NIO库在JDK1.4中引入,它以标准Java代码提供了高速的,面向块的IO,弥补了之前同步IO的不足。
缓冲区Buffer
Buffers是一个对象,包含了一些要写入或读出的数据。在面向流的IO模型中,数据是直接写入或读出到Stream对象中的,在NIO中,所有数据都是用缓冲区处理的,在读取数据时,数据直接读到缓冲区中,写入数据时直接写到缓冲区,在任何时候访问NIO中的数据都要通过缓冲区。缓冲区是基于数组实现的,同时提供了对数据的结构化访问并且维护了读写位置。一个ByteBuffer提供了一组功能用于操作byte数组,每种Java类型都对应了一种缓冲区:CharBuffer字符缓冲区,Shortbuffer短整型缓冲区,IntBuffer整型缓冲区,LongBuffer长整型缓冲区,FloatBuffer浮点型缓冲区,DoubleBuffer双精度浮点缓冲区。每一个Buffer类都是Buffer接口的子实例,每一个Buffer类都有完全一样的操作,只是操作的数据类型不一样,ByteBuffer在一般缓冲区操作外提供了一些特有的操作。
缓冲区是包在一个对象内的基本数据元素数组,其有四个重要属性
容量( Capacity):缓冲区能够容纳的数据元素的最大数量,容量在缓冲区创建时被设定,并且永远不能被改变。
上界(Limit):缓冲区的第一个不能被读或写的元素。或者说,缓冲区中现存元素的计数。
位置(Position):下一个要被读或写的元素的索引。位置会自动由相应的 get( )和 put( )函数更新。
标记(Mark):一个备忘位置。调用 mark( )来设定 mark = postion。调用 reset( )设定 position = mark。标记在设定前是未定义的(undefined)。
四个属性之间的关系如下: 0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
初始时,mark未被设定,position为0,capacity为10,limit为10,第一个元素存放至position为0的位置,capacity不变,其他三个属性会变化。position在调用 put()时,会自动指出了下一个数据元素应该被插入的位置,或者当 get()被调用时指出下一个元素应从何处取出。当put完数据后需要读取时,需要调用flip函数,其将limit设置为position,然后将position设置为0, 之后开始读取。
buffer常见方法如下:
- flip(): 写模式转换成读模式
- rewind():将 position 重置为 0 ,一般用于重复读。
- clear() :清空 buffer ,准备再次被写入 (position 变成 0 , limit 变成 capacity) 。
- compact(): 将未读取的数据拷贝到 buffer 的头部位。
- mark(): reset():mark 可以标记一个位置, reset 可以重置到该位置。
通道Channel
Channel是一个通道,如水管一样,网络数据通过Channel读取和写入,通道是双向的,流是单向的,一个流必须是InputStream或者OutputStream的子类,通道可以用于读写同时进行,所以它是全双工的。Channel可以分为两大类,用于网络读写的SelectableChannel和用于文件操作的FileChannel,ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel都是SelectableChannel的子类。
Channel接口类只定义了两个方法(isOpen和close),分别表示通道是否打开和关闭通道,具体细节需要子类实现。
IO操作可分为File IO和Stream IO,对应通道也有它们是文件( file)通道和套接字( socket)通道 。通道可以有多种方式创建。Socket 通道有可以直接创建新 socket 通道的工厂方法。但File通道不能直接创建,只能通过在一个打开的RandomAccessFile、FileInputStream或FileOutputStream的对象上调用getChannel( )方法来获取。
通道将数据传输给 ByteBuffer 对象或者从 ByteBuffer 对象获取数据进行传输,通道可以是单向或者双向的。一个 channel 类可能实现定义read( )方法的 ReadableByteChannel 接口,而另一个 channel 类也许实现 WritableByteChannel 接口以提供 write( )方法。实现这两种接口其中之一的类都是单向的,一个类同时实现这两个接口,那么它是双向的,如ByteChannel 接口。从 FileInputStream 对象的getChannel( )方法获取的 FileChannel 对象是只读的,不过从接口声明的角度来看却是双向的,因为FileChannel 实现 ByteChannel 接口。在这样一个通道上调用 write( )方法将抛出未经检查的NonWritableChannelException 异常,因为 FileInputStream 对象总是以 read-only 的权限打开文件。
通道会连接一个特定 I/O 服务且通道实例( channel instance)的性能受它所连接的 I/O 服务的特征限制。如一个连接到只读文件的 Channel 实例不能进行写操作,即使该实例所属的类可能有 write( )方法。
通道可以以阻塞( blocking)或非阻塞( nonblocking)模式运行,非阻塞模式的通道永远不会让调用的线程休眠。请求的操作要么立即完成,要么返回一个结果表明未进行任何操作。只有面向流的( stream-oriented)的通道,如 sockets 和 pipes 才能使用非阻塞模式。通道不能被重复使用,一个打开的通道即代表与一个特定 I/O 服务的特定连接并封装该连接的状态。当通道关闭时,连接会丢失,通道将不再连接任何东西。
1. FileChannel写文件,读文件
public class FileChannelTest {
static void write() throws IOException {
File file = new File("test");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
FileChannel channel = outputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
String string = "123 456 abcd EFG !@#$% 测试";
buffer.put(string.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
channel.write(buffer);
channel.close();
outputStream.close();
}
static void read() throws IOException {
File file = new File("test.txt");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel channel = inputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
String string = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.print(string);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
write();
read();
}
}
---
2.使用Channel接收和发送数据
public class ChannelServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); ServerSocket serverSocket = serverSocketChannel.socket(); serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)); int count = 0; SocketChannel socketChannel = null; ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512); while (count < 20) { if (socketChannel == null) { socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); } else { count++; byteBuffer.clear(); socketChannel.read(byteBuffer); byteBuffer.flip(); String message = getString(byteBuffer); System.out.println(count + " server received: " + message); byteBuffer.clear(); byteBuffer.put(message.getBytes()); byteBuffer.flip(); socketChannel.write(byteBuffer); System.out.println(count + " server send: " + message); } TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); } serverSocketChannel.close(); } public static String getString(ByteBuffer buffer) { Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); CharBuffer charBuffer = charset.decode(buffer); return charBuffer.toString(); } }
---
public class ChannelClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(); socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)); ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512); int count = 0; while (count < 20) { count++; String message = "message " + count; byteBuffer.clear(); byteBuffer.put(message.getBytes()); byteBuffer.flip(); socketChannel.write(byteBuffer); System.out.println(count + " client send: " + message); byteBuffer.clear(); int readBytes = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer); if (readBytes > 0) { byteBuffer.flip(); System.out.println(count + " client receive: " + getString(byteBuffer)); } } socketChannel.close(); } public static String getString(ByteBuffer buffer) { Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); CharBuffer charBuffer = charset.decode(buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer()); return charBuffer.toString(); } }
---
多路复用Selector
Selector是NIO的基础,Selector提供了选择已经就绪的任务的能力,它会不断的轮询注册在其上的Channel,如果某个Channel上发生读或者写事件,这个Channel就出于就绪状态,会被Selector轮询出来,然后通过SelectingKey可以获取就绪的Channel集合,进行后续的IO操作。一个Selector可以同时轮询多个Channel,由于JDK使用了epoll代替传统的select实现,所以它并没有最大连接句柄的限制。
选择器管理一个被注册的通道集合的信息和它们的就绪状态,通道和选择器一起被注册,并且选择器可更新通道的就绪状态,也可将被唤醒的线程挂起,直到有通道就绪。
SelectableChannel 可被注册到 Selector 对象上,同时可以指定对那个选择器而言,哪种操作是感兴趣的。一个通道可以被注册到多个选择器上,但对每个选择器而言,只能被注册一次,通道在被注册到一个选择器上之前,必须先设置为非阻塞模式,通过调用通道的configureBlocking(false)方法即可。这意味着不能将FileChannel与Selector一起使用,因为FileChannel不能切换到非阻塞模式,而套接字通道都可以。
选择键封装了特定的通道与特定的选择器的注册关系,选择键对象被SelectableChannel.register( ) 方法返回并提供一个表示这种注册关系的标记。选择键包含了两个比特集(以整数的形式进行编码),指示了该注册关系所关心的通道操作及通道已经准备好的操作。
3. 使用Selector发送和接收数据
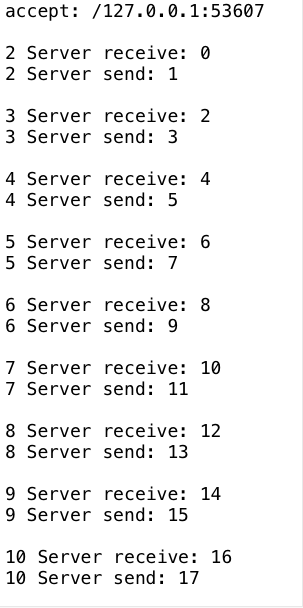
package com.luangeng.jdk.nio; import com.luangeng.utils.Q; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class NioServer { private static final Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int count = 0; int msgValue = 0; //打开ServerSocketChannel,用于监听客户端的连接,是所有客户端连接的父管道 ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //绑定监听端口,设置连接为非阻塞模式 serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)); serverChannel.configureBlocking(false); //创建Reactor线程,创建多路复用器并启动线程 Selector selector = Selector.open(); //将SercerSocketChannel注册到Reactor线程的多路复用器Selector上监听ACCEPT事件 serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); while (true) { //多路复用器在线程run方法中无限循环体内轮询准备就绪的Key int num = selector.select(); if (num == 0) { continue; } Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { count++; SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) it.next(); if (key.isAcceptable()) { //多路复用器监听到有新的客户端接入,处理新的接入请求,完成TCP三次握手,建立物理链路 SocketChannel channel = serverChannel.accept(); //设置客户端链路为非阻塞状态 channel.configureBlocking(false); channel.socket().setReuseAddress(true); //将新接入的客户端连接注册到Reactor线程的多路复用器上,监听读操作,读取客户端发送的网络信息 channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); Q.p("accept: " + channel.getRemoteAddress()); } if (key.isReadable()) { SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); //异步读取客户端请求消息到缓冲区 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); channel.read(buffer); buffer.flip(); String msg = charset.decode(buffer).toString(); Q.p(count + " Server receive: " + msg); msgValue = Integer.valueOf(msg.trim()) + 1; buffer.clear(); } if (key.isValid() && key.isWritable()) { SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); channel.write(charset.encode("" + msgValue)); Q.p(count + " Server send: " + msgValue); } Q.p(); it.remove(); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } //if (msgValue==100){ // break; //} } //关闭 //selector.close(); //serverChannel.close(); } }
---
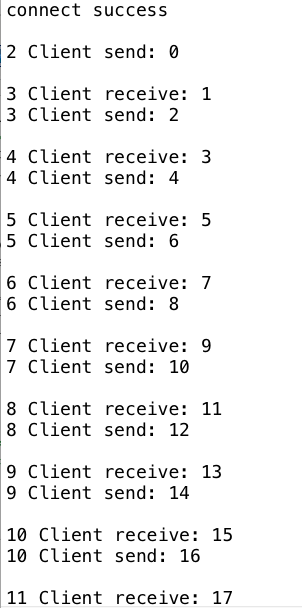
package com.luangeng.jdk.nio; import com.luangeng.utils.Q; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.Socket; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class NioClient { private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024; private static final Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int count = 0; int msgValue = 0; //打开SocketChannel,绑定客户端本地地址(可选,默认系统会随机分配一个可用的本地地址) SocketChannel clientChannel = SocketChannel.open(); //设置SocketChannel为非阻塞模式,同时设置客户端连接的TCP参数 clientChannel.configureBlocking(false); Socket socket = clientChannel.socket(); socket.setReuseAddress(true); socket.setReceiveBufferSize(BUFFER_SIZE); socket.setSendBufferSize(BUFFER_SIZE); //创建Reactor线程,创建多路复用器并启动线程 Selector selector = Selector.open(); //异步连接服务端 boolean connected = clientChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)); //向Reactor线程的多路复用器注册OP_CONNECT状态位,监听服务器端的TCP ACK应答 clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); while (true) { //多路复用器在线程run方法的无限循环体内轮询准备就绪的Key int num = selector.select(); if (num == 0) { continue; } Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { count++; SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) it.next(); //接收connect事件进行处理 if (key.isConnectable()) { //判断连接成功,如果成功,注册读事件到多路复用器 if (clientChannel.finishConnect()) { Q.p("connect success"); //clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); } } if (key.isReadable()) { //异步读取客户端请求消息到缓冲区 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); clientChannel.read(buffer); buffer.flip(); String msg = charset.decode(buffer).toString(); Q.p(count + " Client receive: " + msg); msgValue = Integer.valueOf(msg.trim()) + 1; buffer.clear(); } if (key.isValid() && key.isWritable()) { //调用SocketChannel的异步write接口,将消息异步发送给客户端 clientChannel.write(charset.encode("" + msgValue)); Q.p(count + " Client send: " + msgValue); } Q.p(); it.remove(); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } if (msgValue == 20) { clientChannel.finishConnect(); Q.p("finish"); //break; } } //关闭连接 //selector.close(); //clientChannel.close(); } }
---
输出:
end