Eclipse版本:2021-03 (4.19.0)
Java:8
Spring Boot:spring-boot-starter-parent#2.5.2(对于的spring-core/context/beans的版本为 5.3.8)
项目:nothing - 非Web项目,web - Web项目
技能GET:Debug(调试,Step Into/Over/Return)
目录
第一步) new SpringApplication(primarySources)
---
Spring Boot依赖于Spring Framework,而Spring Framework的核心是 Spring Core、Spring Context、Spring Beans。
Spring容器 是其中的核心,用来管理(装) Spring应用的 所有Bean及其关系,涉及到 BeanFactory、ApplicationContext 两个核心接口,其中,ApplicationContext 是 BeanFactory 的子孙接口。
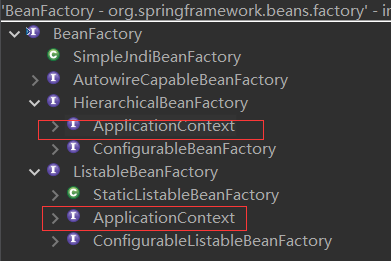
ApplicationContext 接口:
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver { // ... }
ApplicationContext 除了 Bean管理外,还有其它的功能,所以才继承了更多接口。
ApplicationContext 也有很多子孙接口及实现类,用来搭配不同的应用——非Web、Web-Servlet、Web-Reactive应用 3种(参考 WebApplicationType 枚举类)。
调用静态函数 SpringApplication#run
1 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(NothingApplication.class, args); 2 3 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(WebApplication.class, args);
其下调用了:
1 new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
分为两步:
第一步)new SpringApplication(primarySources)
第二步).run(args)
启动完毕后,返回一个 ConfigurableApplicationContext 对象,这个对象是 ApplicationContext 接口的 子接口:
1 public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable { 2 }
通过这个 ConfigurableApplicationContext 对象,可以获取 Spring容器中 所有Bean的信息,比如,总数、各个Bean的名称等。
非Web应用 Bean数量: 44 Web应用 Bean数量: 137
当然,ApplicationContext 在开发时还有更多用途。
下面分别介绍启动的两步对 ApplicationContext 的影响——主要是 容器中 Bean的变化。
第一步) new SpringApplication(primarySources)
添加断点:
开始调试(Debug As):
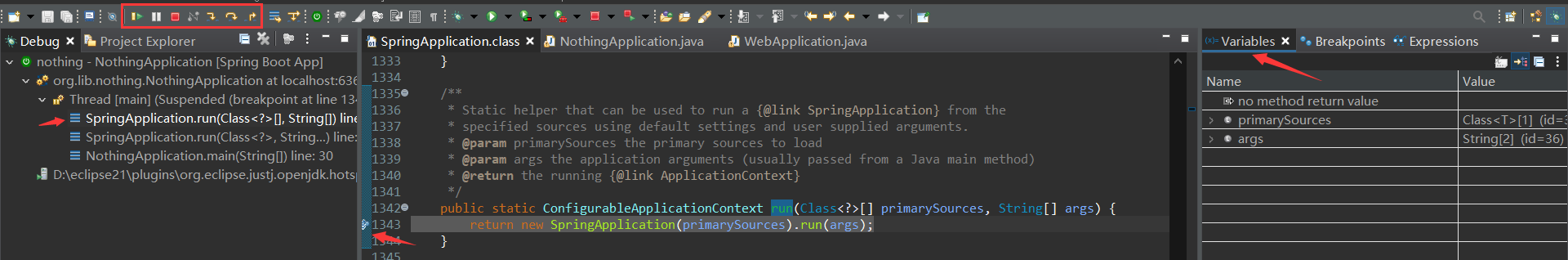
程序停止了上面。
点击 左上角的 Step Into,进入 SpringApplication 构造函数。再次Step Into 可以进入下面的构造函数:
1 @SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) 2 public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { 3 this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; 4 Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); 5 this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); 6 this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); 7 this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories(); 8 setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); 9 setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); 10 this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); 11 }
点击Step Over可以一步一步检查执行情况:构造函数会调到基本参数设置的地方,最后才进入 构造函数 上面的函数体。
第6行 判断 应用类型,结果是 前面提到的 3种。Step Over到这一行后,可以执行 Step Into 进入查看:
1 static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() { 2 if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) 3 && !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) { 4 return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE; 5 } 6 for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) { 7 if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) { 8 return WebApplicationType.NONE; 9 } 10 } 11 return WebApplicationType.SERVLET; 12 }
在本文的项目中,nothing 返回的是 NONE,web返回的是 SERVLET。
项目不同,建立的 ApplicationContext 也不同,这也是上面 两个项目初始化时 容器中具有不同 Bean数量的原因。
查看完毕,可以点击Step Return直接返回。
SpringApplication 初始化最后是 设置 bootstrapRegistryInitializers、initializers、listeners,都会调用 getSpringFactoriesInstances 函数获取实例。
Step Over到最后一步时,可以查看 右边 this对象(SpringApplication对象)的各个参数的值:
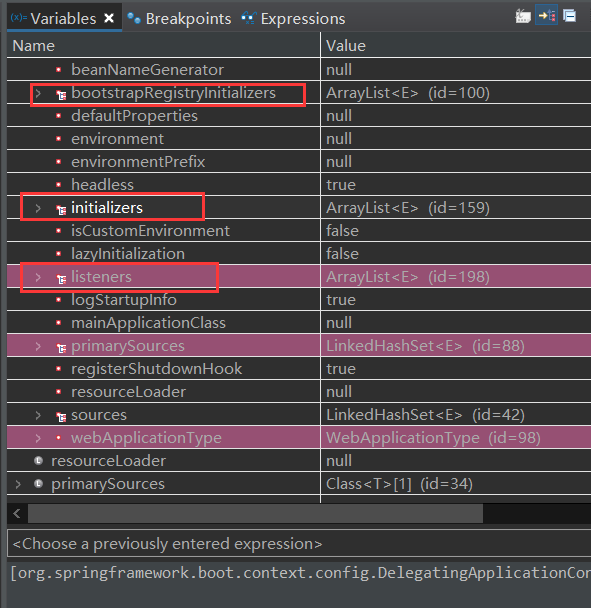
上面 红框中的 initializers、listeners 是有值的——在后面的步骤中会用到,bootstrapRegistryInitializers为空:
# initializers [org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer@55de24cc,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer@dc7df28,
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer@30f842ca,
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer@69c81773,
org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer@4d14b6c2,
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer@7e990ed7,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener@c05fddc] # listeners [org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener@25df00a0,
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener@4d15107f,
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener@7b4c50bc,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer@5884a914,
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener@50378a4,
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener@60f00693,
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener@79207381,
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener@491b9b8]
执行完毕, 即 SpringApplication 对象初始化完毕,接下来执行第二步——回到断点行时,再次执行 Step Into。
进入 run函数,来看看源码:
1 public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { 2 StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); 3 stopWatch.start(); 4 DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext(); 5 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; // 需要返回的 ApplicationContext对象 6 configureHeadlessProperty(); 7 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); 8 listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass); // 开始启动 9 try { 10 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); 11 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments); 12 configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); 13 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); // 执行Banner输出,可以配置不输出 14 context = createApplicationContext(); // 重点1:创建ApplicationContext 15 context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup); 16 prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // 重点2:执行后,将主类对象添加到 spring容器 17 refreshContext(context); // 重点3:执行后更改了更多Context的属性,并添加了更多Bean!!! 18 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); 19 stopWatch.stop(); // 上下文启动完毕,下面 通知应用已启动 started 20 if (this.logStartupInfo) { 21 new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); 22 } 23 listeners.started(context); 24 callRunners(context, applicationArguments); // 运行 ApplicationRunner、CommandLineRunner 25 } 26 catch (Throwable ex) { 27 handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners); 28 throw new IllegalStateException(ex); 29 } 30 31 try { 32 listeners.running(context); // 通知应用已运行起来了 33 } 34 catch (Throwable ex) { 35 handleRunFailure(context, ex, null); 36 throw new IllegalStateException(ex); 37 } 38 return context; 39 }
下面分析重点代码行。
11行: prepareEnvironment,,不同应用类型,有不同的 环境变量
1 private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() { 2 if (this.environment != null) { 3 return this.environment; 4 } 5 switch (this.webApplicationType) { 6 case SERVLET: 7 return new ApplicationServletEnvironment(); 8 case REACTIVE: 9 return new ApplicationReactiveWebEnvironment(); 10 default: 11 return new ApplicationEnvironment(); 12 } 13 }
14行:createApplicationContext()
1 protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { 2 return this.applicationContextFactory.create(this.webApplicationType); 3 }
这里的create函数 是 ApplicationContextFactory接口 的 DEFAULT 对象,它根据不同的 webApplicationType 来创建不同的 ApplicationContext:
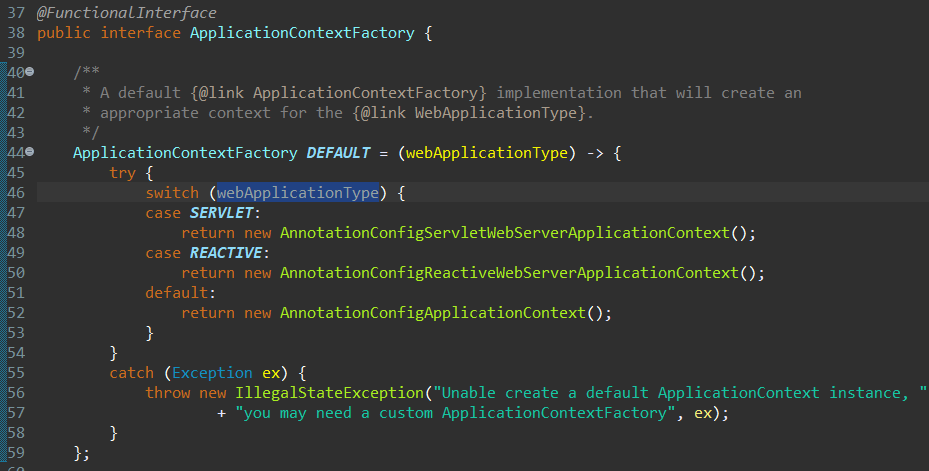
注意,这里无法使用 Step Over 进入 DEFAULT 对象的执行体。
非Web应用:
1 public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() { 2 StartupStep createAnnotatedBeanDefReader = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.annotated-bean-reader.create"); 3 this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); 4 createAnnotatedBeanDefReader.end(); 5 this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); 6 }
Web-Sevlet应用:
1 public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() { 2 this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); 3 this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); 4 }
Web-Reactive应用:
1 public AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext() { 2 this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); 3 this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); 4 }
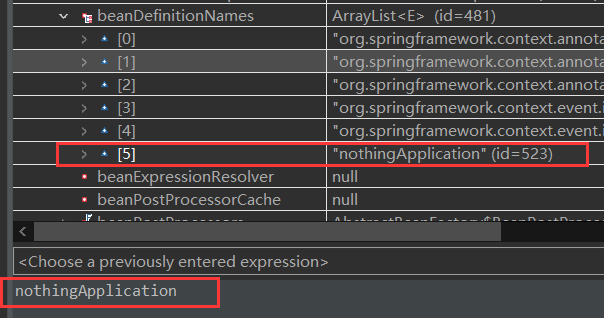
执行完 第14行 后,context变量不再是 null了,其下的 beanFactory对象下的 beanDefinitionNames也要 5个对象了:
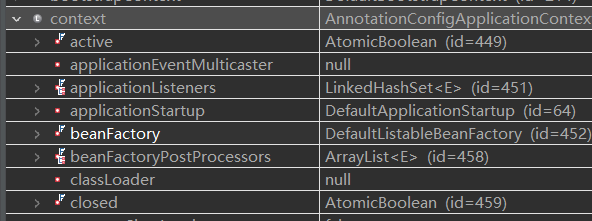
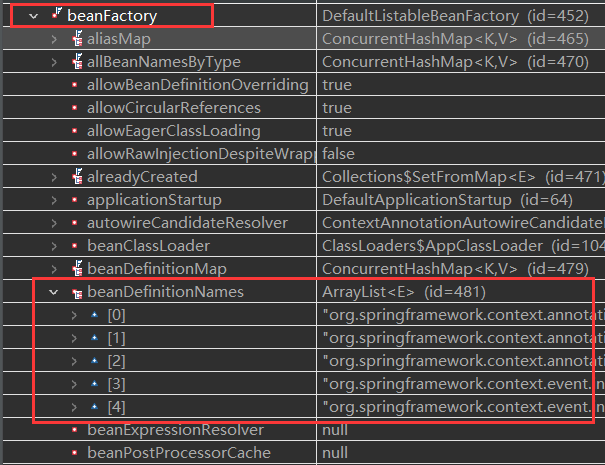
这个就是 Spring容器,更多的 Bean将在 后面的步骤中装入其中。
在 非Web、Web-Servlet应用 中,上面 beanDefinitionNames的 5个元素的值是相同的,列举如下:
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
16行:prepareContext 函数调用,添加主类到容器
17行:refreshContext
24行:callRunners
1 private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) { 2 List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>(); 3 runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values()); 4 runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values()); 5 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners); 6 for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) { 7 if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) { 8 callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args); 9 } 10 if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) { 11 callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args); 12 } 13 } 14 }
上面运行完毕,返回context,此时,项目已成功启动。
更多问题:
1、这些Bean 是怎么找到的呢?
答案在 17行 refreshContext(context) 的执行过程中,可以更进一步 调试。由于没有外部配置文件,主要是根据 主类的配置(注解:默认 或 自定义的)去查找需要的 Bean。
2、怎么改造启动过程呢——为了更好地使用?
说明,
1、Debug的确挺好用的。除了在Debug前加断点,在Debug中也可以加断点,再控制执行到自己需要的行。
2、结合Spring相关文档,阅读源码时可以收获更多。因为,文档中还提到不少 可扩展的地方,结合在一起,就可以更好地使用Spring来开发应用了。
参考资料
非常好的一篇文章!必读!
3、