线性布局中,有 4 个及其重要的参数,直接决定元素的布局和位置,这四个参数是
android:layout_gravity ( 是本元素相对于父元素的重力方向 )
android:gravity (是本元素所有子元素的重力方向)
android:orientation (线性布局以列或行来显示内部子元素)
android:layout_weight (线性布局内子元素对未占用空间【水平或垂直】分配权重值,其值越小,权重越大。
前提是子元素 设置了 android:layout_width = "fill_parent" 属性(水平方向)
或 android:layout_height = "fill_parent" 属性(垂直方向)
如果某个子元素的 android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
或 android:layout_height =" wrap_content” ,
则 android:layout_weight 的设置值 对该方向上空间的分配刚好相反。
下面以一个简单例子来说明这 4个参数
<? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8" ?>
< LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height = "200dp"
android:layout_width = "200dp"
android:background = "#AABBCC"
android:orientation= "horizontal"
android:layout_gravity= "center" >
< TextView android:text = "ONE"
android:background = "#aa0000"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_margin = "1dp" />
< TextView android:text = "TWO"
android:background = "#aa0000"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_margin = "1dp" />
</ LinearLayout >
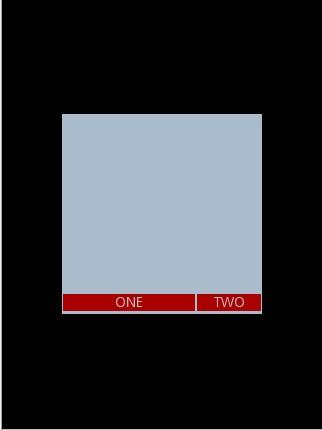
说明:在上面的例子中,根布局是LinearLayout, 其包含有2 个TextView 视图,为了对参数 android:layout_gravity有直观的了解,对根布局 LinearLayout 特意加了 3 个参数
android:layout_height = "200dp"
android:layout_width = "200dp"
android:background = "#AABBCC"
为布局指定了固定的宽度和高度,以及背景颜色,上面的例子运行后效果如下图:
说明:对LinearLayout 中的参数android:layout_gravity 来说,其意义是指定本布局相对于父布局的重力方向,由于该布局的已经是根布局,其父布局是整个屏幕,那么该参数设置的是相对于屏幕的位置,可以换不同的参数top|bottom|left|right 等等参数来试验。
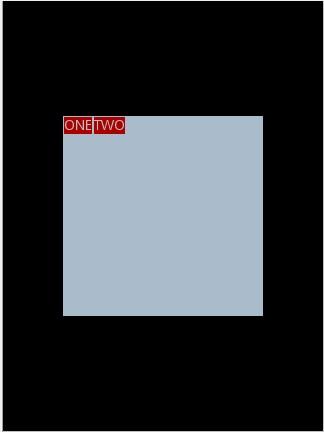
现在增加参数 android:gravity = "bottom|right" 完整 XML 如下,看看效果
<? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8" ?>
< LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height = "200dp"
android:layout_width = "200dp"
android:background = "#AABBCC"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_gravity= "center"
android:gravity = "bottom|right " >
< TextView android:text = "ONE"
android:background = "#aa0000"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_margin = "1dp" />
< TextView android:text = "TWO"
android:background = "#aa0000"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_margin = "1dp" />
</ LinearLayout >

通过改变android:gravity 参数的值可以看到实际效果。
参数 android:orientation= " horizontal " 决定了每个子元素各占一列,如果
参数 android:orientation= " vertical " , 则每个子元素各占一行,也就是从上到下排列了。
对于 LinearLayout 布局的子元素,给每个子元素加上参数 android:layout_weight
看看效果
<? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8" ?>
< LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height = "200dp"
android:layout_width = "200dp"
android:background = "#AABBCC"
android:layout_gravity = "center"
android:gravity = "bottom|right"
android:orientation = "horizontal" >
< TextView android:text = "ONE"
android:background = "#aa0000"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_margin = "1dp"
android:layout_weight = "1" />
< TextView android:text = "TWO"
android:background = "#aa0000"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_margin = "1dp"
android:layout_weight = "2" />
</ LinearLayout >
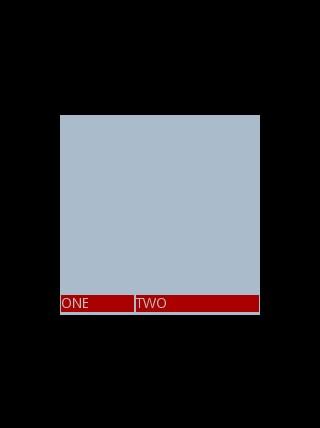
Text 为ONE 的权重为1 ,但明显占的宽度比TWO 的小,百思不得其解,后来得知,如果把TextView 的参数android:layout_width = "wrap_content" 全部修改为 android:layout_width = "fill_parent", 则 ok ,代码如下
<? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8" ?>
< LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height = "200dp"
android:layout_width = "200dp"
android:background = "#AABBCC"
android:layout_gravity = "center"
android:gravity = "bottom|right"
android:orientation = "horizontal" >
< TextView android:text = "ONE"
android:background = "#aa0000"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_width = " fill_parent "
android:layout_margin = "1dp"
android:layout_weight = "1" />
< TextView android:text = "TWO"
android:background = "#aa0000"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_width = " fill_parent "
android:layout_margin = "1dp"
android:layout_weight = "2" />
</ LinearLayout >