有段时间没有写博客了,刚才看了看,上一篇写的时候还是在九月十四号,而现在已经是十月二十二号了。这段时间去哪里了?其实是去准备推免的复试。过程虽说有些艰辛,好在坚持了下来,最后是去了华东师范大学,地图学与地理信息系统的硕士,然后又在外面,一个人四处旅行,结实了三五好友,前几天才回来。回来既要准备科目二,又在学习HTML和CSS,Numpy的东西自然也不能落下。有一个感觉很明显:二十多天不碰,很多概念都已经生疏,再去接触,觉得很陌生。或许学习的状态就是如此,熟能生巧,用的少了,自然也就遗忘了。所以,还是得赶紧拾回来才行。
今天写的,是关于Numpy中的一些便捷函数,前面几次的练习也已经体会到内置函数的优越,这次会接触到更多。
Example1
股票相关性分析
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#股票相关性分析 #提取数据 bhp = np.loadtxt("D:LearnCodepythonexerciseBHP.csv", delimiter=",", usecols=(6,), unpack=True) bhp_returns = np.diff(bhp) / bhp[:-1]
vale = np.loadtxt("D:LearnCodepythonexerciseVALE.csv", delimiter=",", usecols=(6,), unpack=True) vale_returns = np.diff(vale) / vale[:-1]
#计算协方差矩阵 covariance = np.cov(bhp_returns, vale_returns) print "Covariance", covariance
#查看对角线元素 print "Covariance diagonal", covariance.diagonal()
# 计算迹 print "Covariance trace", covariance.trace()
#计算相关系数 print covariance / (bhp_returns.std()*vale_returns.std())
#下面的才是真正的相关系数矩阵 print "Covariance coefficient", np.corrcoef(bhp_returns, vale_returns)
# 判断走势是否同步 difference = bhp - vale avg = np.mean(difference) dev = np.std(difference) # 判断最后一次交易是否同步 if np.abs(difference[-1]-avg) > 2*dev: print "out of sync" else: print "in the sync"
# 绘图 t = np.arange(len(bhp_returns)) plt.plot(t, bhp_returns, lw=1.0) plt.plot(t, vale_returns, lw=2.0) plt.show() |
结果如下:


Example2
多项式拟合
# 多项式拟合 bhp = np.loadtxt("D:LearnCodepythonexerciseBHP.csv", delimiter=",", usecols=(6, ), unpack=True) vale = np.loadtxt("D:LearnCodepythonexerciseVALE.csv", delimiter=",", usecols=(6, ), unpack=True)
# 设置拟合次数 N = 3
# 调用拟合函数ployfit t = np.arange(len(bhp)) poly = np.polyfit(t, bhp-vale, N) print "Polynomial fit", poly
# 计算多项式函数的值 vals = np.polyval(poly, t)
# 判断下一个值 print "Next value", np.polyval(poly, t[-1]+1)
# 寻找零值 print "Roots", np.roots(poly)
# 求导 der = np.polyder(poly) print "Derivative", der
# 导数的根即为函数的极值 print "Extremas", np.roots(der)
# 计算最大最小值 print "Max", np.argmax(vals) print "Min", np.argmin(vals)
# 绘图 plt.plot(t, bhp-vale) plt.plot(t, vals) plt.show() |
结果如下:

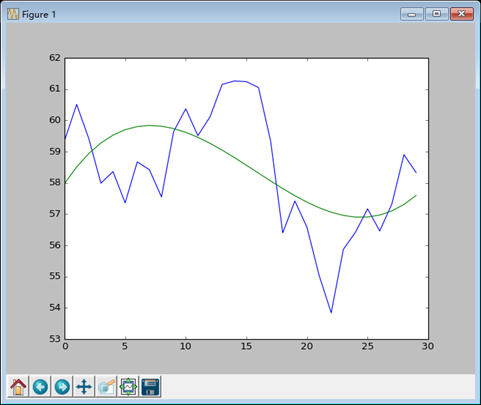
Example3
净额成交量
以某日为基期,逐日累计每日上市股票总成交量,若隔日指数或股票上涨,则基期OBV加上本日成交量为本日OBV,反之则相反。
# 净额成交量 c, v = np.loadtxt("D:LearnCodepythonexerciseBHP.csv", delimiter=",", usecols=(6, 7), unpack=True)
change = np.diff(c) print "Change", change
#计算正负,两种方法 signs = np.sign(change) print "Signs", signs pieces = np.piecewise(change, [change < 0, change > 0], [-1, 1]) print "Pieces", pieces # 检查两次输出是否一致 print "Array equal?", np.array_equal(signs, pieces)
# 计算OBV(净额成交量) print "on balance volume", v[1:] * signs |
结果如下:

Example4
交易过程模拟
# 交易过程模拟 o, h, l, c = np.loadtxt("D:LearnCodepythonexerciseBHP.csv", delimiter=",", usecols=(3, 4, 5, 6), unpack=True)
# 设置购买价与开盘价的比率 N = 0.99999
# 自定义一个相对利润函数 def calc_profit(open, high, low, close): buy = open * N if low < buy < high: return (close-buy)/buy else: return 0
# 矢量化函数 func = np.vectorize(calc_profit) profits = func(o, h, l, c)
print "Profits", profits
# 绘图 t = np.arange(len(o)) y = np.zeros(len(o)) plt.plot(t, profits) plt.plot(t, y, 'r--') plt.show()
# 计算交易的天数,并计算平均值 real_trades = profits[profits != 0] print "Number of trades", len(real_trades), round(100*len(real_trades)/len(c), 2), '%' print "Average profit/loss", round(100*np.mean(real_trades), 2), "%" |
结果如下:

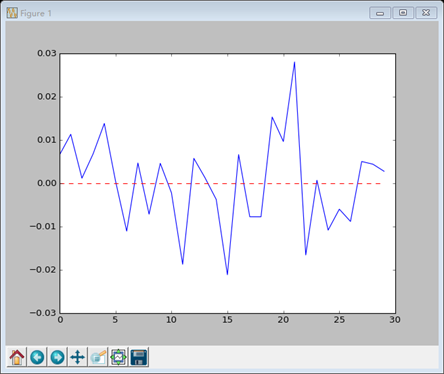
Example5
数据平滑
上一次用到了简单移动平均线对数据进行卷积运算,从而实现数据的平滑,这一次我们用Numpy内置的函数。
# 数据平滑
# 设置窗口的大小,并计算权重 N = 8 weights = np.hanning(N) print "Weights", weights
# 卷积运算 bhp = np.loadtxt("D:LearnCodepythonexerciseBHP.csv", delimiter=",", usecols=(6, ), unpack=True) bhp_returns = np.diff(bhp)/bhp[:-1] smooth_bhp = np.convolve(weights/weights.sum(), bhp_returns)[N-1:-N+1] vale = np.loadtxt("D:LearnCodepythonexerciseVALE.csv", delimiter=",", usecols=(6, ), unpack=True) vale_returns = np.diff(vale)/vale[:-1] smooth_vale = np.convolve(weights/weights.sum(), vale_returns)[N-1:-N+1]
# 绘图 t = np.arange(N-1, len(bhp_returns)) plt.subplot(211) plt.plot(t, bhp_returns[N-1:],'g--') plt.plot(t, smooth_bhp,'g-',lw=2.0 ) plt.subplot(212) plt.plot(t, vale_returns[N-1:], 'b--') plt.plot(t, smooth_vale,'b-',lw=2.0 ) plt.show() # 多项式拟合 K = 8 # 拟合次数 poly_bhp = np.polyfit(t, smooth_bhp, K) poly_vale = np.polyfit(t, smooth_vale, K)
# 计算拟合函数交叉点 poly_sub = np.polysub(poly_bhp, poly_vale) xpoints = np.roots(poly_sub) print "Intersection points", xpoints # 判断是否为实数 reals = np.isreal(xpoints) print "Real?", reals # select函数选择 xpoints = np.select([reals], [xpoints]) xpoints = xpoints.real print "Real Intersection points", xpoints
# trim_zeros函数可以去掉一维数组中开头为0的元素 print "Real Real Intersection points", np.trim_zeros(xpoints) |
结果如下:
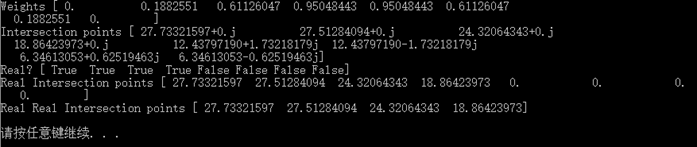

总结:一段时间没有写,的确感觉很生疏,以前的一些基本概念也已经含混不清,还得是回过头去看,当然,学习的过程本就是这样,遗忘在所难免,这也就是我为什么倾向于迭代的学习,忘了的东西可以再去看,理解就是在这过程中慢慢深刻起来的。这一章的练习整体上不是很难,还是沿袭了Numpy的思路,熟练地使用是关键。
源代码:https://github.com/Lucifer25/Learn-Python/blob/master/Numpy/exercise3.py