基于XML的声明式
基于 XML 的声明式是指通过 Spring 配置文件的方式定义切面、切入点及声明通知,而所有的切面和通知都必须定义在 <aop:config> 元素中。
下面通过案例演示 Spring 中如何使用基于 XML 的声明式实现 AOP 的开发。
1. 导入 JAR 包
使用 AspectJ 除了需要导入 Spring AOP 的 JAR 包以外,还需要导入与 AspectJ 相关的 JAR 包,具体如下。
- spring-aspects-3.2.13.RELEASE.jar:Spring 为 AspectJ 提供的实现,在 Spring 的包中已经提供。
- com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar:是 AspectJ 提供的规范,可以在官方网址https://repo.spring.io/webapp/#/search/quick/ 中搜索并下载。
2. 创建切面类 MyAspect
在 src 目录下创建一个名为 com.mengma.aspectj.xml 的包,在该包下创建切面类 MyAspect,编辑后如下所示。
package com.mengma.aspectj.xml; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; //切面类 public class MyAspect { // 前置通知 public void myBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.print("前置通知,目标:"); System.out.print(joinPoint.getTarget() + "方法名称:"); System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName()); } // 后置通知 public void myAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.print("后置通知,方法名称:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getName()); } // 环绕通知 public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { System.out.println("环绕开始"); // 开始 Object obj = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); // 执行当前目标方法 System.out.println("环绕结束"); // 结束 return obj; } // 异常通知 public void myAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable e) { System.out.println("异常通知" + "出错了" + e.getMessage()); } // 最终通知 public void myAfter() { System.out.println("最终通知"); } }
上述代码中,分别定义了几种不同的通知类型方法,在这些方法中,通过 JoinPoint 参数可以获得目标对象的类名、目标方法名和目标方法参数等。需要注意的是,环绕通知必须接收一个类型为 ProceedingJoinPoint 的参数,返回值必须是 Object 类型,且必须抛出异常。异常通知中可以传入 Throwable 类型的参数,用于输出异常信息。
3. 创建 Spring 配置文件
在 com.mengma.aspectj.xml 包下创建 applicationContext.xml 的配置文件,如下所示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd"> <!--目标类 --> <bean id="customerDao" class="com.mengma.dao.CustomerDaoImpl" /> <!--切面类 --> <bean id="myAspect" class="com.mengma.aspectj.xml.MyAspect"></bean> <!--AOP 编程 --> <aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="myAspect"> <!-- 配置切入点,通知最后增强哪些方法 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution ( * com.mengma.dao.*.* (..))" id="myPointCut" /> <!--前置通知,关联通知 Advice和切入点PointCut --> <aop:before method="myBefore" pointeut-ref="myPointCut" /> <!--后置通知,在方法返回之后执行,就可以获得返回值returning 属性 --> <aop:after-returning method="myAfterReturning" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" returning="returnVal" /> <!--环绕通知 --> <aop:around method="myAround" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" /> <!--抛出通知:用于处理程序发生异常,可以接收当前方法产生的异常 --> <!-- *注意:如果程序没有异常,则不会执行增强 --> <!-- * throwing属性:用于设置通知第二个参数的名称,类型Throwable --> <aop:after-throwing method="myAfterThrowing" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" throwing="e" /> <!--最终通知:无论程序发生任何事情,都将执行 --> <aop:after method="myAfter" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" /> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
上述代码中,首先在第 4、7、8 行代码中分别导入了 AOP 的命名空间。第 12 行代码指定了切面类。
第 17、18 行代码配置了切入点,通知需要增强哪些方法,expression="execution(*com.mengma.dao.*.*(..))的意思是增强 com.mengma.dao 包下所有的方法。
第 20~32 行代码用于关联通知(Advice)和切入点(PointCut)。以第 20 行代码前置通知为例,<aop:before> 标签的 method 属性用于指定通知,pointcut-ref 属性用于指定切入点,也就是要增强的方法,其他几种通知的配置可以参考代码注释。
4. 创建测试类
在 com.mengma.aspectj.xml 包下创建测试类 XMLTest,如下所示。
package com.mengma.aspectj.xml; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.mengma.dao.CustomerDao; public class XMLTest { @Test public void test() { String xmlPath = "com/mengma/aspectj/xml/applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( xmlPath); // 从spring容器获取实例 CustomerDao customerDao = (CustomerDao) applicationContext .getBean("customerDao"); // 执行方法 customerDao.add(); } }
5. 运行项目并查看结果
使用 JUnit 测试运行 test() 方法,运行成功后,控制台的输出结果如图 1 所示。
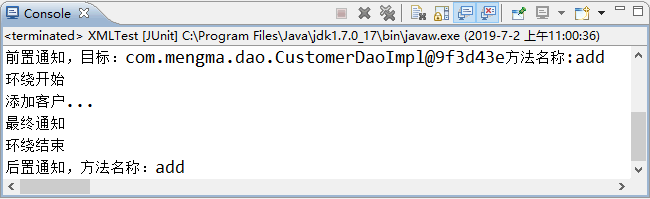
图 1 运行结果
为了更好地演示异常通知,接下来在 CustomerDaoImpl 类的 add() 方法中添加一行会抛出异常的代码,如“int i=1/0;”,重新运行 XMLTest 测试类,可以看到异常通知执行了,此时控制台的输出结果如图 2 所示。
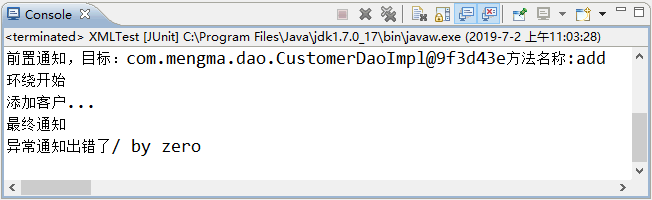
图 2 运行结果
从图 1 和图 2 的输出结果中可以看出,基于 XML 声明式的 AOP 开发已经成功实现。