Remoting技术简介
什么是Remoting
什么是Remoting,简而言之,我们可以将其看作是一种分布式处理方式。从微软的产品角度来看,可以说Remoting就是DCOM的一种升级,它改善了很多功能,并极好的融合到.Net平台下。Microsoft® .NET Remoting 提供了一种允许对象通过应用程序域与另一对象进行交互的框架。这也正是我们使用Remoting的原因。为什么呢?在Windows操作系统中,是将应用程序分离为单独的进程。这个进程形成了应用程序代码和数据周围的一道边界。如果不采用进程间通信(RPC)机制,则在一个进程中执行的代码就不能访问另一进程。这是一种操作系统对应用程序的保护机制。然而在某些情况下,我们需要跨过应用程序域,与另外的应用程序域进行通信,即穿越边界。
在Remoting中是通过通道(channel)来实现两个应用程序域之间对象的通信的。
优点:
1、能让我们进行分布式开发
2、Tcp通道的Remoting速度非常快
3、虽然是远程的,但是非常接近于本地调用对象
4、可以做到保持对象的状态
5、没有应用程序限制,可以是控制台,winform,iis,Windows服务承载远程对象
缺点:
1、非标准的应用因此有平台限制
2、脱离iis的话需要有自己的安全机制
Remoting的模式
l 服务器/客服端模式
l 如果实现端对端(Peer-to-Peer)
Remoting 开发过程
Remoting 框架图
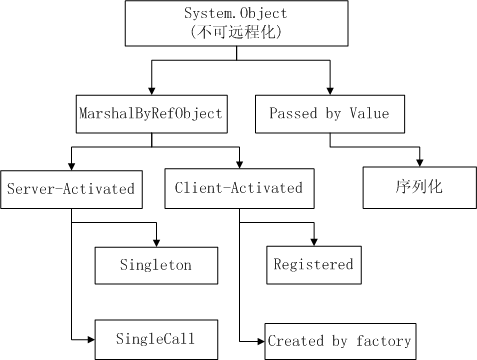
远程对象的两个含义:
操作远程对象
- 对象运行在远程,客户端向他发送消息。
- MarshalByRefObject
传梯远程对象
- 将远程的对象拿到本地,或者将本地对象发送过去。
- 对副本进行操作。
- 序列化【Serializable】
通道(Channels)
一个远程对象使用通道发送和接受消息
- 服务器选择一个通道来监听请求(request)
- 客服端选择通道来和服务器通讯
Remoting 提供了内置的通道
- TCP通道(TcpChannel )和HTTP通道(HttpChannel)
- 你也可以自己编写自己的通道
传递参数:
传递简单类型(int doulbe string enum ………………)
传递可序列化的类型(ArrayList DataSet Hashtable ………………)
传递自定义类型 ( Serializable )
开发Remoting三步走
1、 远程对象:
建立类库项目:General
public class HelloServer : MarshalByRefObject
{
public HelloServer()
{
Console.WriteLine("HelloServer activated");
}
public String HelloMethod(String name)
{
Console.WriteLine(
"Server Hello.HelloMethod : {0}", name);
return "Hi there " + name;
}
public MySerialized GetMySerialized()
{
return new MySerialized(4711);
}
public MyRemote GetMyRemote()
{
return new MyRemote(4712);
}
}
//Class1.cs
[Serializable]
public class MySerialized
{
public MySerialized(int val)
{
a = val;
}
public void Foo()
{
Console.WriteLine("MySerialized.Foo called");
}
public int A
{
get
{
Console.WriteLine("MySerialized.A called");
return a;
}
set
{
a = value;
}
}
protected int a;
}
public class MyRemote : System.MarshalByRefObject
{
public MyRemote(int val)
{
a = val;
}
~MyRemote()
{
Console.WriteLine("MyRemote destructor");
}
public void Foo()
{
Console.WriteLine("MyRemote.Foo called");
}
public int A
{
get
{
Console.WriteLine("MyRemote.A called");
return a;
}
set
{
a = value;
}
}
protected int a;
}
Serialization vs MarshalByRefObject (远程对象类型)
按值列集(Serialization )
- 得到远程对象的副本。
- 对副本的操作不影响远程对象。
- 不论远程对象是Singleton 还是SingleCall
[Serializable]
public class MySerialized{...........}
按引用列集(MarshalByRefObject)
- 得到远程对象引用,本地创建代理(Proxy)
- 通过(Proxy)对远程对象访问。
- Singleton记录更改,SingleCall无状态。
public class MyObject:MarshalByRefObject
{ ………………… }
2、服务端建立控制台项目:Server
{
public static int Main(string [] args)
{
//1、注册通道
TcpChannel chan1 = new TcpChannel(8085);
HttpChannel chan2 = new HttpChannel(8086);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(chan1);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(chan2);
//2、注册远程对象
RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownServiceType
(
typeof(HelloServer),
"SayHello",
WellKnownObjectMode.SingleCall // 无状态模式
);
System.Console.WriteLine("Press Enter key to exit");
System.Console.ReadLine();
return 0;
}
}
WellKnownObjectMode.Singleton 介绍如下:
- Singleton ( 单实例) 有状态模式
Ø 在服务器端只实例化一次
Ø 以后每次调用都访问同一个实例。不论同一客服端还是不同客服端。
Ø 可以维持状态
- SingleCall( 单调用) 无状态模式
Ø 每次调用都实例化新的实例。
Ø 跟好的支持无状态编程模型。
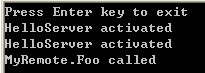
服务器运行结果:
3、客户端:建立控制台项目:Client
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//使用TCP通道得到远程对象
TcpChannel chan1 = new TcpChannel();
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(chan1);
//WellKnown激活模式
HelloServer obj1 = (HelloServer)Activator.GetObject(
typeof(RemotingSamples.HelloServer),
"tcp://localhost:8085/SayHello");
if (obj1 == null)
{
System.Console.WriteLine( "Could not locate TCP server");
}
//获取 Serializable 对象
MySerialized ser = obj1.GetMySerialized();
if (!RemotingServices.IsTransparentProxy(ser))
{
Console.WriteLine("ser is not a transparent proxy");
}
ser.Foo();
//获取 MarshalByRefObject 对象
MyRemote rem = obj1.GetMyRemote();
if (RemotingServices.IsTransparentProxy(rem))
{
Console.WriteLine("ser is a transparent proxy");
}
rem.Foo(); //在服务器端显示
System.Console.ReadLine();
}
}
 View Code
View Code typeof(RemotingSamples.HelloServer),
"tcp://localhost:8080/SayHello");
ServerRemoteObject.ServerObject serverObj = new
客服端运行结果:
![]()


