一、kubectl命令与资源管理
1、资源管理操作概述

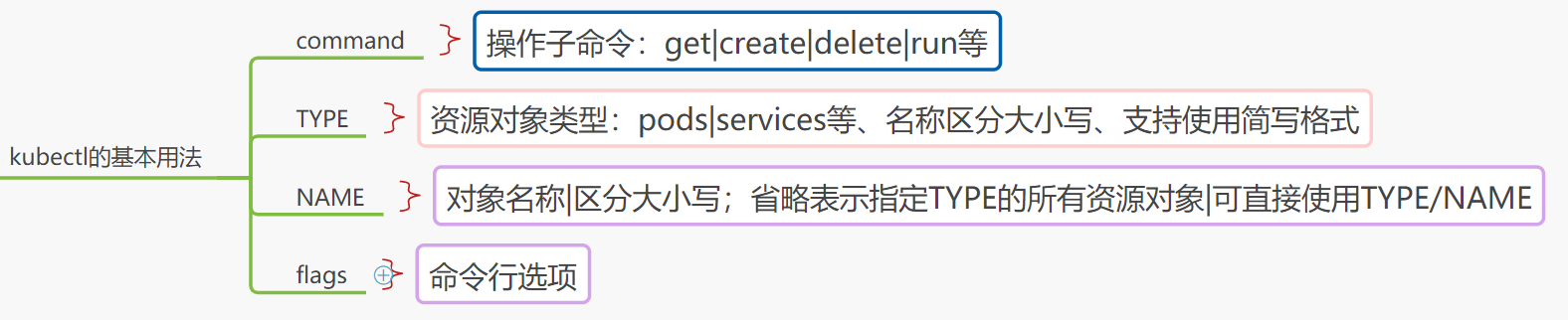
2、kubectl的基本用法
二、kubectl的子命令列表
[root@master ~]# kubectl -h kubectl controls the Kubernetes cluster manager. Find more information at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/ Basic Commands (Beginner): #期初命令(初级) create Create a resource from a file or from stdin. #通过文件或标准输入创建资源 expose Take a replication controller, service, deployment or pod and expose it as a new Kubernetes Service #基于rc svc depoy或创建svc资源 run Run a particular image on the cluster #通过创建deploy在集群中运行指定的镜像 set Set specific features on objects #设置指定资源的特定属性 Basic Commands (Intermediate): #期初命令(中级) explain Documentation of resources #打印资源文档 get Display one or many resources #显示一个或多个资源 edit Edit a resource on the server #编辑资源 delete Delete resources by filenames, stdin, resources and names, or by resources and label selector #基于文件名、stdin、资源或名字、以及资源和选择器删除资源 Deploy Commands: #部署命令 rollout Manage the rollout of a resource #管理资源的滚动更新 scale Set a new size for a Deployment, ReplicaSet or Replication Controller #伸缩deploy、rs、rc或job的规模 autoscale Auto-scale a Deployment, ReplicaSet, or ReplicationController #伸缩deploy、rs、rc进行自动伸缩 Cluster Management Commands: #集群管理命令 certificate Modify certificate resources. #配置数字证书资源 cluster-info Display cluster info #打印集群信息 top Display Resource (CPU/Memory/Storage) usage. #打印资源(cpu/mem/storage)使用率 cordon Mark node as unschedulable #将node设定为 不可用unschedulable状态 uncordon Mark node as schedulable #将node设定为 不可用schedulable状态 drain Drain node in preparation for maintenance #排干指定的node的负载以进入维护模式 taint Update the taints on one or more nodes #为node声明污点及标准行为 Troubleshooting and Debugging Commands: #排除及调试命令 describe Show details of a specific resource or group of resources #显示指定的资源或资源组的详细信息 logs Print the logs for a container in a pod #显示一个POD内某容器的日志 attach Attach to a running container #附加终端至一个运行中的容器 exec Execute a command in a container #在容器中执行指定命令 port-forward Forward one or more local ports to a pod #将本地的一个或多个端口转发至指定的pod proxy Run a proxy to the Kubernetes API server #创建能够访问Kubernetes API Server的代理 cp Copy files and directories to and from containers. #在容器间复制文件或目录 auth Inspect authorization #打印授权信息 Advanced Commands: #高级命令 diff Diff live version against would-be applied version apply Apply a configuration to a resource by filename or stdin #基于文件或stdin将配置应用于资源 patch Update field(s) of a resource using strategic merge patch #使用策略合并补丁更新资源字段 replace Replace a resource by filename or stdin #基于文件或stdin替换一个资源 wait Experimental: Wait for a specific condition on one or many resources. convert Convert config files between different API versions #为不同的API版本转换配置文件 kustomize Build a kustomization target from a directory or a remote url. Settings Commands: #设置命令 label Update the labels on a resource #更新指定资源的label annotate Update the annotations on a resource #更新资源的annotation completion Output shell completion code for the specified shell (bash or zsh) #输出指定的shell的补全代码 Other Commands: #其他命令 alpha Commands for features in alpha api-resources Print the supported API resources on the server #打印服务器上支持的API资源 api-versions Print the supported API versions on the server, in the form of "group/version" #以 group/version格式打印服务器支持的API版本信息 config Modify kubeconfig files #配置kubeconfig文件的内容 plugin Provides utilities for interacting with plugins. #运行命令行插件 version Print the client and server version information #打印服务端和客户端的版本信息 Usage: kubectl [flags] [options] Use "kubectl <command> --help" for more information about a given command. Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
三、kubectl get命令的常用输出格式
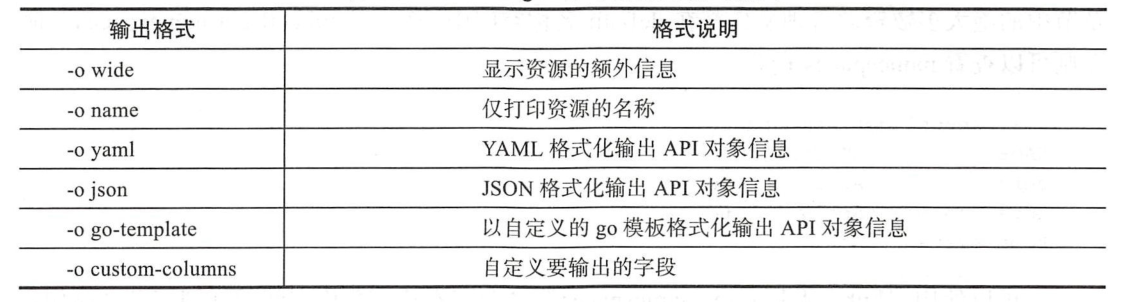
1、kubectl get命令的常用输出格式
[root@master ~]# kubectl get -h
Display one or many resources
......
Examples:
# List all pods in ps output format.
kubectl get pods
# List all pods in ps output format with more information (such as node name).
kubectl get pods -o wide #显示资源的详细信息
# List a single replication controller with specified NAME in ps output format.
kubectl get replicationcontroller web
# List deployments in JSON output format, in the "v1" version of the "apps" API group:
kubectl get deployments.v1.apps -o json #JSON格式输出API对象信息
# List a single pod in JSON output format.
kubectl get -o json pod web-pod-13je7
# List a pod identified by type and name specified in "pod.yaml" in JSON output format.
kubectl get -f pod.yaml -o json #JSON格式输出API对象信息
# List resources from a directory with kustomization.yaml - e.g. dir/kustomization.yaml.
kubectl get -k dir/
# Return only the phase value of the specified pod.
kubectl get -o template pod/web-pod-13je7 --template={{.status.phase}}
# List resource information in custom columns.
kubectl get pod test-pod -o custom-columns=CONTAINER:.spec.containers[0].name,IMAGE:.spec.containers[0].image
#以自定义的go模板格式化输出API对象信息
# List all replication controllers and services together in ps output format.
kubectl get rc,services
# List one or more resources by their type and names.
kubectl get rc/web service/frontend pods/web-pod-13je7
-o, --output='': Output format. One of:
json|yaml|wide|name|custom-columns=...|custom-columns-file=...|go-template=...|go-template-file=...|jsonpath=...|jsonpath-file=...
See custom columns [http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/kubectl-overview/#custom-columns], golang template
[http://golang.org/pkg/text/template/#pkg-overview] and jsonpath template
[http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/jsonpath].
--output-watch-events=false: Output watch event objects when --watch or --watch-only is used. Existing objects are
2、kubectl 通用选项
[root@master ~]# kubectl options
The following options can be passed to any command:
--add-dir-header=false: If true, adds the file directory to the header
--alsologtostderr=false: log to standard error as well as files
--as='': Username to impersonate for the operation
--as-group=[]: Group to impersonate for the operation, this flag can be repeated to specify multiple groups.
--cache-dir='/root/.kube/http-cache': Default HTTP cache directory
--certificate-authority='': Path to a cert file for the certificate authority
--client-certificate='': Path to a client certificate file for TLS
--client-key='': Path to a client key file for TLS
--cluster='': The name of the kubeconfig cluster to use
--context='': The name of the kubeconfig context to use
--insecure-skip-tls-verify=false: If true, the server's certificate will not be checked for validity. This will
make your HTTPS connections insecure
--kubeconfig='': Path to the kubeconfig file to use for CLI requests.
--log-backtrace-at=:0: when logging hits line file:N, emit a stack trace
--log-dir='': If non-empty, write log files in this directory
--log-file='': If non-empty, use this log file
--log-file-max-size=1800: Defines the maximum size a log file can grow to. Unit is megabytes. If the value is 0,
the maximum file size is unlimited.
--log-flush-frequency=5s: Maximum number of seconds between log flushes
--logtostderr=true: log to standard error instead of files
--match-server-version=false: Require server version to match client version
-n, --namespace='': If present, the namespace scope for this CLI request
--password='': Password for basic authentication to the API server
--profile='none': Name of profile to capture. One of (none|cpu|heap|goroutine|threadcreate|block|mutex)
--profile-output='profile.pprof': Name of the file to write the profile to
--request-timeout='0': The length of time to wait before giving up on a single server request. Non-zero values
should contain a corresponding time unit (e.g. 1s, 2m, 3h). A value of zero means don't timeout requests.
-s, --server='': The address and port of the Kubernetes API server
--skip-headers=false: If true, avoid header prefixes in the log messages
--skip-log-headers=false: If true, avoid headers when opening log files
--stderrthreshold=2: logs at or above this threshold go to stderr
--tls-server-name='': Server name to use for server certificate validation. If it is not provided, the hostname
used to contact the server is used
--token='': Bearer token for authentication to the API server
--user='': The name of the kubeconfig user to use
--username='': Username for basic authentication to the API server
-v, --v=0: number for the log level verbosity
--vmodule=: comma-separated list of pattern=N settings for file-filtered logging
四、管理名称空间资源
1、查看名称空间及其资源对象
1、查看namespaces资源
[root@master ~]# kubectl get ns NAME STATUS AGE default Active 41h ingress-nginx Active 33h kube-node-lease Active 41h kube-public Active 41h kube-system Active 41h
2、查看特定名称空间信息信息
[root@master ~]# kubectl describe ns default Name: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Status: Active No resource quota. No LimitRange resource.
3、查看kube-system下的所有pod资源
[root@master ~]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE coredns-66bff467f8-d9xjc 1/1 Running 0 41h coredns-66bff467f8-lvldb 1/1 Running 0 41h etcd-master 1/1 Running 0 41h kube-apiserver-master 1/1 Running 0 41h kube-controller-manager-master 1/1 Running 0 41h kube-flannel-ds-amd64-5zsxg 1/1 Running 0 33h kube-flannel-ds-amd64-kmsb5 1/1 Running 0 33h kube-flannel-ds-amd64-lzh2b 1/1 Running 0 33h kube-proxy-lg58q 1/1 Running 0 41h kube-proxy-qcztn 1/1 Running 0 41h kube-proxy-rf6fz 1/1 Running 0 41h kube-scheduler-master 1/1 Running 0 41h metrics-server-79c86dd576-6h2b7 1/1 Running 0 33
4、查看小结

2、管理namespace资源
1、声明式
[root@master chapter3]# kubectl apply -f namespace-example.yaml namespace/dev created
2、陈述式命令
[root@master ~]# kubectl create ns luoahong namespace/luoahong created
3、删除
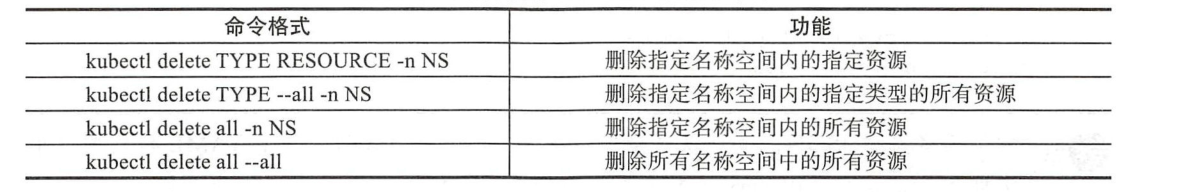
4、管理小结

五、pod资源的基础管理操作:陈述式对象配置管理方式
1、创建pod资源
[root@master chapter3]# kubectl create -f pod-example.yaml pod/pod-example created
2、查看pod状态
[root@master chapter3]# kubectl get -f pod-example.yaml
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-example 1/1 Running 0 40s
[root@master chapter3]# kubectl get -f pod-example.yaml -o custom-columns=NMAE:metadata.name,STATUS:status.phase
NMAE STATUS
pod-example Running
[root@master chapter3]# kubectl describe -f pod-example.yaml
Name: pod-example
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: node2/192.168.118.20
Start Time: Wed, 05 Aug 2020 17:12:48 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.2.7
IPs:
IP: 10.244.2.7
Containers:
myapp:
Container ID: docker://fc64d4153a6a5bb315fc1669c6cdcbf4ad37ce1541eb655ba1bc62919b50f5db
Image: ikubernetes/myapp:v2
Image ID: docker-pullable://ikubernetes/myapp@sha256:85a2b81a62f09a414ea33b74fb8aa686ed9b168294b26b4c819df0be0712d358
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Running
Started: Wed, 05 Aug 2020 17:13:06 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-pwl2t (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-pwl2t:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-pwl2t
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Pulling 3m7s kubelet, node2 Pulling image "ikubernetes/myapp:v2"
Normal Scheduled 3m6s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/pod-example to node2
Normal Pulled 2m51s kubelet, node2 Successfully pulled image "ikubernetes/myapp:v2"
Normal Created 2m50s kubelet, node2 Created container myapp
Normal Started 2m50s kubelet, node2 Started container myapp
3、更新pod资源
[root@master chapter3]# kubectl get pods pod-example -o yaml > pod-exaple-update.yaml [root@master chapter3]# sed -i 's@(image:).*@ikubernetes/myapp:v2@' pod-exaple-update.yaml [root@master chapter3]# kubectl replace -f pod-exaple-update.yaml pod/pod-example created replaces
更新活动对象的配置时,replace命令要重构整个资源对象、故此它必须基于完整格式的配置信息才能进行活动对象的完全替换若要基于此前的配置文件进行替换
就必须使用--force选项删除此前的活动对象、而后再进行新建操作、否则命令会返回错误信息
4、删除pod资源
[root@master chapter3]# kubectl delete -f pod-example.yaml pod "pod-example" deleted [root@master chapter3]# kubectl get -f pod-example.yaml Error from server (NotFound): pods "pod-example" not found
六、pod资源的基础管理操作:声明式对象配置管理方式
1、创建pod资源
对于生产环境来说、声明式对象配置操作在管理资源对象时将配置信息保存于目标对象的注解中
并通过比较活动对象的当前配置、前一次管理操作时保存于注解中的配置,一级当前命令提供的配置生成更新补丁、从而完成活动对象的不定时更新操作
[root@master chapter3]# kubectl apply -f pod-example.yaml pod/pod-example created
命令结果显示资源重新配置完成并且已经生效,
2、更新pod资源
[root@master chapter3]# vim pod-example.yaml 把image: ikubernetes/myapp:v1修改image: ikubernetes/myapp:v2 [root@master chapter3]# kubectl apply -f pod-example.yaml pod/pod-example configured
事实上、此类操作也完全能够使用patch命令直接进行补丁操作、而资源对象的删除操作依然可以使用apply命令但要同是使用--prune选项
kubectl apply -f pod_example.yaml --prune -l <labels>
需要注意的是,此命令异常凶险,因为它将基于标签选择器过滤出所有符合条件的对象,并检查由-f指定的目录中是否存在某配置文件已经定义了相应的资源对象
那些不存在相应定义的资源对象讲被删除、因此、删除资源对象的操作依然建议使用陈述式、对象配置方式的命令:#kubectl delete 进行,这样的命令格式操作目标明确且不易出现偏差