一.实验总结:
章节总结:
区别点 |
抽象类 |
接口 |
|---|---|---|
|
定义 |
包含一个抽象方法的类 |
抽象方法和全局变量的集合 |
|
组成 |
构造方法、抽象方法、普通方法、常量、变量 |
常量、抽象方法 |
|
使用 |
子类继承抽象类(extends) |
子类实现接口(implements) |
|
关系 |
抽象类可以实现多个接口 |
接口不能继承抽象类,但允许继承多个接口 |
|
常见设计模式 |
模板设计 |
工厂设计,代理设计 |
|
局限 |
抽象类有单继承的局限 |
接口没有单继承的局限 |
实验四 类的继承
- 实验目的
- 理解抽象类与接口的使用;
- 了解包的作用,掌握包的设计方法。
- 实验要求
- 掌握使用抽象类的方法。
- 掌握使用系统接口的技术和创建自定义接口的方法。
- 了解 Java 系统包的结构。
- 掌握创建自定义包的方法。
(一)抽象类的使用:
- 设计一个类层次,定义一个抽象类--形状,其中包括有求形状的面积的抽象方法。 继承该抽象类定义三角型、矩形、圆。 分别创建一个三角形、矩形、圆存对象,将各类图形的面积输出。
注:三角形面积s=sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)) 其中,a,b,c为三条边,p=(a+b+c)/2
2.编程技巧
(1) 抽象类定义的方法在具体类要实现;
(2) 使用抽象类的引用变量可引用子类的对象;
(3) 通过父类引用子类对象,通过该引用访问对象方法时实际用的是子类的方法。可将所有对象存入到父类定义的数组中。
1:三角形:
package test; public class Delta extends Shape { private double a; private double b; private double c; public Delta(double a,double b,double c) { this.setA(a); this.setB(b); this.setC(c); } public void setA(double a) { this.a=a; } public double getA() { return a; } public void setB(double b) { this.b=b; } public double get() { return b; } public void setC(double c) { this.c=c; } public double getC() { return c; } public double getArea() { return Math.sqrt((a+b+c)/2*((a+b+c)/2-a)*((a+b+c)/2-b)*((a+b+c)/2-c)); } }
2:圆:
public class dome3 extends dome { public double redius; public dome3(double redius) { this.redius = redius; } public double getRedius() { return redius; } public void setRedius(double redius) { this.redius = redius; } public double S() { double s = Math.pow(redius, 2) * 3.14; return s; }
3:矩形:
package test; public class Rectangle extends Shape { private double hight; private double width; public Rectangle(double width, double hight) { this.setWidth(width); this.setHight(hight); } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setHight(double hight) { this.hight = hight; } public double getArea() { return hight * width; } }
4:测试类:
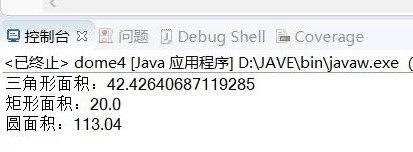
public class dome { public static void main(String[] args) { dome1 g = new dome1(9, 10, 11); dome2 h = new dome2(4, 5); dome3 j = new dome3(6); System.out.println("三角形面积:" + g.S()); System.out.println("矩形面积:" + h.S()); System.out.println("圆面积:" + j.S()); } }
截图:
(二)使用接口技术:
1:直线:
package test; public class Steep implements Shape1 { private double hight; public Steep(double hight) { this.setHight(hight); } public void setHight(double hight) { this.hight = hight; } public double getHight() { return hight; } public double getPerimeter() { return this.hight; } public double getArea() { return 0; } }
2:圆:
package test; public class Round1 implements Shape1 { private double radius; public Round1() { } public Round1(double radius) { this.setRadius(radius); } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public double getArea() { return Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2); } public double getPerimeter() { return Math.PI * 2 * radius; } }
3:测试类:
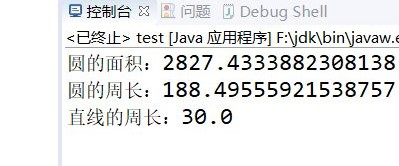
package test; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { Shape1 c = new Round1(30); Shape1 s = new Steep(30); System.out.println("圆的面积:" + c.getArea()); System.out.println("圆的周长:" + c.getPerimeter()); System.out.println("直线的周长:" + s.getPerimeter()); }
4:截图: