1.线程的一些基本信息
public class thread { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread.currentThread(); //获得当前线程 int i = Thread.NORM_PRIORITY; //线程正常优先级 i=Thread.MAX_PRIORITY; //最高优先级 i=Thread.MIN_PRIORITY; //最低优先级 Thread.activeCount(); //线程的激活数目 } }
2.实现线程的两种方式,一是继承,二是实现接口。
一般实现简易选择接口,因为接口可以多实现,而继承只能单继承。
class Eat extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("I am eating"); } } class Drink implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("I am drinking"); } } public class test1{ public static void main(String[] args) { Eat eat=new Eat(); eat.start(); Drink drink=new Drink(); new Thread(drink).start(); } }
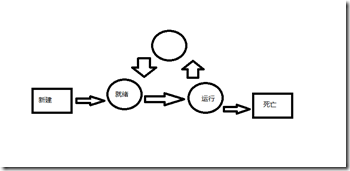
3.线程的状态
新建 --->就绪--->运行--->阻塞--->死亡
4.守护线程
守护线程就是守护其他的用户线程的,没有用户线程就守护主线程。
下面的例子三个线程,做饭,做菜,主线程
class Fan extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) { System.out.print("做饭" + i+" "+this.getName()); System.out.println(); try { Thread.sleep(250); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } class Cai extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) { System.out.print(" 炒菜" + i+" "+Thread.currentThread().getName()); System.out.println(); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable { Fan fan=new Fan(); Cai cai=new Cai(); // cai.setDaemon(true); //调用run是不会产生新的走向的,所有的都还是原来的线程中执行 //申请新的空间,使用start,自动调用run fan.start(); cai.start(); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Thread.currentThread().sleep(200); System.out.println(" 主线程"+i); } } }
没有设置守护前,所有的循环都会执行完,设置了之后,当用户线程(做饭)停止了,那么守护就没人守护了,也就一起停止了。
5.多线程之间的数据共享
1).数据为静态共享资源
class DataCenter { public static int count = 100; } class F112 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized ("joe") { if (DataCenter.count <= 0) { System.out.println("F112票卖完了"); return; } System.out.println("F112获取的票号是" + (DataCenter.count--)); } } } } class F411 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized ("joe") { if (DataCenter.count <= 0) { System.out.println("F411票卖完了"); return; } System.out.println("F411获取的票号是" + (DataCenter.count--)); } } } } public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { F112 f112 = new F112(); F411 f411 = new F411(); f411.start(); f112.start(); } }
2).共享代码体
public class codeShare { public static void main(String[] args) { Code code1=new Code(); new Thread(code1).start(); Code code2=new Code(); new Thread(code2).start(); } } class Code implements Runnable{ int i=9; @Override public void run() { for(;i>0;i--){ System.out.println("线程循环"); } } }
6.线程同步的几种方法
同步代码块。锁对象为字符串“joe”
class School { private static Object[] stus = new Object[52]; private static int index = 0; public void addStu(Object stu) {// 静态方法synchronized默认对象是类可行,成员方法是new // 出来的对象,不可行 synchronized ("joe") { stus[index++] = stu; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { System.out.print(stus[i] + " "); } System.out.println("数据添加完毕,现在的数量是" + index); } } }
方法锁,锁对象为调用这个方法的对象。
public class codeShare { public synchronized void run(){ Code code1=new Code(); new Thread(code1).start(); } } class Code implements Runnable{ int i=9; @Override public void run() { for(;i>0;i--){ System.out.println("线程循环"); } } }
静态方法锁。锁对象为类对象,codeShare.class
public class codeShare { public static synchronized void run(){ Code code1=new Code(); new Thread(code1).start(); } } class Code implements Runnable{ int i=9; @Override public void run() { for(;i>0;i--){ System.out.println("线程循环"); } } }
lock锁
public class Bank { private int account=100; private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); //声明锁 public int getAccount(){ return account; } public void save (int money){ lock.lock(); //锁上 try { account+=money; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ lock.unlock(); //肯定执行的解锁操作,避免死锁 } } }
7.线程中断,有个stop方法,过时了,不要用,而且不安全,数据会出现不一致的情况,可以使用interrupt方法+return实现。interrupt只是打个标记而已。
public class test{ public static void main(String[] args) { Test1 test1=new Test1(); test1.start(); test1.interrupt(); } } class Test1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ if(this.isInterrupted() && i==30){ return; } System.out.println("线程"+(i+1)+"运行中"); } } }
8.join
api上是等待线程死亡,个人简单理解就是插队
public class Join { public static void main(String[] args) { Eat eat=new Eat(); Sleep sleep=new Sleep(); Thread thread = new Thread(sleep); try { thread.start(); thread.join(); //插队到这,主线程必须等待它死亡才可以继续走下去后面的代码 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } new Thread(eat).start();; } } class Eat implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { try { Thread.currentThread().sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("我是Eat线程"); } } class Sleep implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { try { Thread.currentThread().sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("我是Sleep线程"); } }