循环:
例如打印九九乘法表:
for (int x = 1; x <= 9; x++) { for (int y = 1; y <= x; y++) { Console.Write($"{y}x{x}={x * y} "); } Console.WriteLine(" "); } Console.WriteLine("请按任意键退出"); Console.ReadLine();
关键字:
1,continue常用于循环中,当运行到continue时,会直接进入下一次循环,循环体中continue之后的代码不再执行。
2,return的作用:(1),运行时遇到return结束本方法;(2),返回方法执行得到的结果
四种范围修饰符(private->protected->internal->public)范围依次变大
1,private:只在本类中调用
2,protected:在本类和子类中调用
3,internal:在本项目中所有类中调用
4,public:在所有项目中都可以调用
调试方式:

F5:从第一个断点直接运行到第二个断点
F10:每次运行一行代码(遇到调用的方法不进去)
F11:每次运行一行代码(遇到调用的方法,进入调用的方法中逐行调试)
数据类型:
基类:派生与System.ValueType
值类型:byte》short,int,long,float,double,decimal,char,bool,enum,struct
值类型:在声明变量时不论是否赋值,编译器都会为其在栈中分配内存空间
基类:Object
引用类型:object,string,Array(int [ ]),class,interface,delegate(委托)
引用类型:在声明或定义一个类时,只在栈中分配一小片内存存储地址,并没有为其分配堆上面的内存空间,当用new创建(实例化)一个类时,才分配堆上的空间,并把堆空间的地址保存在栈上的一小片内存中。
值类型与引用类型:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Test1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int age1 = 18; int age2 = 25; Console.WriteLine($"调用前:{age1}-{age2}"); Program program = new Program(); program.AgeChange(age1,age2); //引用类型与值类型存储空间不同 Console.WriteLine($"调用后:{ age1}-{age2}"); //输出的是值类型 } public void AgeChange(int age1,int age2) { int temp = age1; age1 = age2; age2 = temp; } } }
结果:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Test1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int age1 = 18; int age2 = 25; Console.WriteLine($"调用前:{age1}-{age2}"); Program program = new Program(); program.AgeChange(ref age1,ref age2); //ref可以将值类型临时转为引用类型,ref转换前,值类型必须初始化, Console.WriteLine($"调用后:{ age1}-{age2}"); } public void AgeChange(ref int age1,ref int age2) { int temp = age1; age1 = age2; age2 = temp; } } }
结果:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Test1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Program program = new Program(); int age3=18; int age4=25; Console.WriteLine($"调用前:{age3}-{age4}"); program.AgeChange(out age3,out age4); //out可以将值类型转换为引用类型,out转换前值类型不用赋值,但必须在方法结束前赋值。 Console.WriteLine($"调用后:{ age3}-{age4}"); } public void AgeChange(out int age1,out int age2) { age1 = 25; age2 = 18; } } }
结果:

处理字符串常用的方法:

IndexOf( )查找某个字符在字符串中的位置,从左向右找,左边第一位为0;
LastIndexOf( )查找某个字符在字符串中的位置,从右向左找,左边第一位为0;
例如:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Test1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { while(true) { Console.Write("请输入你的邮箱账号:"); string email = Console.ReadLine(); int rs = email.IndexOf('@'); int rt = email.LastIndexOf('@'); if (rs < 0) Console.WriteLine("邮箱格式不正确,请重新输入!"); else { Console.WriteLine("邮箱格式基本正确"); Console.WriteLine($"第一个@的位置在第{rs}+1位,最后一个@的位置在第{rt}+1位"); } } } } }
结果:

SubString:从字符串中第n位截取一段字符串
例如:
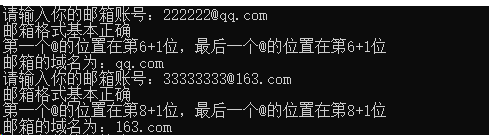
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Test1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { while(true) { Console.Write("请输入你的邮箱账号:"); string email = Console.ReadLine(); int rs = email.IndexOf('@'); int rt = email.LastIndexOf('@'); if (rs < 0) Console.WriteLine("邮箱格式不正确,请重新输入!"); else { Console.WriteLine("邮箱格式基本正确"); Console.WriteLine($"第一个@的位置在第{rs}+1位,最后一个@的位置在第{rt}+1位"); string ym = email.Substring(rs + 1); Console.WriteLine($"邮箱的域名为:{ym}"); } } } } }
结果:
ToLower( )将字符串转为小写字母
ToUpper( )将字符串转为大写字母
例如:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Test1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { while(true) { Console.Write("请输入你的邮箱账号:"); string email = Console.ReadLine(); int rs = email.IndexOf('@'); int rt = email.LastIndexOf('@'); if (rs < 0) Console.WriteLine("邮箱格式不正确,请重新输入!"); else { Console.WriteLine("邮箱格式基本正确"); Console.WriteLine($"第一个@的位置在第{rs}+1位,最后一个@的位置在第{rt}+1位"); string ym = email.Substring(rs + 1); Console.WriteLine($"邮箱的域名为:{ym}"); string emailt = email.ToLower(); string emailtt = email.ToUpper(); Console.WriteLine($"邮箱账号转为小写:{emailt};邮箱账号转为大写:{emailtt}"); } } } } }
结果:

Equals( m)判断字符串与m的值是否相等,“==”判断两个变量的地址是否相等,“Equals”判断两个string类型的变量的值是否相等。
Join(“x”,m )连接字符串
Split(' x')根据字符x分割字符串
例如:
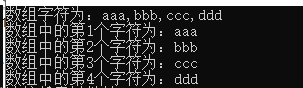
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Test1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string[] str = { "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd" }; string newst = string.Join(",", str); //根据字符,将字符串数组中的字符连接 Console.WriteLine($"数组字符为:{newst}"); string[] newstrs = newst.Split(','); //根据字符,将字符串分割放在新的数组 for (int i = 0; i < newstrs.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine($"数组中的第{i + 1}个字符为:{newstrs[i]}"); } } } }
结果: