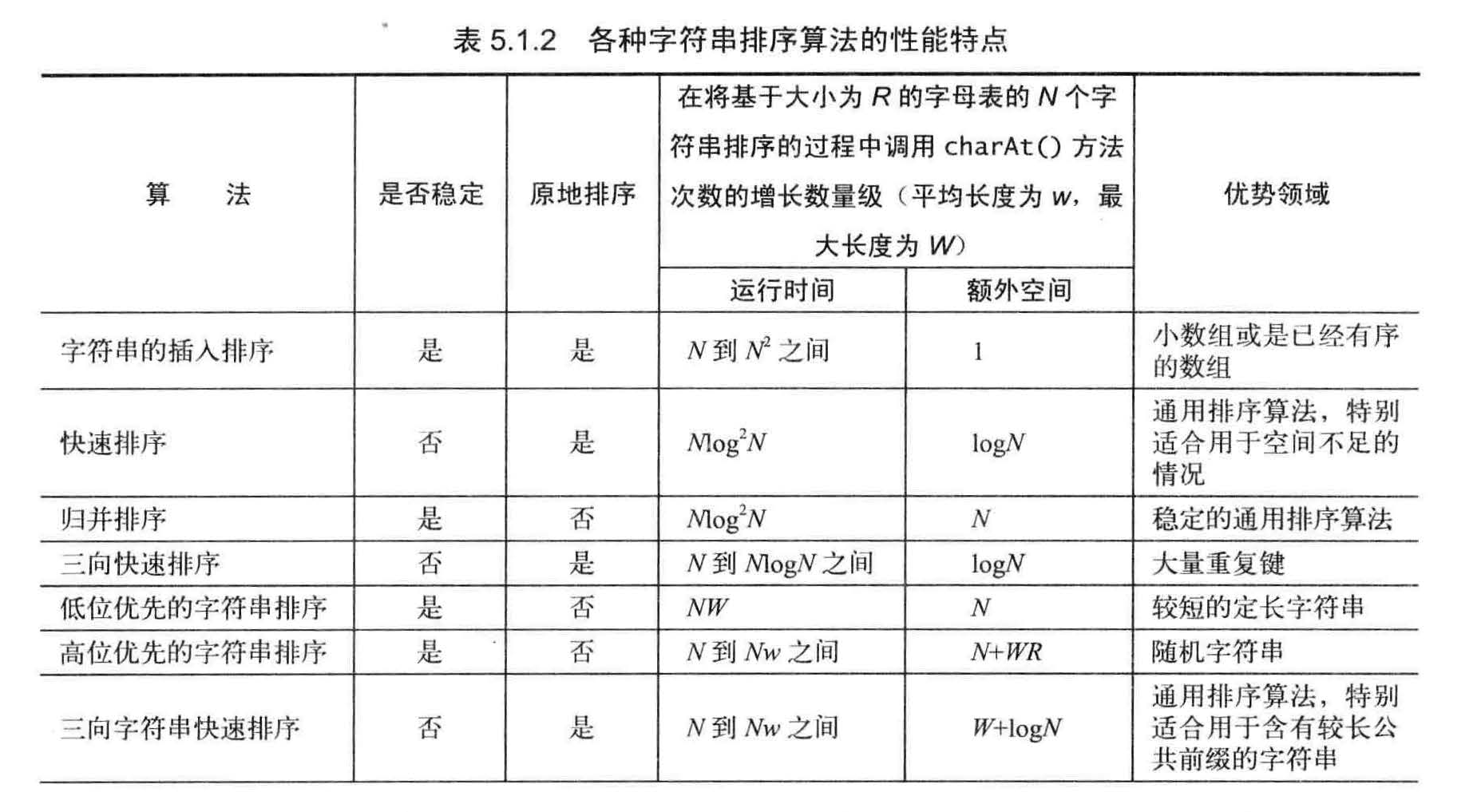
第一类方法会从右到左检查键中的字符。这种方法一般被称为低位优先(LSD ) 的字符串排序。使用数字(digit) 代替字符(character ) 的原因要追溯到相同方法在各种数字类型中的应用。
第二类方法会从左到右检查键中的字符,首先查看的是最高位的字符。这些方法通常称为高位优先(MSD) 的字符串排序。高位优先的字符串排序的吸引人之处在于,它们不一定需要检查所有的输入就能够完成排序。高位优先的字符串排序和快速排序类似,因为它们都会将需要排序的数组切分为独立的部分并递归地用相同的方法处理子数组来完成排序。
键索引计数法
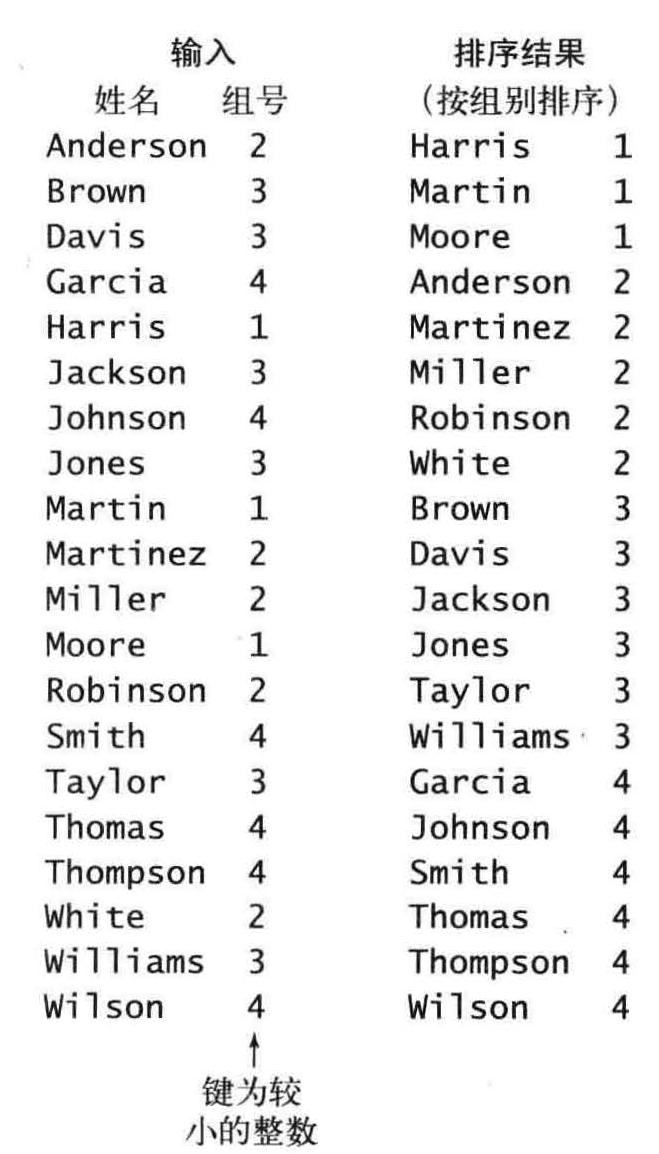
假设数组a [] 中的每个元素都保存了一个名字和一个组号,其中组号在0 到R -1 之间, 代码a[i].key () 会返回指定学生的组号。
频率统计和频率转化成索引
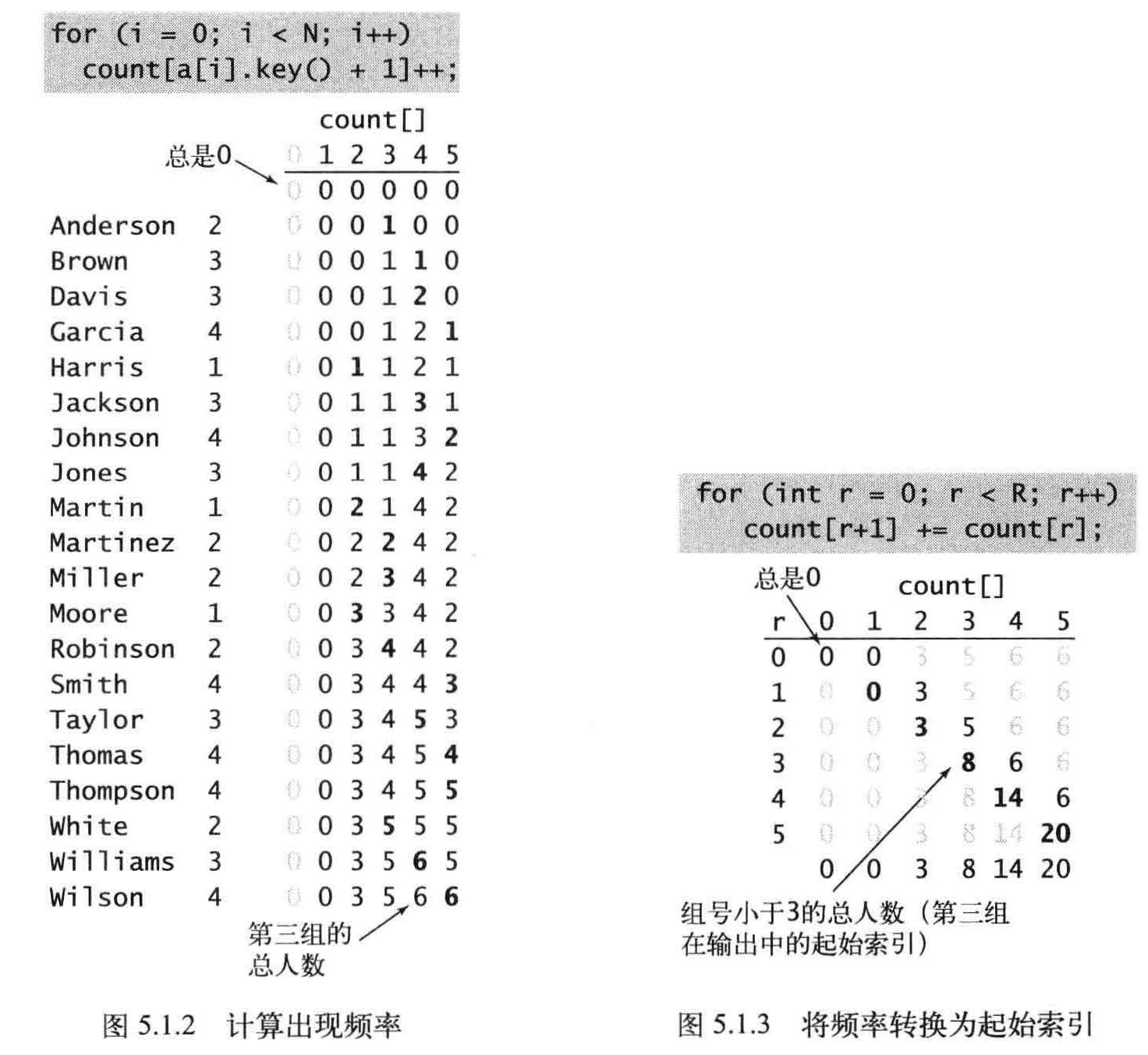
使用int 数组count [] 计算每个键出现的频率,对于数组a[]中的每个元素,都使用它的键访问count[] 中的相应元素并将其加1 。如果键为r , 则将count[r+1] 加1 。首先将count[3] 加1 , 因为Anderson 在第二组中,然后会将count[4] 加2, 因为Brown 和Davis 都在第三组中.
数据分类和回写
将所有元素(学生)移动到一个辅助数组aux[]中以进行排序。每个元素在aux[] 中的位置是由它的键(组别)对应的count[] 值决定,在移动之后将count[] 中对应元素的值加1 , 以保证count[r] 总是下一个键为r 的元素在aux[] 中的索引位置。这个过程只需遍历一遍数据即可产生排序结果,

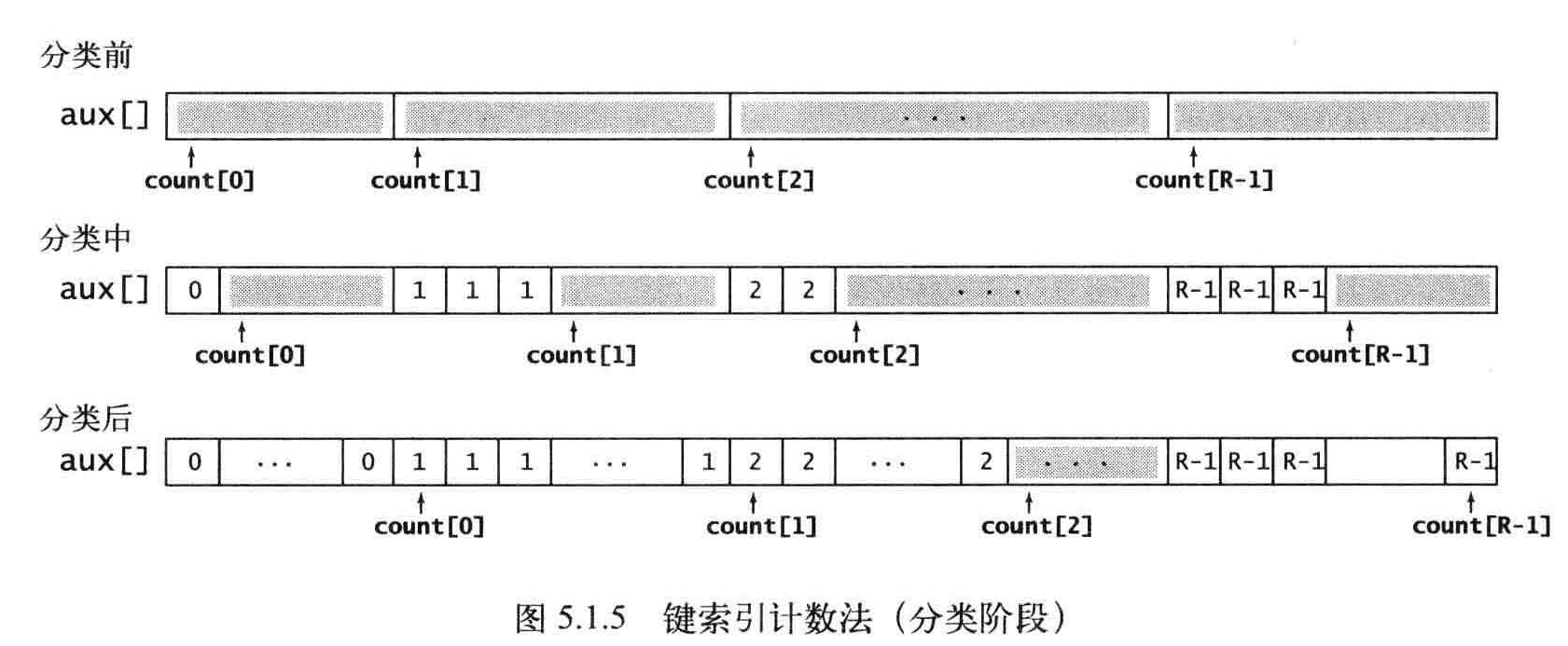
回写就是将aux[]写到源数组a[]
键索引计数法排序N个键为0到R-1之间的整数的元素需要访问数组11N+ 4R+ 1 次。
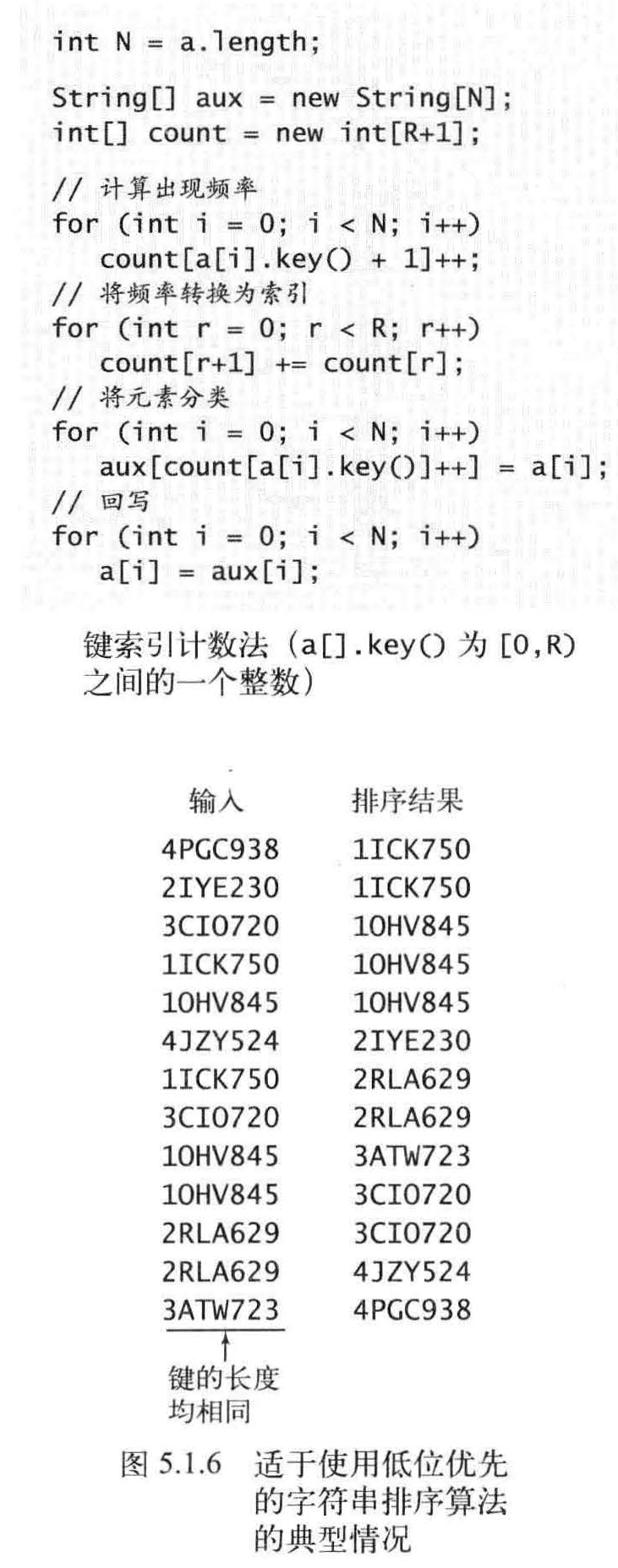
低位优先字符串排序
如果字符串的长度均为W, 那就从右向左以每个位置的字符作为键,用键索引计数法将字符串排序W 遍。
低位优先的字符串排序算法能够稳定地将定长字符串排序。
低位优先的字符串排序的意义重大,因为它是一种适用于一般应用的线性时间排序算法。无论N 有多大,它都只遍历W 次数据。
public class LSD
{
private static readonly int BITS_PER_BYTE = 8;
private LSD() { }
/// <summary>
/// 根据前w个字符进行排序
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="w"></param>
public static void Sort(string[] a, int w)
{
int n = a.Length;
int R = 256; // extend ASCII alphabet size
string[] aux = new string[n];
for (int d = w - 1; d >= 0; d--)
{
//根据d个字符用键索引计数法排序
// 计算出现频率
int[] count = new int[R + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[a[i][d] + 1]++;
// 将频率转化成索引
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// 将元素分类
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
aux[count[a[i][d]]++] = a[i];
// 回写
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = aux[i];
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 以升序重新排列32位整数数组。
/// 这比Arrays.sort()快2-3倍。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
public static void Sort(int[] a)
{
int BITS = 32; // each int is 32 bits
int R = 1 << BITS_PER_BYTE; // each bytes is between 0 and 255
int MASK = R - 1; // 0xFF
int w = BITS / BITS_PER_BYTE; // each int is 4 bytes
int n = a.Length;
int[] aux = new int[n];
for (int d = 0; d < w; d++)
{
// 计算出现频率
int[] count = new int[R + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int c = (a[i] >> BITS_PER_BYTE * d) & MASK;
count[c + 1]++;
}
// 将频率转化成索引
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// for most significant byte, 0x80-0xFF comes before 0x00-0x7F
//对于最高有效字节,0x80-0xFF位于0x00-0x7F之前
if (d == w - 1)
{
int shift1 = count[R] - count[R / 2];
int shift2 = count[R / 2];
for (int r = 0; r < R / 2; r++)
count[r] += shift1;
for (int r = R / 2; r < R; r++)
count[r] -= shift2;
}
//分类
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int c = (a[i] >> BITS_PER_BYTE * d) & MASK;
aux[count[c]++] = a[i];
}
// 回写
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = aux[i];
}
}
}
测试
[TestMethod]
public void LSDFixture()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\words3.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
List<string> lines=new List<string>();
while (!stream.EndOfStream)
{
lines.Add(stream.ReadLine().Trim());
}
var a = lines.ToArray();
int n = a.Length;
// 检查固定长度
int w = a[0].Length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i].Length != w)
{
throw new ArgumentException($"{a[i]} length is error");
}
}
// sort the strings
LSD.Sort(a, w);
// print results
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
}
}
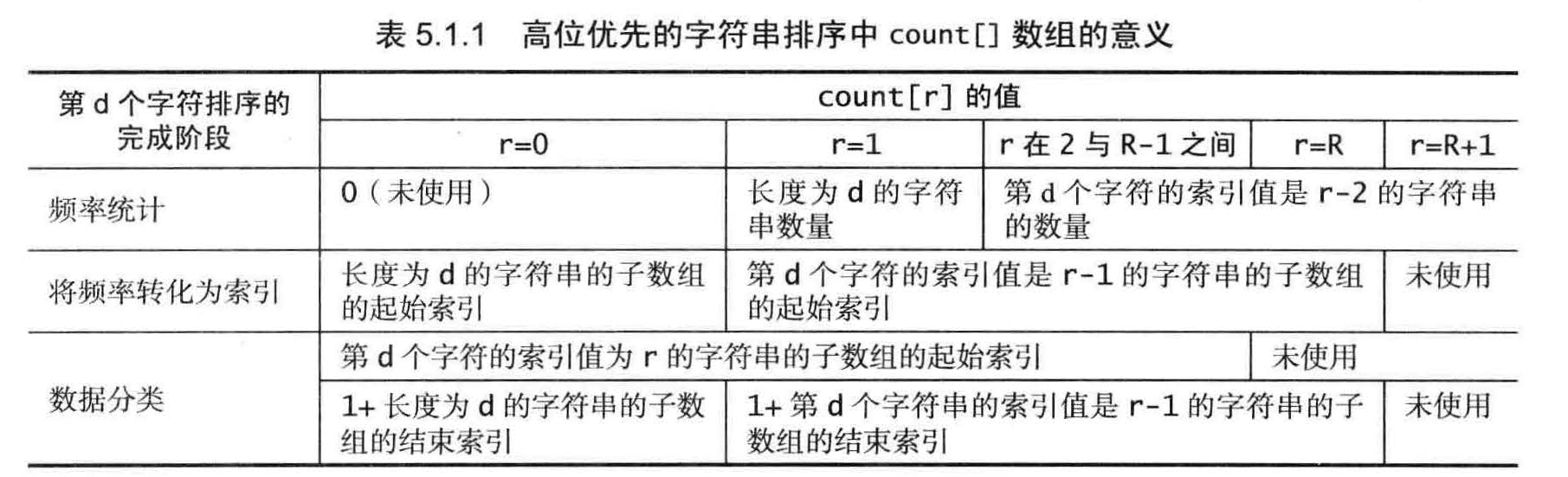
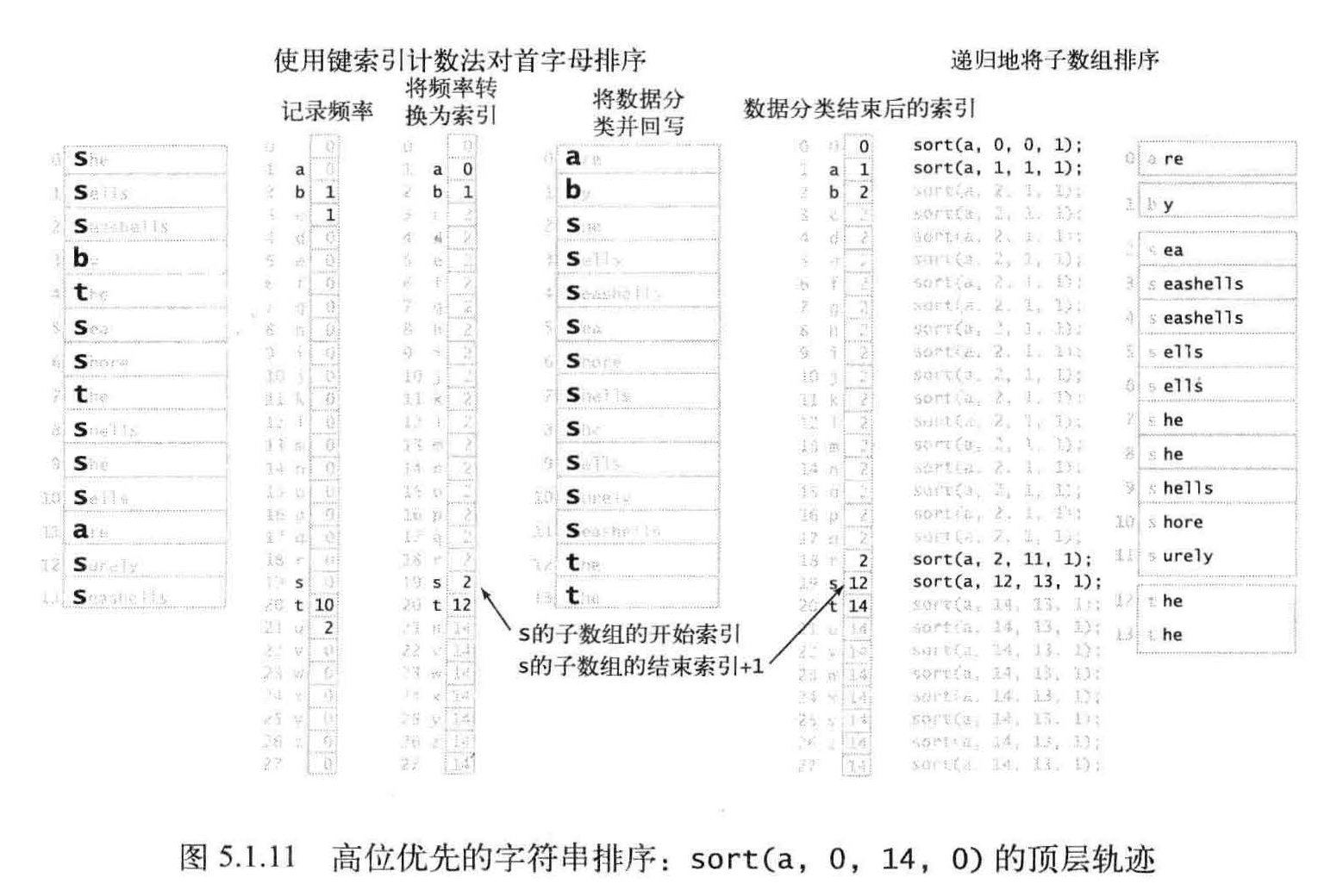
高位优先的字符串排序
从左向右遍历所有字符。我们知道,以a 开头的字符串应该排在以b 开头的字符串前面实现这种思想的一个很自然方法就是一种递归算法,被称为高位优先(MSD) 的字符串排序,
高位优先的字符串排序会将数组切分为能够独立排序的子数组来完成排序任务,但它的切分会为每个首字母得到一个子数组,
使用了一个接受两个参数的私有方法toChar()来将字符串中字符索引转化为数组索引,当指定的位置超过了字符串的末尾时该方法返回-1 。然后将所有返回值加1 , 得到一个非负的int 值并用
它作为count[] 的索引。这种转换意味着字符串中的每个字符都可能产生R+1 中不同的值: 0 表示字符串的结尾, 1 表示字母表
的第一个字符, 2 表示字母表的第二个字符,等等,int count[] = new int[R+2]; 创建记录统计频率的数组(将所有值设为0) 。
高位优先的字符串排序的成本与字母表中的字符数量有很大关系。我们可以很容易地令排序算法修接受一个Alphabet 对象作为参数,以改进基于较小的字母表的字符串排序程序的性能。完成这一点需要进行如下改动:
- 在构造函数中用一个 alpha 对象保存字母表 ;
- 在构造函数中将R 设为alpha.R();
- 在charAt() 方法中将s.charAt(d) 替换为alpha.tolndex(s.charAt(d)) 。

public class MSD
{
private static readonly int BITS_PER_BYTE = 8;
private static readonly int BITS_PER_INT = 32;
/// <summary>
/// extended ASCII alphabet size
/// 基数
/// </summary>
private static readonly int R = 256;
/// <summary>
/// cutoff to insertion sort
/// 小数组切换的阈值
/// </summary>
private static readonly int CUTOFF = 15;
private MSD() { }
/// <summary>
/// Rearranges the array of extended ASCII strings in ascending order.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
public static void Sort(string[] a)
{
int n = a.Length;
string[] aux = new string[n];
Sort(a, 0, n - 1, 0, aux);
}
/// <summary>
/// return dth character of s, -1 if d = length of string
/// </summary>
/// <param name="s"></param>
/// <param name="d"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private static int CharAt(string s, int d)
{
if(d >= 0 && d <= s.Length)
{
throw new ArgumentException("d and s is not match");
}
if (d == s.Length) return -1;
return s[d];
}
/// <summary>
/// sort from a[lo] to a[hi], starting at the dth character
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="lo"></param>
/// <param name="hi"></param>
/// <param name="d"></param>
/// <param name="aux"></param>
private static void Sort(string[] a, int lo, int hi, int d, String[] aux)
{
//以第d 个字符为键,将a[lo] 至a[hi] 排序
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
// 小数组切换插入排序
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF)
{
Insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
// compute frequency counts
//计算频率
int[] count = new int[R + 2];
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
{
int c = CharAt(a[i], d);
count[c + 2]++;
}
// transform counts to indicies
// 转化成索引
for (int r = 0; r < R + 1; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
// distribute
//分类
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
{
int c = CharAt(a[i], d);
aux[count[c + 1]++] = a[i];
}
// copy back
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
a[i] = aux[i - lo];
// recursively sort for each character (excludes sentinel -1)
//递归的以每个字符为键进行排序
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
Sort(a, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1, d + 1, aux);
}
/// <summary>
/// insertion sort a[lo..hi], starting at dth character
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="lo"></param>
/// <param name="hi"></param>
/// <param name="d"></param>
private static void Insertion(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && Less(a[j], a[j - 1], d); j--)
Exch(a, j, j - 1);
}
/// <summary>
/// exchange a[i] and a[j]
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="i"></param>
/// <param name="j"></param>
private static void Exch(String[] a, int i, int j)
{
String temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
/// <summary>
/// is v less than w, starting at character d
/// </summary>
/// <param name="v"></param>
/// <param name="w"></param>
/// <param name="d"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private static bool Less(String v, String w, int d)
{
// assert v.substring(0, d).equals(w.substring(0, d));
for (int i = d; i < Math.Min(v.Length, w.Length); i++)
{
if (v[i] < w[i]) return true;
if (v[i] > w[i]) return false;
}
return v.Length < w.Length;
}
/// <summary>
/// Rearranges the array of 32-bit integers in ascending order.
/// Currently assumes that the integers are nonnegative.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
public static void Sort(int[] a)
{
int n = a.Length;
int[] aux = new int[n];
Sort(a, 0, n - 1, 0, aux);
}
/// <summary>
/// MSD sort from a[lo] to a[hi], starting at the dth byte
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="lo"></param>
/// <param name="hi"></param>
/// <param name="d"></param>
/// <param name="aux"></param>
private static void Sort(int[] a, int lo, int hi, int d, int[] aux)
{
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF)
{
Insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
// compute frequency counts (need R = 256)
int[] count = new int[R + 1];
int mask = R - 1; // 0xFF;
int shift = BITS_PER_INT - BITS_PER_BYTE * d - BITS_PER_BYTE;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
{
int c = (a[i] >> shift) & mask;
count[c + 1]++;
}
// transform counts to indicies
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r + 1] += count[r];
/************* BUGGGY CODE.
// for most significant byte, 0x80-0xFF comes before 0x00-0x7F
if (d == 0) {
int shift1 = count[R] - count[R/2];
int shift2 = count[R/2];
for (int r = 0; r < R/2; r++)
count[r] += shift1;
for (int r = R/2; r < R; r++)
count[r] -= shift2;
}
************************************/
// distribute
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
{
int c = (a[i] >> shift) & mask;
aux[count[c]++] = a[i];
}
// copy back
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
a[i] = aux[i - lo];
// no more bits
if (d == 4) return;
// recursively sort for each character
if (count[0] > 0)
Sort(a, lo, lo + count[0] - 1, d + 1, aux);
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
if (count[r + 1] > count[r])
Sort(a, lo + count[r], lo + count[r + 1] - 1, d + 1, aux);
}
/// <summary>
/// TODO: insertion sort a[lo..hi], starting at dth character
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="lo"></param>
/// <param name="hi"></param>
/// <param name="d"></param>
private static void Insertion(int[] a, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && a[j] < a[j - 1]; j--)
Exch(a, j, j - 1);
}
// exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void Exch(int[] a, int i, int j)
{
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
测试
[TestMethod]
public void MSDFixture()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\shells.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
List<string> lines = new List<string>();
while (!stream.EndOfStream)
{
lines.AddRange(stream.ReadLine().Trim().Split(' '));
}
var a = lines.ToArray();
int n = a.Length;
// sort the strings
MSD.Sort(a);
// print results
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
}
}
小型数组
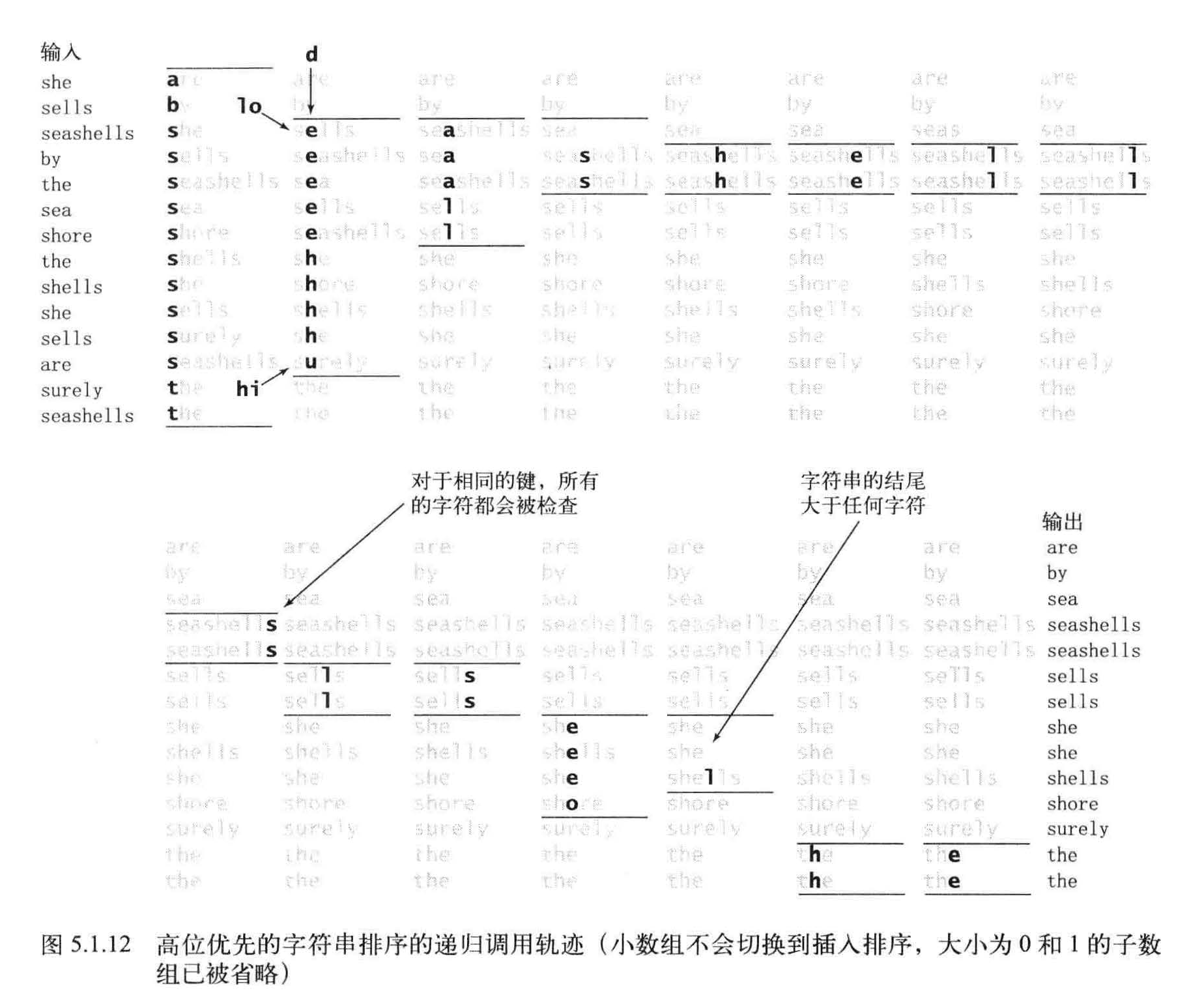
算法需要处理大量微型数组, 因此必须快速处理它们。小型子数组对于高位优先的字符串排序的性能至关重要。将小数组切换到插入排序对于高位优先的字符串排序算法是必须的。为了避免重复检查已知相同的字符所带来的成本,对于高位优先的字符串排序算法它节约的时间是非常可观的。
等值键
高位优先的字符串排序中的第二个陷阱是,对于含有大址等值键的子数组的排序会较慢。如果相同的子字符串出现得过多,切换排序方法条件将不会出现,那么递归方法就会检查所有相同键中的每一个字符。因此,高位优先的字符串排序的最坏情况就是所有的键均相同。大量含有相同前缀的键也会产生同样的问题,这在一般的应用场景中是很常见的。
额外空间
高位优先的算法使用了两个辅助数组: 一个用来将数据分类的临时数组(aux[])和
一个用来保存将会被转化为切分索引的统计频率的数组(count[])。如果牺牲稳定性,则可以去掉aux[] 数组

三向字符串快速排序
根据高位优先的字符串排序算法改进快速排序,根据键的首字母进行三向切分,仅在中间千数组中的下一个字符
三向字符串快速排序根据的仍然是键的首字母并使用递归方法将其余部分的键排序。对于字符串的排序,这个方法比普通的快速排序和高位优先的字符串排序更友好。实际上,它就是这两种算法的结合。
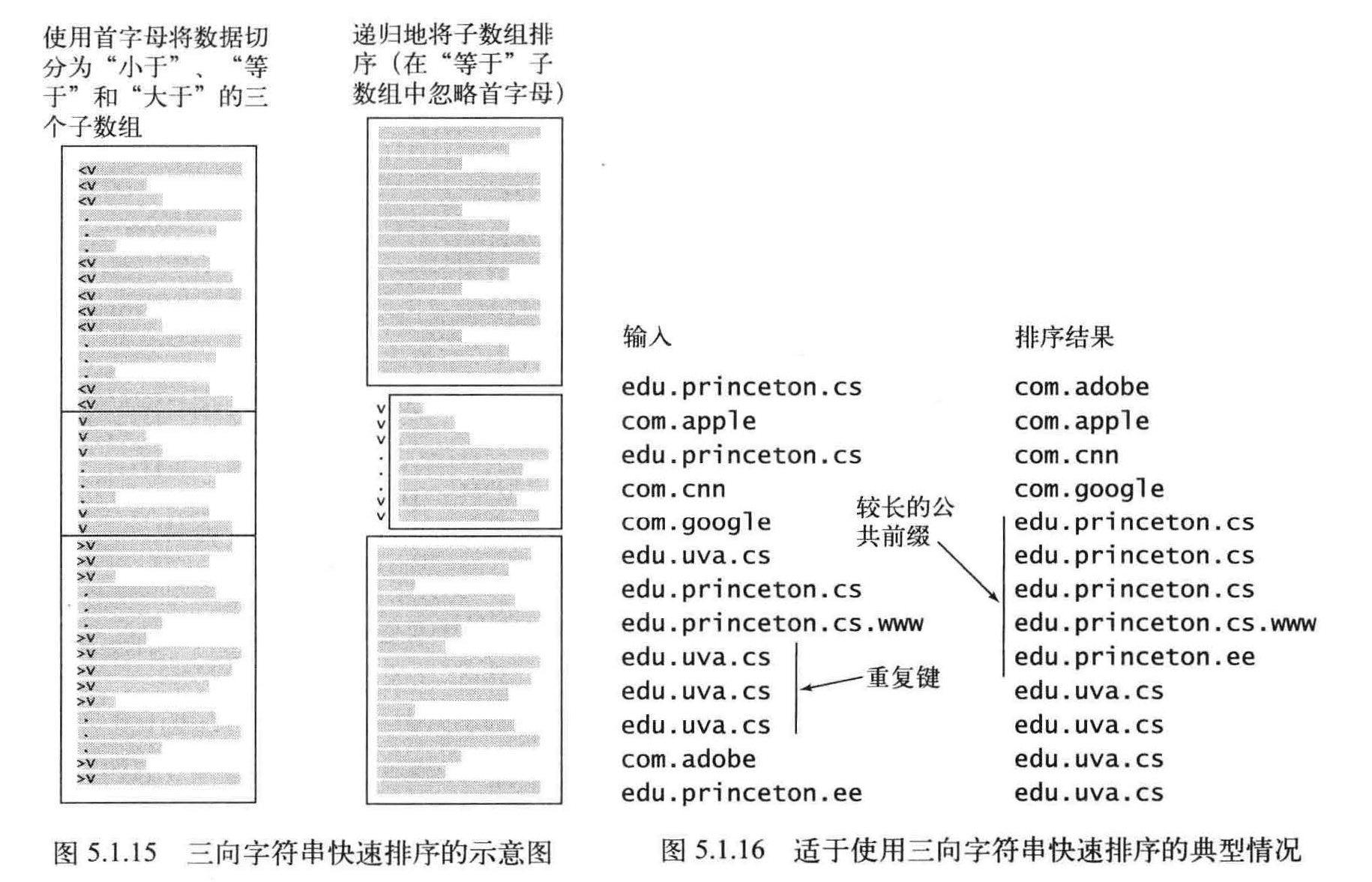
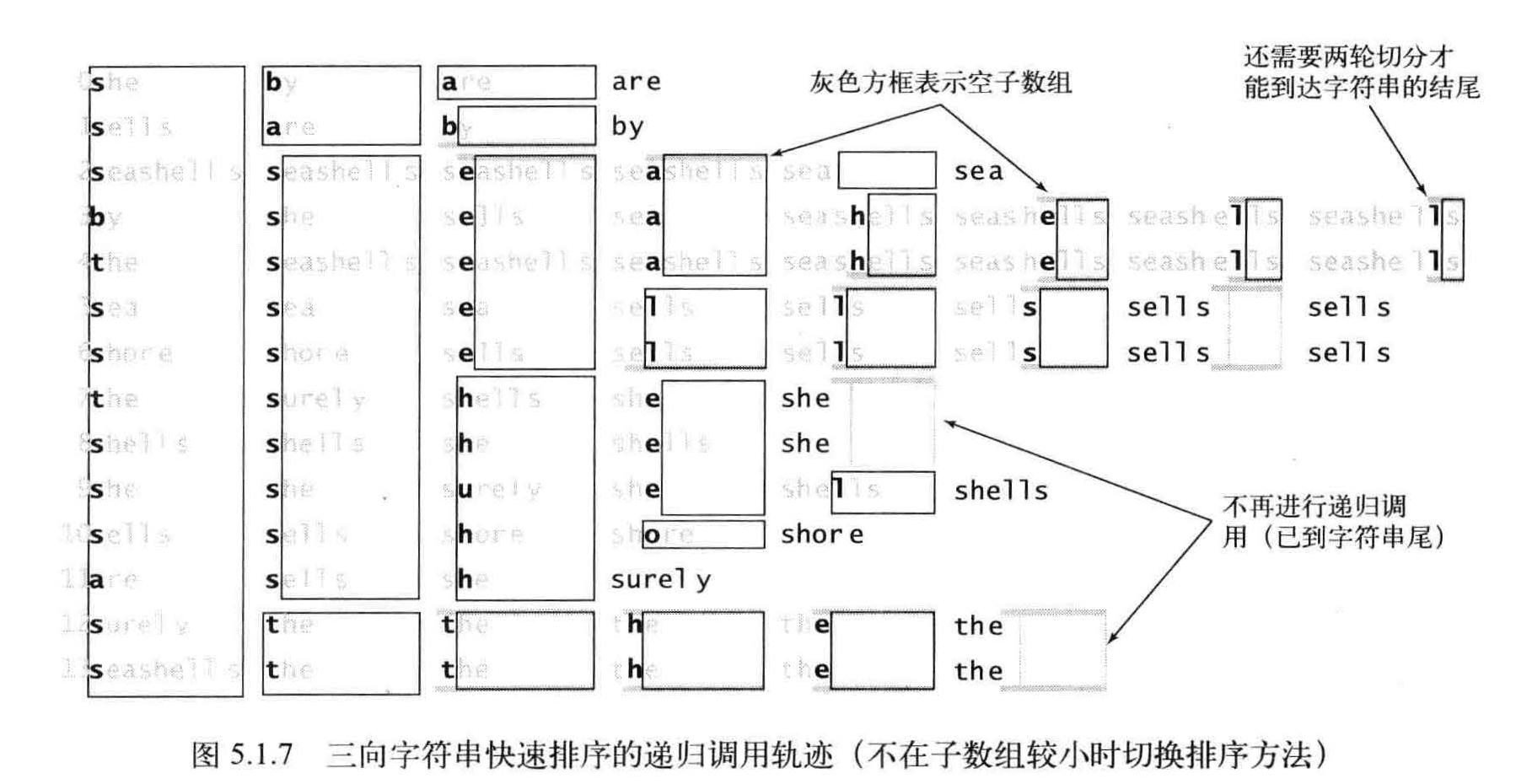
在将字符串数组a[] 排序时, 根据它们的首字母进行三向切分,然后(递归地)将得到的三个子数组排序: 一个含有所有首字母小于切分字符的字符串子数组,一个含有所有首字母等于切分字符的字符串的子数组(排序时忽略它们的首字母), 一个含有所有首字母大于切分字符的字符串的子数组。
随机化
和快速排序一样,最好在排序之前将数组打乱或是将第一个元素和一个随机位置的元素交换以得到一个随机的切分元素。
性能
要将含有N个随机字符串的数组排序,三向字符串快速排序平均需要比较字符~2NInN次。
假设你架设了一个网站并希望分析它产生的流量. 。你可以从系统管理员那里得到网站的所有活动,每项活动的信息中都含有发起者的域名
public class Quick3string
{
private static readonly int CUTOFF = 15;
private Quick3string() { }
public static void Sort(string[] a)
{
UtilGuard.Shuffle(a);
Sort(a, 0, a.Length - 1, 0);
if (!IsSorted(a))
{
throw new ArgumentException("list is not sorted");
} ;
}
private static int CharAt(string s, int d)
{
if (d < 0 && d > s.Length)
{
throw new ArgumentException("");
};
if (d == s.Length) return -1;
return s[d];
}
private static void Sort(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF)
{
Insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
int lt = lo, gt = hi;
int v = CharAt(a[lo], d);
int i = lo + 1;
while (i <= gt)
{
int t = CharAt(a[i], d);
if (t < v) Exch(a, lt++, i++);
else if (t > v) Exch(a, i, gt--);
else i++;
}
// a[lo..lt-1] < v = a[lt..gt] < a[gt+1..hi].
Sort(a, lo, lt - 1, d);
if (v >= 0) Sort(a, lt, gt, d + 1);
Sort(a, gt + 1, hi, d);
}
private static void Insertion(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d)
{
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && Less(a[j], a[j - 1], d); j--)
Exch(a, j, j - 1);
}
private static void Exch(String[] a, int i, int j)
{
String temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
private static bool Less(String v, String w, int d)
{
if( !v.Substring(0, d).Equals(w.Substring(0, d)))
throw new ArgumentException($"{v}; {w}");
for (int i = d; i < Math.Min(v.Length, w.Length); i++)
{
if (v[i] < w[i]) return true;
if (v[i] > w[i]) return false;
}
return v.Length< w.Length;
}
private static bool IsSorted(String[] a)
{
for (int i = 1; i < a.Length; i++)
if (a[i].CompareTo(a[i - 1]) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
}
测试
[TestMethod]
public void Quick3StringFixture()
{
var data = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "Data\shells.txt");
Console.WriteLine(data);
using (StreamReader stream = new StreamReader(data))
{
List<string> lines = new List<string>();
while (!stream.EndOfStream)
{
lines.AddRange(stream.ReadLine().Trim().Split(' '));
}
var a = lines.ToArray();
int n = a.Length;
CodeTimer.Time("Quick3String sort:", 1, () =>
{
// sort the strings
Quick3string.Sort(a);
});
// print results
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
}
//Quick3String sort:
// Time Elapsed: 3ms
// Time Elapsed (one time):3ms
// CPU time: 0ns
// CPU time (one time): 0ns
// Gen 0: 0
// Gen 1: 0
// Gen 2: 0
}
字符串排序算法的选择