原题:
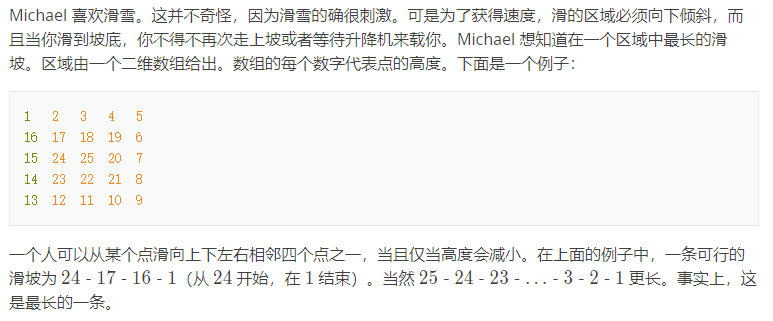

思路:
首先考虑暴搜。
对于每一个点,我记录到这一格为止,走过了多少路。然后枚举四个方向继续递归。直到彻底走不动之后,就停下来更新答案。
但是有个问题——数据规模最大100行100列,如果我以一次递归4个方向来计算,第一层4种,第二层16种,第三层64种,第四层256种,而假设我们从整个地图的中间开始找,至少要花50步找到边界,而此时共有450种方案,这个数是1,267,650,600,228,229,401,496,703,205,376
![]()
这个数肯定爆炸
所以我们想到那些我们常用的优化。
第一,剪枝。
对于每一个到达的点,我们开一个数组记忆到这个点的最长步数。
如果最长步数大于这次到达这个点时的步数,我们可以不继续。
第二,记忆化搜索。
仍然记忆最长步数,如果这个点之前走过直接返回这个值。
对于每一个点的记忆值,我们选四个方向的返回值中最大的那个+1
由这个,我们想到了DP。
DP思路与上述记忆化搜索差不多废话记忆化搜索就是DP,详见下附代码
代码:
DP:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m,maxn;
int mp[105][105];
int f[105][105];
struct node
{
int x;
int y;
int w;
}N[10005];
int cnt;
bool cmp(struct node a,struct node b)
{
return a.w<b.w;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
cnt++;
cin >> mp[i][j];
N[cnt].x=i;
N[cnt].y=j;
N[cnt].w=mp[i][j];
f[i][j]=1;
}
sort(N+1,N+1+cnt,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)
{
int x=N[i].x;
int y=N[i].y;
int w=N[i].w;
if(w>mp[x-1][y])
f[x][y]=max(f[x][y],f[x-1][y]+1);
if(w>mp[x][y-1])
f[x][y]=max(f[x][y],f[x][y-1]+1);
if(w>mp[x+1][y])
f[x][y]=max(f[x][y],f[x+1][y]+1);
if(w>mp[x][y+1])
f[x][y]=max(f[x][y],f[x][y+1]+1);
if(maxn<f[x][y])
maxn=f[x][y];
}
cout << maxn << endl;
return 0;
}
剪枝(这个写法有一个点超时,吸了氧过的,或许有更好写法):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
int sx,sy;
int cnt;
int mp[150][150];
int f[150][150];
bool bk[150][150];
bool vis[150][150];
int tmp;
int ans;
int nxt[4][2]={{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
struct node
{
int x,y,height;
}N[10050];
bool cmp(struct node a,struct node b)
{
return a.height>b.height;
}
void dfs(int x,int y,int stp)
{
bk[x][y]=false;
cnt++;
if(f[x][y]>stp)
return;
f[x][y]=stp;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int tx=x+nxt[i][0];
int ty=y+nxt[i][1];
if(tx<=0||tx>n||ty<=0||ty>m)
continue;
if(mp[tx][ty]<mp[x][y]&&!vis[tx][ty])
{
vis[tx][ty]=true;
dfs(tx,ty,stp+1);
vis[tx][ty]=false;
}
}
if(stp>ans)
ans=stp;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
cin >> mp[i][j];
//下面的循环是重点
//如果只从最高点开始搜索
//一旦遇到
/*0 94 93 92 0
96 95 98 91 90
97 98 0 98 89
98 0 99 0 98*/
//就会被卡
//其原因在于
//从最高点开始搜索,则搜索轨迹是
/*
*****
*****
**#**
*###*
*/
//就这么结束了
//显然不能覆盖所有点
//就无法得出正确答案
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
if(!bk[i][j])
{
f[i][j]=1;
dfs(i,j,1);
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}