一、说明
shell中获取参数可以直接使用$1、$2等形式来获取,但这种方式有明显的限制:每个参数的位置是固定的。比如如果在设计上$1是ip地址$2是端口,那在执行时就必须第一个参数是ip第二个参数是端口而不能反过来。
shell提供了getopt和getopts来解析参数,getopt比getopts功能强一些getopts比getopt简单一些;总体而言getopt和getopts都差强人意。
二、使用getopt解析参数
getopt比getopts强一些复杂一些:能在命令行中单独使用、支持长选项格式、支持选项值可选。更多说明见注释。
#/bin/bash usage(){ echo " Usage: -i, --ip target server ip -p, --port target service port -h, --help display this help and exit example1: testGetopt -i192.168.1.1 -p80 example2: testGetopt --ip=192.168.1.1 --port=80 " # 短格式中,选项值为可选的选项,选项值只能紧接选项而不可使用任何符号将其他选项隔开;如-p80,不要写成性-p 80 # 短格式中,选项值为必有的选项,选项值既可紧接选项也可以使用空格与选项隔开;如-i192.168.1.1,也可写成-i 192.168.1.1 # 长格式中,选项值为可选的选项,选项值只能使用=号连接选项;如--port=80,不可写成性--port80或--port 80 # 长格式中,选项值为必有的选项,选项值既可使用=号连接选项也可使用空格连接选项;如--ip=192.168.1.1,也可写成--ip 192.168.1.1 # 为简便起见,建议凡是短格式都使用“选项+选项值”的形式(-p80),凡是长格式都使用“选项+=+选项值”的形式(--port=80) } main(){ while true do case "$1" in -i|--ip) ip="$2" echo "ip: $ip" shift ;; -p|--port) port="$2" echo "port: $port" shift ;; -h|--help) usage # 打印usage之后直接用exit退出程序
exit ;; --) shift break ;; *) echo "$1 is not option" ;; esac shift done # 剩余所有未解析到的参数存在$@中,可通过遍历$@来获取 #for param in "$@" #do # echo "Parameter #$count: $param" #done } # 如果只注册短格式可以如下这样子 # set -- $(getopt i:p::h "$@") # 如果要注册长格式需要如下这样子 # -o注册短格式选项 # --long注册长格式选项 # 选项后接一个冒号表示其后为其参数值,选项后接两个冒号表示其后可以有也可以没有选项值,选项后没有冒号表示其后不是其参数值 set -- $(getopt -o i:p::h --long ip:,port::,help -- "$@") # 由于是在main函数中才实现参数处理,所以需要使用$@将所有参数传到main函数 main $@
持行效果:
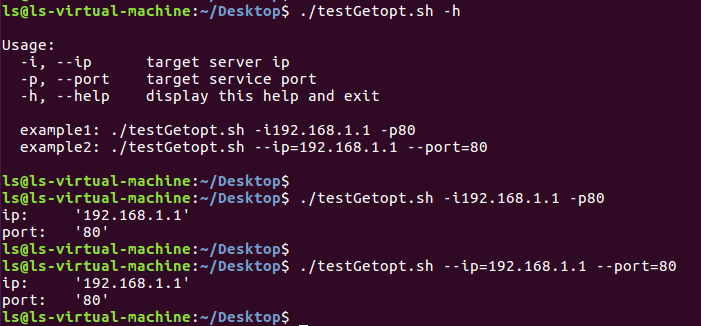
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/wh211212/article/details/53750366
http://yejinxin.github.io/parse-shell-options-with-getopt-command
三、使用getopts解析参数
getopts比getopt弱一些简单一些:不能在命令行中单独使用、不支持长选项格式、不支持选项值可选。更多说明见注释。
#!/bin/bash usage(){ echo " Usage: -i, --ip target server ip -p, --port target service port -h, --help display this help and exit example1: ./testGetopts.sh -i192.168.1.1 -p80 example2: ./testGetopts.sh -i 192.168.1.1 -p 80 " # getopts只能在shell脚本中使用,不能像getopt一样在命令行中单独使用 # getopts只支持短格式不支持长格式 # getopts如果设定有选项值的选项,如果没提供选项值那么会直接报错 # getopts选项要么有选项值要么没有选项值,没有可有也可以没有 # getopts选项后可紧接选项值,也可以使用空格隔开;为与getopt统一建议使用紧接格式 } main(){ # 选项有:表示该选项需要选项值 while getopts "i:p:h" arg do case $arg in i) #参数存在$OPTARG中 ip="$OPTARG" echo "ip: $ip" ;; p) port="$OPTARG" echo "port: $port" ;; h) usage
# 打印usage之后直接用exit退出程序
exit ;; ?) #当有不认识的选项的时候arg值为? echo "unregistered argument" exit 1 ;; esac done } main $@
执行效果:
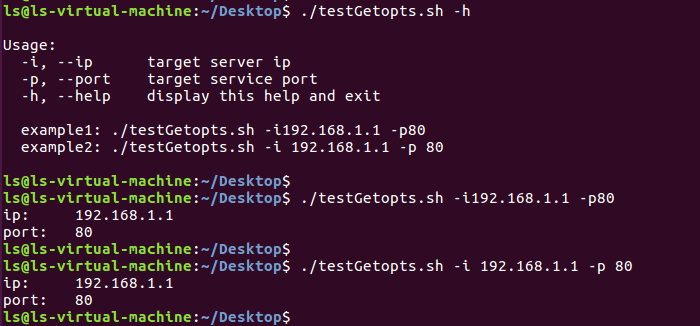
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/FrankTan/archive/2010/03/01/1634516.html