代码图片来自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_31865983/article/details/103788358
VM_Thread 就是大家平时说的 JVM线程,只有一个实例,也就是虚拟机创建过程中只会被创建一次(C++层面),并且在虚拟机销毁的时候被销毁
具体的作用是 开启一个无限循环(while (true)), 然后不断地从一个 VM_Operation 队列中取出 VM_Operation 并且执行,如果没有 VM_Operation 就等待一会
VM_Operation 是通过其他线程 放入到队列中的,所以类似 生产者-消费者 模式。VM_Operation 有许多种,大概有四类
从注释上看,应该都是一些堆内存的分配操作?
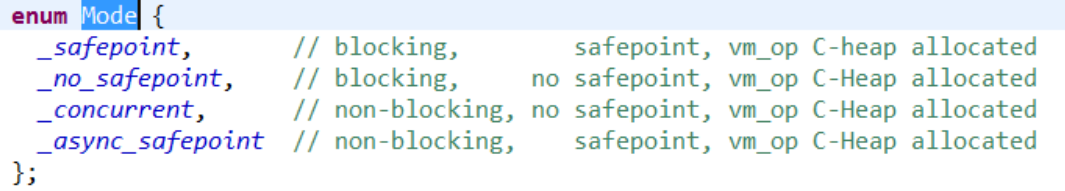
细分的话,具体操作如下:

#define VM_OP_ENUM(type) VMOp_##type, // Note: When new VM_XXX comes up, add 'XXX' to the template table. #define VM_OPS_DO(template) template(Dummy) template(ThreadStop) template(ThreadDump) template(PrintThreads) template(FindDeadlocks) template(ForceSafepoint) template(ForceAsyncSafepoint) template(Deoptimize) template(DeoptimizeFrame) template(DeoptimizeAll) template(ZombieAll) template(UnlinkSymbols) template(Verify) template(PrintJNI) template(HeapDumper) template(DeoptimizeTheWorld) template(CollectForMetadataAllocation) template(GC_HeapInspection) template(GenCollectFull) template(GenCollectFullConcurrent) template(GenCollectForAllocation) template(ParallelGCFailedAllocation) template(ParallelGCSystemGC) template(CGC_Operation) template(CMS_Initial_Mark) template(CMS_Final_Remark) template(G1CollectFull) template(G1CollectForAllocation) template(G1IncCollectionPause) template(DestroyAllocationContext) template(EnableBiasedLocking) template(RevokeBias) template(BulkRevokeBias) template(PopulateDumpSharedSpace) template(JNIFunctionTableCopier) template(RedefineClasses) template(GetOwnedMonitorInfo) template(GetObjectMonitorUsage) template(GetCurrentContendedMonitor) template(GetStackTrace) template(GetMultipleStackTraces) template(GetAllStackTraces) template(GetThreadListStackTraces) template(GetFrameCount) template(GetFrameLocation) template(ChangeBreakpoints) template(GetOrSetLocal) template(GetCurrentLocation) template(EnterInterpOnlyMode) template(ChangeSingleStep) template(HeapWalkOperation) template(HeapIterateOperation) template(ReportJavaOutOfMemory) template(JFRCheckpoint) template(Exit) template(LinuxDllLoad) template(RotateGCLog) template(WhiteBoxOperation) template(ClassLoaderStatsOperation)
比较值得注意的是 加载Linux 的 动态链接库:
比较重要的就是GC操作:

每个线程通过 VMThread::execute 把 VM_Operation 放入队列的之前会通过doit_prologue方法做检查,检查是否能把这个 VM_Operation 放入队列。
因为VM_Operation有可能会被多个Java线程入队,但是实际上只用一个入队就够了。
有一种比较典型的情况就是GC操作可能会被多个Java线程入队,但实际只用GC一次就够了。
实际执行 VM_Operation 是在 VM_Operation::evaluate 中
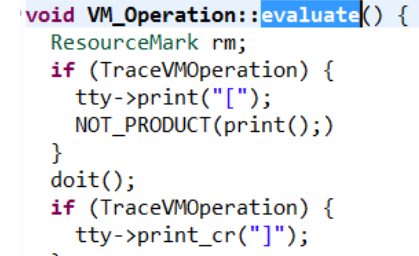
具体过程伪代码:
Java方法投递该VM_operation
VMThread::execute (VM_Operation op)
不是 VM_Thread来执行投递方法:
if (op::doit_prologue()) {
enqueue(op);
op::doit_epilogue();
}
如果是VM_Thread的话,可以直接执行evaluate方法

void VMThread::execute(VM_Operation* op) { Thread* t = Thread::current(); if (!t->is_VM_thread()) { SkipGCALot sgcalot(t); // avoid re-entrant attempts to gc-a-lot // JavaThread or WatcherThread bool concurrent = op->evaluate_concurrently(); // only blocking VM operations need to verify the caller's safepoint state: if (!concurrent) { t->check_for_valid_safepoint_state(true); } // New request from Java thread, evaluate prologue if (!op->doit_prologue()) { return; // op was cancelled } // Setup VM_operations for execution op->set_calling_thread(t, Thread::get_priority(t)); // It does not make sense to execute the epilogue, if the VM operation object is getting // deallocated by the VM thread. bool execute_epilog = !op->is_cheap_allocated(); assert(!concurrent || op->is_cheap_allocated(), "concurrent => cheap_allocated"); // Get ticket number for non-concurrent VM operations int ticket = 0; if (!concurrent) { ticket = t->vm_operation_ticket(); } // Add VM operation to list of waiting threads. We are guaranteed not to block while holding the // VMOperationQueue_lock, so we can block without a safepoint check. This allows vm operation requests // to be queued up during a safepoint synchronization. { VMOperationQueue_lock->lock_without_safepoint_check(); bool ok = _vm_queue->add(op); op->set_timestamp(os::javaTimeMillis()); VMOperationQueue_lock->notify(); VMOperationQueue_lock->unlock(); // VM_Operation got skipped if (!ok) { assert(concurrent, "can only skip concurrent tasks"); if (op->is_cheap_allocated()) delete op; return; } } if (!concurrent) { // Wait for completion of request (non-concurrent) // Note: only a JavaThread triggers the safepoint check when locking MutexLocker mu(VMOperationRequest_lock); while(t->vm_operation_completed_count() < ticket) { VMOperationRequest_lock->wait(!t->is_Java_thread()); } } if (execute_epilog) { op->doit_epilogue(); } } else { // invoked by VM thread; usually nested VM operation assert(t->is_VM_thread(), "must be a VM thread"); VM_Operation* prev_vm_operation = vm_operation(); if (prev_vm_operation != NULL) { // Check the VM operation allows nested VM operation. This normally not the case, e.g., the compiler // does not allow nested scavenges or compiles. if (!prev_vm_operation->allow_nested_vm_operations()) { fatal(err_msg("Nested VM operation %s requested by operation %s", op->name(), vm_operation()->name())); } op->set_calling_thread(prev_vm_operation->calling_thread(), prev_vm_operation->priority()); } EventMark em("Executing %s VM operation: %s", prev_vm_operation ? "nested" : "", op->name()); // Release all internal handles after operation is evaluated HandleMark hm(t); _cur_vm_operation = op; if (op->evaluate_at_safepoint() && !SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint()) { SafepointSynchronize::begin(); op->evaluate(); SafepointSynchronize::end(); } else { op->evaluate(); } // Free memory if needed if (op->is_cheap_allocated()) delete op; _cur_vm_operation = prev_vm_operation; } }
进入队列之后的 op 们,会在 VM_Thread run方法 的 loop 循环中被取出执行,当然,这个队列被取出时要加锁 MutexLockerEx(具体通过pthread_cond_wait等pthread库函数实现)
run方法是在新的操作系统线程中执行的。
具体在Threads::create_vm中体现:

具体os是怎么开始run方法的?
起始是有一个 叫 java_start 的方法,调用了 run 方法
然后 os_start 调用 pthread_start 创建一个操作系统层面的线程去执行 java_start

