参考的资料:
hello world https://www.cnblogs.com/bitor/p/9608725.html
linux内核监控模块——系统调用的截获 https://www.cnblogs.com/lxw315/p/4773566.html
实现:
实验目的:
内核模块的编写:完成一个Linux/Windows内核/驱动模块的编写,
能够实现对文件访问的监控、或者对键盘设备、USB设备、网络设备、
蓝牙设备等的监控。
实验内容:
通过linux内核模块编程,写一个模块使得进程访问文件时会把进程的进程名,进程id,文件名打印到系统日志,然后通过dmesg查看相关信息。
实验步骤:
1.思路
“截获”的过程是:修改系统调用表中调用函数的地址,将其执行我们自己实现的函数,再在我们自己的函数中完成我们想做的事情后,在返回到原来的系统调用执行流程中。
实现文件访问监控的思路为:截获sys_open系统调用。当进程打开文件时会调用系统中断sys_open,通过修改中断向量表使得先执行我们编写的函数my_sys_open,功能为打印当前访问的进程名,进程号,文件名,然后再执行sys_open。这样就相当于监控到了信息,信息通过printk打印到系统日志,通过dmesg查看即可。
2.代码实现
函数asmlinkage long my_sys_open(char * filename, int flags, int mode),就是自己实现的调用函数,这里的形参是参考系统原有的open调用函数的原型。
在my_sys_open()中,打印了当前是哪个进程在访问(进程名和进程号的信息),访问的是哪个文件(文件的绝对路径),打印完后跳转到原来的系统调用函数。
在模块初始化的过程中,执行start_hook()函数。在start_hook()函数中,先获得系统调用表的地址,将系统调用表中的原有open函数的地址保存下来,再将my_sys_open()函数的地址赋到系统调用表中。
修改系统调用表时,由于内核中的很多东西,比如系统调用表sys_call_table是只读的,需要修改一下权限才能修改。由于控制寄存器CR0的第16位若置位1,则表示禁止系统进程写只有只读权限的文件,所以在修改系统调用表sys_call_table之前先将CR0的第16位清零,在修改完后再恢复置位。
代码的close_cr()函数,是将CR0第16位清零,open_cr()函数是将CR0第16位恢复。
最后在卸载modu模块的时候,将系统调用表的内容还原。
#include<linux/init.h> #include<linux/module.h> #include<linux/moduleparam.h> #include<linux/unistd.h> #include<linux/sched.h> #include<linux/syscalls.h> #include<linux/string.h> #include<linux/fs.h> #include<linux/fdtable.h> #include<linux/uaccess.h> #include<linux/rtc.h> MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); #define _DEBUG #ifdef _DEBUG #define kprintk(fmt,args...) printk(KERN_ALERT fmt,##args) #define kprintf(fmt,args...) printf(fmt,##args) #define kperror(str) perror(str) #else #define kprintk #define kprintf #define kperror #endif /*Function declaration*/ long * get_sys_call_table(void); unsigned int close_cr(void); void open_cr(unsigned int oldval); void start_hook(void); asmlinkage long (*orig_open)(char __user *filename, int flags, int mode); long * g_sys_call_table = NULL; //save address of sys_call_table long g_old_sys_open = 0; //save old address of sys_open long g_oldcr0 = 0; //save address of cr0 struct _idtr{ //中断描述符表寄存器 unsigned short limit; unsigned int base; }__attribute__((packed)); struct _idt_descriptor{ unsigned short offset_low; unsigned short sel; unsigned char none,flags; unsigned short offset_high; }__attribute__((packed)); unsigned int close_cr(void){ unsigned int cr0 = 0; unsigned int ret; asm volatile("movl %%cr0,%%eax":"=a"(cr0)); ret = cr0; cr0 &= 0xfffeffff; asm volatile("movl %%eax,%%cr0"::"a"(cr0)); return ret; } void open_cr(unsigned int oldval){ asm volatile("movl %%eax,%%cr0"::"a"(oldval)); } /*Get the address of sys_call_table*/ long * get_sys_call_table(void){ //在idtr寄存器 struct _idt_descriptor * idt; struct _idtr idtr; unsigned int sys_call_off; int sys_call_table=0; unsigned char* p; int i; asm("sidt %0":"=m"(idtr)); //汇编,sidt指令获得中断描述符表基地址 kprintk(" address of idtr: 0x%x\n",(unsigned int)&idtr); idt=(struct _idt_descriptor *)(idtr.base+8*0x80); //0x80中断为系统调用中断 这是一个描述符,下面的操作得到描述符指向的具体地址 sys_call_off=((unsigned int)(idt->offset_high<<16)|(unsigned int)idt->offset_low); kprintk(" address of idt 0x80: 0x%x\n",sys_call_off); //0x80位 p=(unsigned char *)sys_call_off; for(i=0;i<100;i++){ if(p[i]==0xff&&p[i+1]==0x14&&p[i+2]==0x85){ sys_call_table=*(int*)((int)p+i+3); kprintk(" address of sys_call_table: 0x%x\n",sys_call_table); return (long*)sys_call_table; } } return 0; } //My own sys_open asmlinkage long my_sys_open(char * filename, int flags, int mode){ //打印当前使用sys-open函数的进程信息和文件名 kprintk("The process is \"%s\"(pid is %i)\n",current->comm,current->pid); kprintk("The file is being accessed is \"%s\"\n",filename); return orig_open(filename,flags,mode); } void start_hook(void){ //得到系统调用表地址,寻找sys-open项,替换为my_sys-open,cr0寄存器16位置0,可以写只读项 g_sys_call_table = get_sys_call_table(); if(!g_sys_call_table){ kprintk("Get sys_call_table error!\n"); return; } if(g_sys_call_table[__NR_close] != (unsigned long)sys_close){ kprintk("Incorrect sys_call_table address!\n"); return; } g_old_sys_open = g_sys_call_table[__NR_open]; orig_open = (long(*)(char *, int, int))g_sys_call_table[__NR_open]; g_oldcr0=close_cr(); g_sys_call_table[__NR_open] = my_sys_open; open_cr(g_oldcr0); } int monitor_init(void){ //启动模块 kprintk("Monitor init\n"); start_hook(); return 0; } void monitor_exit(void){ //退出模块 恢复系统调用表sys_open函数所在项地址为原sys_open,cr0寄存器16位置1,禁止写只读文件 if(g_sys_call_table && g_old_sys_open){ g_oldcr0 = close_cr(); g_sys_call_table[__NR_open] = g_old_sys_open; open_cr(g_oldcr0); } kprintk("Monitor exit\n"); } module_init(monitor_init); module_exit(monitor_exit);
3. Makefile
obj-m += hello.o #generate the path CURRENT_PATH:=$(shell pwd) #the current kernel version number LINUX_KERNEL:=$(shell uname -r) #the absolute path LINUX_KERNEL_PATH:=/usr/src/linux-headers-$(LINUX_KERNEL) #complie object all: make -C $(LINUX_KERNEL_PATH) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) modules #clean clean: make -C $(LINUX_KERNEL_PATH) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) clean
obj-m := hello.o PWD := $(shell pwd) KVER := $(shell uname -r) KDIR :=/lib/modules/$(KVER)/build/ all: $(MAKE) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) clean: rm -rf *.o *.mod.c *.mod.o *.ko *.symvers *.order *.a
4.加载内核模块,卸载内核模块
通过insmod XX.ko加载模块,rmmod xx.ko卸载模块。
cat /proc/modules查看模块信息,lsmod查看所有的模块。
遇到的问题及解决:
1.编写完makefile 执行Make时报错 nothing to be done for all
原因:这是因为空格和tab的转换问题
比如下面两个make就不一样。

解决:删掉前面的空格,改成tab
2.insmod后ubuntu系统卡死
原因:VMware的问题,换成virtual box就可以正常运行。
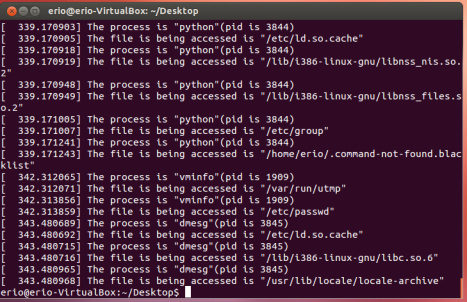
实验结果记录:
insmod 后dmesg,查看系统日志,可见记录了一些访问文件的进程名,id和文件名,于是实现了文件监控