1.数组概述
- 相同类型的有序结合
2.数组的声明创建
java数组的声明主要有两种方式
- dataType[] num = new dataType[size];
- dataType num[] = new dataType[size];
- 从 0 开始, 有length属性
package com.luckylight.array;
public class ArrayDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[50];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++ ) {
a[i] = i + 1;
}
long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++ ) {
sum += a[i];
}
System.out.println("数组总和=" + sum);
}
}
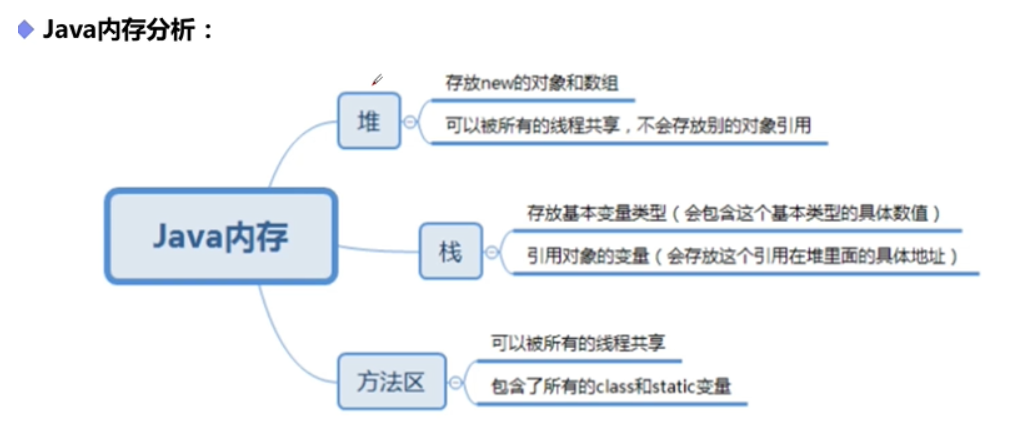
java内存简单介绍
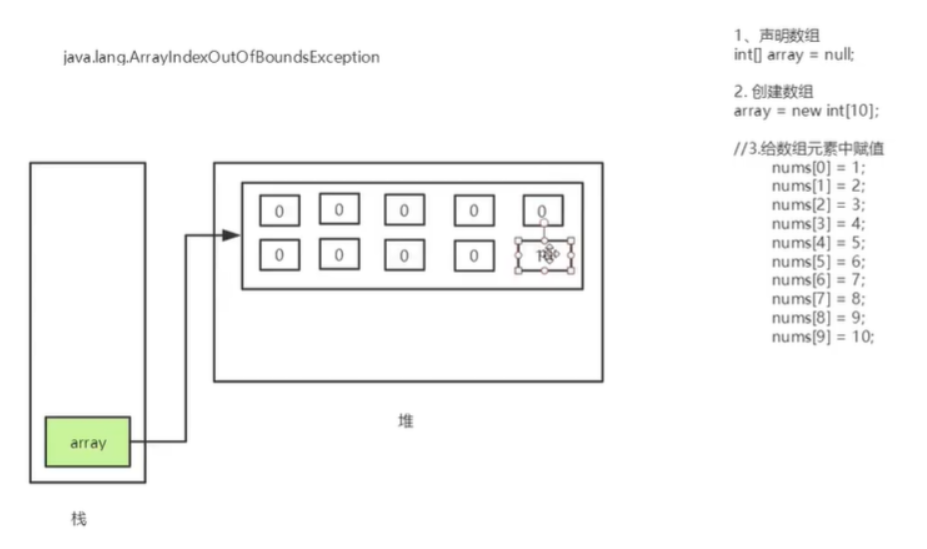
具体是声明一个数组,然后进行初始化,内存分配如下所示:
数组的初始化
- 静态初始化 + 赋值
int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 5}; // 基本类型
Max[] mans = {new Man(), new Man()}; // 引用类型
- 动态初始化 包含默认初始化,有些数据默认为0, 有些数据默认为 none
int[] b = new int[10];
数组的四个基本特点
-
数组长度是确定的,一旦被创建,他的大小就不可被改变,想要变就需要new一个新的。
-
元素必须是相同类型,不允许出现混合类型(和python的list, tuple不一样)
-
数组中的元素可以使任何数据类型,包括基本类型和引用类型
-
数组变量属于引用类型,数组也可以看做对象,数组中的 每个元素相当于该对象的成员变量。数组本身就是对象,java中的对象实在堆中的,因此数组无论保存原始类型还是其他对象类型,数组对象本身就在堆中。
package com.luckylight.array;
public class ArrayDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[5];
System.out.println(a.length);
// a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}; 这个会报错
a = new int[8];
System.out.println(a.length);
int[] b = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println(b.length);
b = new int[8];
System.out.println(b.length);
}
}
3. 数组的遍历
数组下标合法区间 0 ~ (length-1);
数组越界会显示:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
普通型循环,和增强型循环遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++ ) {
a[i] = i;
}
for (int x : a) {
System.out.println(x);
}
数组可以作为参数,也可以作为函数返回值
package com.luckylight.array;
public class ArrayDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[20];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++ ) {
a[i] = i;
}
PrintArray(a);
for (int x : a) { // 这个只是会取出来数字,并不会和数组元素所在的内存联系起来(不存在引用关系)
x = 0;
}
PrintArray(a);
int[] b = reverse(a);
PrintArray(b);
}
public static int[] reverse(int []a) {
int []b = new int[a.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++ ) {
b[i] = a[a.length - 1 - i];
}
return b;
}
public static void PrintArray(int []a) {
String res = "";
for(int x : a) {
res = res + x + ", ";
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
4. 多维数组的创建与遍历
数组的创建
int[][] a = new int[3][2];
int b[][] = new int[3][2];
int c[][] = {{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}};
a[0].length, a.length;
多维数组的尝试
package com.luckylight.array;
public class ArrayDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = new int[2][3];
int[][] b = {{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}}; // 注意内部 {} 之间是 分号 ;
System.out.println(a.length);
System.out.println(a[0].length);
System.out.println(b.length);
System.out.println(b[0].length);
System.out.println("================");
for (int[] x : b) {
for (int y : x) {
System.out.println(y);
}
}
}
}
5. Arrays类
- java提供一种工具类 java.util.Arrays
- 在工具类 Arrays中,提供了一系列对数据对象的基本操作
有问题可以直接查看 JDK 的帮助文档,或者是 直接看 Arrays里面的源码
- 有以下几种常见的方法
- fill 方法
- sort 方法
- equals 方法
- binarySearch 方法
- 这些方法都是 static 修饰的方法,可以直接通过类名调用,当然也可以通过定义对象来进行调用。
package com.luckylight.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {0, 3, 2, 1, 4, 6, 5};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
Arrays.fill(a, 0, 2, 100); // 并不会真正到达 2这里离,修改的是 st ~ ed-1
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a, a)); // 比较是否相等
}
}
这里介绍写一个简单的冒泡排序,直接上代码就好
package com.luckylight.array;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {5, 7, 3, 9, 1, -0, 35, 8, 100, -40, 1};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
a = bubbleSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
/**
* @author luckyLight
* @version 1.2.3
* @param a
* @return
*/
public static int[] bubbleSort(int []a) {
int n = a.length;
boolean flag = true;
int tmp = 0;
// 进行 n - 1 次大循环
// 这个边界问题一定要注意
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i ++ ) {
flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j <= n - i - 1; j ++ ) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
tmp = a[j]; a[j] = a[j + 1]; a[j + 1] = tmp;
flag = false;
}
}
if (flag) {
break;
}
}
return a;
}
}
6. 稀疏数组
对于二维数组而言,就是把行数值,列数值,存储内容出起来就ok了。。。
确切的的说是离散化(具体如何的快速查找,就需要数据结构和算法的支持,比如说hash,折半查找等等)
package com.luckylight.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 未 Hash前的数组并输出
int[][] a = new int[20][20];
a[0][5] = 10;
a[3][7] = 8;
a[12][9] = 77;
a[18][18] = 57;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++ ) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j ++ ) {
System.out.print(a[i][j] + ", ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
// 构造Hash数组
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++ ) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j ++ ) {
if (a[i][j] != 0) {
cnt ++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("cnt=" + cnt);
int[][] aHash = new int[cnt][3];
aHash[0][0] = a.length; aHash[0][1] = a[0].length; aHash[0][2] = cnt - 1;
cnt = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++ ) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j ++ ) {
if (a[i][j] != 0) {
aHash[cnt][0] = i; aHash[cnt][1] = j; aHash[cnt][2] = a[i][j];
cnt ++;
}
}
}
// 输出 Hash数组
for (int i = 0; i < aHash.length; i ++ ) {
System.out.printf("(%d, %d)=%d
", aHash[i][0], aHash[i][1], aHash[i][2]);
}
// 进行未 Hash稀疏之前的还原
int[][] b = new int[aHash[0][0]][aHash[0][1]]; // 默认初始化为 0
for (int i = 1; i < aHash.length; i ++ ) {
b[aHash[i][0]][aHash[i][1]] = aHash[i][2];
}
// 输出还原后的 b 数组
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i ++ ) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b[i]));
}
}
}