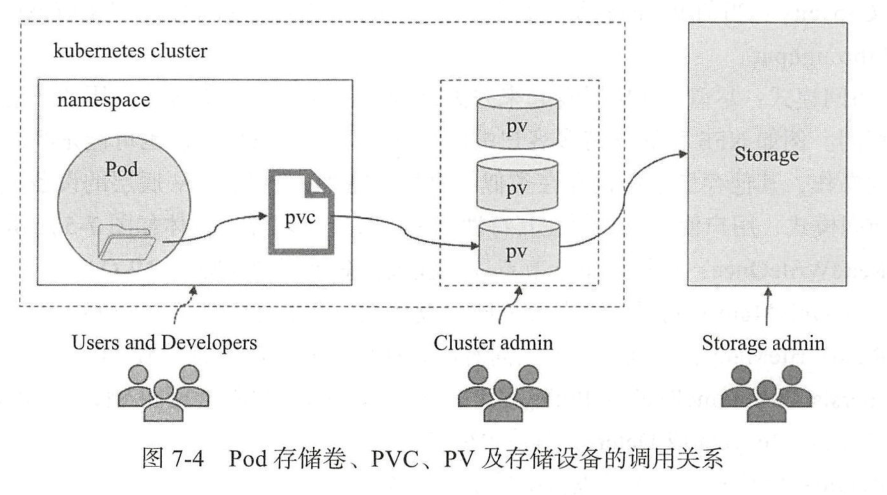
一、Pod存储卷、PVC、PV及存储设备的调用关系
二、PV对存储系统的支持可通过插件来实现、目前Kubernetes支持如下类型的插件
GCEPersistentDisk AWSElasticBlockStore AzureFile AzureDisk CSI FC (Fibre Channel) FlexVolume Flocker NFS iSCSI RBD (Ceph Block Device) CephFS Cinder (OpenStack block storage) Glusterfs VsphereVolume Quobyte Volumes HostPath (Single node testing only -- local storage is not supported in any way and WILL NOT WORK in a multi-node cluster) Portworx Volumes ScaleIO Volumes StorageOS
三、PersistentVolume Spec通用字段详解
1、存储能力(Capacity)
Generally, a PV will have a specific storage capacity. This is set using the PV's capacity attribute. See the Kubernetes Resource Model to understand the units expected by capacity. #当前pv的容量;目前Capacity仅支持空间设定 Currently, storage size is the only resource that can be set or requested. Future attributes may include IOPS, throughput, etc. #将来应该还可以指定IOPS和throughput
2、存储卷模式(Volume Mode)
FEATURE STATE: Kubernetes v1.18 [stable] Kubernetes supports two volumeModes of PersistentVolumes: Filesystem and Block. volumeMode is an optional API parameter. Filesystem is the default mode used when volumeMode parameter is omitted. A volume with volumeMode: Filesystem is mounted into Pods into a directory. If the volume is backed by a block device and the device is empty, Kuberneretes creates a filesystem on the device before mounting it for the first time. You can set the value of volumeMode to Block to use a volume as a raw block device. Such volume is presented into a Pod as a block device, without any filesystem on it. This mode is useful to provide a Pod the fastest possible way to access a volume, without any filesystem layer between the Pod and the volume. On the other hand, the application running in the Pod must know how to handle a raw block device. See Raw Block Volume Support for an example on how to use a volume with volumeMode: Block in a Pod #卷模型、用于指定此卷可被用作文件系统还是裸格式的块设备;默认为Filesysyem
3、存储类别(Class)
PV可以设定其存储的类别,通过storageClassName参数指定一个StorageClass资源对象的名称。具有特定类别的PV只能与请求了该类别的PVC进行绑定。未设定类别的PV则只能与不请求任何类别的PVC进行绑定
4、回收策略(Reclaim Policy)
Current reclaim policies are: #pv空间被释放时的处理机制;可用类型仅为Retain、Recycle、Delete Retain -- manual reclamation #保持不动、由管理员随后手动回收 Recycle -- basic scrub (rm -rf /thevolume/*) #空间回收、即删除存储卷目录下的所有文件(包含子目录和隐藏文件)、目前仅NFS和hostPath支持此操作 Delete -- associated storage asset such as AWS EBS, GCE PD, Azure Disk, or OpenStack Cinder volume is deleted #删除存储卷、仅部分云端存储系统支持、如AWS EBS、GCE PD、Azure Disk和Cinder Currently, only NFS and HostPath support recycling. AWS EBS, GCE PD, Azure Disk, and Cinder volumes support deletion
目前,只有NFS和HostPath两种类型的存储支持Recycle策略;AWS EBS、GCE PD、Azure Disk和Cinder volumes支持Delete策略。
5、挂载参数(Mount Options)
目前,以下PV类型支持设置挂载参数:
AWSElasticBlockStore AzureDisk AzureFile CephFS Cinder (OpenStack block storage) GCEPersistentDisk Glusterfs NFS Quobyte Volumes RBD (Ceph Block Device) StorageOS VsphereVolume iSCSI
四、PersistentVolume Spec访问模式(Access Modes)详解
1、访问模式(Access Modes)
A PersistentVolume can be mounted on a host in any way supported by the resource provider. As shown in the table below, providers will have different capabilities and each PV's access modes are set to the specific modes supported by that particular volume. For example, NFS can support multiple read/write clients, but a specific NFS PV might be exported on the server as read-only. Each PV gets its own set of access modes describing that specific PV's capabilities. 尽管在pv层看起来并无差别,但存储设备支持及启动的功能特性却可能不尽相同。例如NFS存储支持多客户端同时挂在及读写操作、但也可能是在共享时仅启用了只读操作,但也可能是在共享时仅启用了指读操作、其他存储系统也存在类似的可配置特性、因此PV顶层的设备或许存在其特有的访问模式,用户使用时必须在其特性范围内设定其功能,具有同如图7所示 The access modes are: ReadWriteOnce -- the volume can be mounted as read-write by a single node #仅可被单节点读写挂载 ReadOnlyMany -- the volume can be mounted read-only by many nodes #可被多个节点同时只读挂载 ReadWriteMany -- the volume can be mounted as read-write by many nodes #可被多个节点同时读写挂载 In the CLI, the access modes are abbreviated to: RWO - ReadWriteOnce #命令行可简写为RWO ROX - ReadOnlyMany #命令行可简写为ROX RWX - ReadWriteMany #命令行可简写为RWX
2、个PV支持的访问模式


四、创建pv
1、NFS示例模板
[root@master chapter7]# cat pv-nfs-0001.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv-nfs-0001
labels:
release: stable
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
storageClassName: slow
mountOptions:
- hard
- nfsvers=4.1
nfs:
path: "/webdata/htdocs"
server: nfs.ikubernetes.io
2、创建状态查看
[root@master chapter7]# kubectl apply -f pv-nfs-0001.yaml persistentvolume/pv-nfs-0001 created [root@master chapter7]# kubectl get pv NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE pv-nfs-0001 5Gi RWX Recycle Available slow 19s [root@master chapter7]# kubectl get pv pv-nfs-0001 -o custom-columns=NAME:metadata.name,STATUS:status.phase NAME STATUS pv-nfs-0001 Available
3、rbd存储后端示例模板
[root@master chapter7]# cat pv-rbd-0001.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv-rbd-0001
labels:
release: "stable"
spec:
capacity:
storage: 2Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
storageClassName: fast
rbd:
monitors:
- 172.16.0.56:6789
- 172.16.0.57:6789
- 172.16.0.58:6789
pool: kube
image: pv-rbd-0001
user: admin
secretRef:
name: ceph-secret
fsType: ext4
readOnly: false
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
创建运行
[root@master chapter7]# kubectl apply -f pv-rbd-0001.yaml persistentvolume/pv-rbd-0001 configured [root@master chapter7]# kubectl get pv NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE pv-nfs-0001 5Gi RWX Recycle Bound default/pvc-nfs-0001 slow 14h pv-rbd-0001 2Gi RWO Retain Bound default/pvc-rbd-0001 fast 3m58s
4、PV空间被释放时的处理机制
A volume will be in one of the following phases: Available -- a free resource that is not yet bound to a claim #可用状态,还未与某个PVC绑定 Bound -- the volume is bound to a claim #已与某个PVC绑定 Released -- the claim has been deleted, but the resource is not yet reclaimed by the cluster #绑定的PVC已经删除,资源已释放,但没有被集群回收。 Failed -- the volume has failed its automatic reclamation #因自动资源回收失败而处于的故障状态 The CLI will show the name of the PVC bound to the PV