开篇明意
ThreadLocal是JDK包提供的线程本地变量,如果创建了ThreadLocal<T>变量,那么访问这个变量的每个线程都会有这个变量的一个副本,在实际多线程操作的时候,操作的是自己本地内存中的变量,从而规避了线程安全问题。
ThreadLocal很容易让人望文生义,想当然地认为是一个“本地线程”。其实,ThreadLocal并不是一个Thread,而是Thread的一个局部变量,也许把它命名ThreadLocalVariable更容易让人理解一些。
来看看官方的定义:这个类提供线程局部变量。这些变量与正常的变量不同,每个线程访问一个(通过它的get或set方法)都有它自己的、独立初始化的变量副本。ThreadLocal实例通常是类中的私有静态字段,希望将状态与线程关联(例如,用户ID或事务ID)。
源码解析
1.核心方法之 set(T t)
1 /** 2 * Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable 3 * to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to 4 * override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue} 5 * method to set the values of thread-locals. 6 * 7 * @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of 8 * this thread-local. 9 */ 10 public void set(T value) { 11 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); 12 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); 13 if (map != null) 14 map.set(this, value); 15 else 16 createMap(t, value); 17 }
解析:
当调用ThreadLocal的set(T t)的时候,代码首先会获取当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal中的静态内部类,同时也作为Thread的成员变量存在,后面会进一步了解ThreadLocalMap),如果ThreadLocalMap存在,将ThreadLocal作为map的key,要保存的值作为value来put进map中(如果map不存在就先创建map,然后再进行put);
2.核心方法值 get()
/** * Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this * thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the * current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned * by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method. * * @return the current thread's value of this thread-local */ public T get() { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); //此处和set方法一致,也是通过当前线程获取对应的成员变量ThreadLocalMap,map中存放的是Entry(ThreadLocalMap的内部类(继承了弱引用))
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
解析:
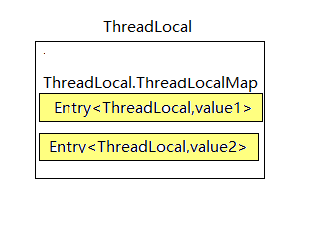
刚才把对象放到set到map中,现在根据key将其取出来,值得注意的是这里的map里面存的可不是键值对,而是继承了WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> 的Entry对象,关于ThreadLocalMap.Entry类,后面会有更加详尽的讲述。
核心方法之 remove()
/** * Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local * variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently * {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be * reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method, * unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread * in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the * {@code initialValue} method in the current thread. * * @since 1.5 */ public void remove() { ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread()); if (m != null) m.remove(this); }
解析:
通过getMap方法获取Thread中的成员变量ThreadLocalMap,在map中移除对应的ThreadLocal,由于ThreadLocal(key)是一种弱引用,弱引用中key为空,gc会回收变量value,看一下核心的m.remove(this);方法
/** * Remove the entry for key. */ private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); //定义Entry在数组中的标号 for (Entry e = tab[i]; //通过循环的方式remove掉Thread中所有的Entry e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { if (e.get() == key) { e.clear(); expungeStaleEntry(i); return; } } }
灵魂提问
问:threadlocal是做什么用的,用在哪些场景当中?
- 基于用户请求线程的数据隔离(每次请求都绑定userId,userId的值存在于ThreadLoca中)
- 跟踪一个请求,从接收请求,处理到返回的整个流程,有没有好的办法 思考:微服务中的链路追踪是否利用了ThreadLocal特性
- 数据库的读写分离
- 还有比如Spring的事务管理,用ThreadLocal存储Connection,从而各个DAO可以获取同一Connection,可以进行事务回滚,提交等操作。
/**
* 重写Threadlocal类中的getMap方法,在原Threadlocal中是返回
* t.theadLocals,而在这么却是返回了inheritableThreadLocals,因为
* Thread类中也有一个要保存父子传递的变量
*/ ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.inheritableThreadLocals; }
/**
* 同理,在创建ThreadLocalMap的时候不是给t.threadlocal赋值
*而是给inheritableThreadLocals变量赋值
*
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.inheritableThreadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); }
解析:因为InheritableThreadLocal重写了ThreadLocal中的getMap 和createMap方法,这两个方法维护的是Thread中的另外一个成员变量 inheritableThreadLocals,线程在创建的时候回复制inheritableThreadLocals中的值 ;
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained * by the ThreadLocal class. */
//Thread类中维护的成员变量,ThreadLocal会维护该变量
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null; /* * InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is * maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class. */
//Thread中维护的成员变量 ,InheritableThreadLocal 中维护该变量
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
//Thread init方法中的关键代码,简单来说是将父类中inheritableThreadLocals中的值拷贝到当前线程的inheritableThreadLocals中(浅拷贝,拷贝的是value的地址引用)
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null) this.inheritableThreadLocals = ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
总结
- ThreadLocal类封装了getMap()、Set()、Get()、Remove()4个核心方法。
- 通过getMap()获取每个子线程Thread持有自己的ThreadLocalMap实例, 因此它们是不存在并发竞争的。可以理解为每个线程有自己的变量副本。
- ThreadLocalMap中Entry[]数组存储数据,初始化长度16,后续每次都是1.5倍扩容。主线程中定义了几个ThreadLocal变量,Entry[]才有几个key。
Entry的key是对ThreadLocal的弱引用,当抛弃掉ThreadLocal对象时,垃圾收集器会忽略这个key的引用而清理掉ThreadLocal对象, 防止了内存泄漏。
tips:上面四个总结来源于其他技术博客,个人认为总结的比较合理所以直接摘抄过来了
拓展:
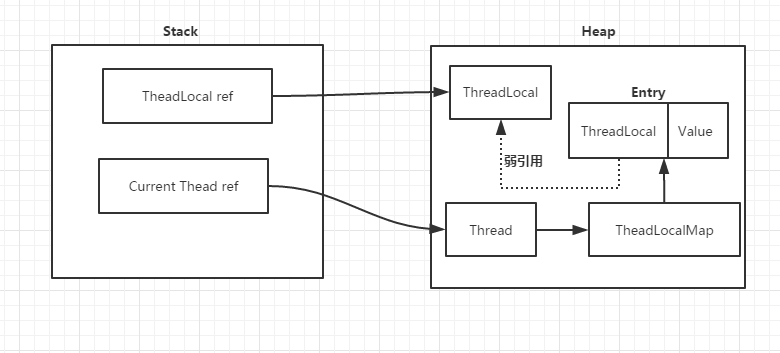
ThreadLocal在线程池中使用容易发生的问题: 内存泄漏,先看下图
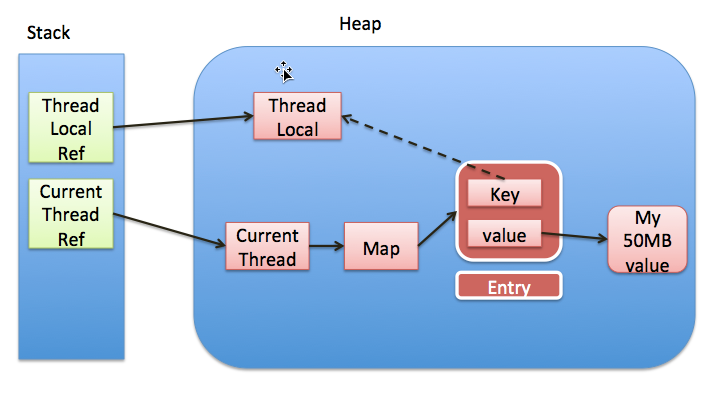
每个thread中都存在一个map, map的类型是ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap. Map中的key为一个threadlocal实例. 这个Map的确使用了弱引用,不过弱引用只是针对key. 每个key都弱引用指向threadlocal. 当把threadlocal实例置为null以后,没有任何强引用指向threadlocal实例,所以threadlocal将会被gc回收. 但是,我们的value却不能回收,因为存在一条从current thread连接过来的强引用. 只有当前thread结束以后, current thread就不会存在栈中,强引用断开, Current Thread, Map, value将全部被GC回收.
所以得出一个结论就是只要这个线程对象被gc回收,就不会出现内存泄露,但在threadLocal设为null和线程结束这段时间不会被回收的,就发生了我们认为的内存泄露。其实这是一个对概念理解的不一致,也没什么好争论的。最要命的是线程对象不被回收的情况,这就发生了真正意义上的内存泄露。比如使用线程池的时候,线程结束是不会销毁的,会再次使用的。就可能出现内存泄露。
PS.Java为了最小化减少内存泄露的可能性和影响,在ThreadLocal的get,set的时候都会清除线程Map里所有key为null的value。所以最怕的情况就是,threadLocal对象设null了,开始发生“内存泄露”,然后使用线程池,这个线程结束,线程放回线程池中不销毁,这个线程一直不被使用,或者分配使用了又不再调用get,set方法,那么这个期间就会发生真正的内存泄露。
- JVM利用设置ThreadLocalMap的Key为弱引用,来避免内存泄露。
- JVM利用调用remove、get、set方法的时候,回收弱引用。
- 当ThreadLocal存储很多Key为null的Entry的时候,而不再去调用remove、get、set方法,那么将导致内存泄漏。
- 当使用static ThreadLocal的时候,延长ThreadLocal的生命周期,那也可能导致内存泄漏。因为,static变量在类未加载的时候,它就已经加载,当线程结束的时候,static变量不一定会回收。那么,比起普通成员变量使用的时候才加载,static的生命周期加长将更容易导致内存泄漏危机。
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/aspirant/p/8991010.html
在线程池中使用ThreadLocal
通过上面的分析可以知道InheritableThreadLocal是通过Thread()的inint方法实现父子之间的传递的,但是线程池是统一创建线程并实现复用的,这样就好导致下面的问题发生:
- 线程不会销毁,ThreadLocal也不会被销毁,这样会导致ThreadLoca会随着Thread的复用而复用
- 子线程无法通过InheritableThreadLocal实现传递性(因为没有单独的调用Thread的Init方法进行map的复制),子线程中get到的是null或者是其他线程复用的错乱值(疑问点还没搞清楚原因,后续补充::在异步线程中会出现null的情况,同步线程不会出现)
ps:线程池中的线程是什么时候创建的?
解决方案:
下面两个链接有详细的说明,我就不重复写了,后续我会将本文进一般优化并添加一些例子来帮助说明,欢迎收藏,关于本文有不同的意见欢迎评论指正……
https://blog.csdn.net/hanziyuan08/article/details/78190863
https://www.cnblogs.com/sweetchildomine/p/8807059.html