类图:
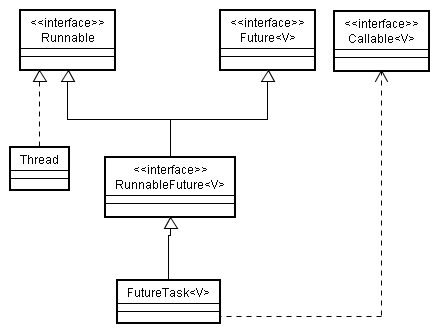
先看各自的源码:
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
public
class Thread implements Runnable {
/* What will be run. */
private Runnable target;
}
Thread与Runnable其实是一个装饰器模式。
public interface Callable<V> {
V call() throws Exception;
}
public interface Future<V> {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {
void run();
}
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {
/** The underlying callable; nulled out after running */
private Callable<V> callable;
/** The result to return or exception to throw from get() */
private Object outcome;
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
}
从类的结构来看:
Runnable,Callable,Future接口本是互相独立的,没有直接的关系。
而Thread的一系列构造函数需要的是Runnable对象,所以Callable对象并不适合Thread构造函数,而是借助于FutureTask这个类,该类实现具有Future和Runnable接口能力的类,同时组合Callable对象,FutureTask在run()方法中调用Callable的call()方法,这是个典型的适配器模式:
Runable是个目标接口,定义了Thread所需的接口;
Callable是被适配接口,定义了一个已经存在的接口方法call()
FutureTask是个适配器类,作为一个转换器,将Runnable和Callable适配,适配器类是适配器模式的核心,它通过实现RunnableFuture和组合Callable使得两者产生关系。