1. 面向对象
1.1 类定义 , 属性 , 初始化
1. 面向对象最重要的概念就是类(Class) 和实例(Instance), 面向对象编程是一种编程设计思想.
class Cat: """这是一个猫类""" # class 关键字 # Cat 类名 同变量名 大驼峰命名法 # 三引号中的内容是解释这个类的用途
2. 实例化对象
kitty = Cat()
3. 属性
kitty = Cat() #添加属性 kitty.color = 'white' kitty.eat = 'fish'
4. 实例化--初始化

1 #Cat实例化 2 class Cat: 3 """猫类""" 4 #初始化方法 5 def __init__(self, color ,eat): 6 self.color = color 7 self.eat = eat 8 9 kitty = Cat('white','fish')
1.2 类和函数

1 #类和函数 2 class Point: 3 """表示二位平面中的一个点""" 4 #初始化方法 5 def __init__(self, x ,y): 6 self.x = x 7 self.y = y 8 9 def distance(self , p2): 10 return ((self.x-p2.x)**2 + (self.y-p2.y)**2)**0.5 11 12 def print_point(self): 13 print('%s,%s'%(self.x,self.y)) 14 15 pp1=Point(1,2) 16 pp2=Point(3,5) 17 Point.distance(pp1,pp2) 18 #函数式调用方法,一般不这么用 19 Point.print_point(pp1) 20 #对象的方式调用 21 pp1.print_point()
2. 网页解析
Web浏览器的作用是读取HTML文档,并以网页的形式显示出它们,浏览器不会显示HTML标签, 而是使用标签来解释页面的内容.
2.1 http解析库 BeautifulSoup4
BeautifulSoup 是一个可以从 html 或xml 文件中提取数据的Python库, 它的使用方式对于正则来说更加的简单方便, 常常能够节省我们大量的时间.
3.BeautifulSoup4
BeautifulSoup 是一个可以从html或xml文件中提取数据的Python库 ,它的使用方式相对于正则来说更加的简单方便,能够节省大量时间.

1 #规定格式 2 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 3 4 import requests 5 zxc_url = 'http://image.baidu.com/search/index?tn=baiduimage&ipn=r&ct=201326592&cl=2&lm=-1&st=-1&fm=result&fr=&sf=1&fmq=1571316186692_R&pv=&ic=&nc=1&z=&hd=&latest=©right=&se=1&showtab=0&fb=0&width=&height=&face=0&istype=2&ie=utf-8&sid=&word=赵小臭' 6 response =requests.get(zxc_url) 7 response.encoding='utf-8' 8 zxc = response.text 9 #解析html 10 soup = BeautifulSoup(zxc) 11 #取标签 12 soup.head 13 #取标签带属性 14 soup.p['class'] 15 #查所有标签 16 soup.find_all('a')
解析器:

节点对象:
1.tag ---tag就是标签的意思, tag还有许多的方法和属性
>>>soup = BeautifulSoup('<b class="boldest">Extremely boldd</b>') >>>tag = soup.b >>>type(tag) <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
2.name ---每一个tag对象都有name属性,为标签的名字
>>>tag.name 'b'
3.Attributes ---在html中, tag可能有多个属性, 所以tag属性的取值跟字典相同.#如果某个tag属性有多个值,那么返回的则是列表格式.['?','??']#
>>>tag['class'] 'boldest'
>>>soup = BeautifulSoup('<p class="body strikeout"></p>')
>>>soup.p['class']
["body","strikeout"]
4.get_text() ---通过get_text() 方法可以获取某个tag 下所有的文本内容.
soup.body.get_text() ##暂不演示###```(懒得打字)
5.NavigableString ---NavigableString 可以遍历字符串,一般被标签包裹在其中的文本就是NavigableString 格式.
>>>soup = BeautifulSoup('<p>No longer bold</p>') >>>soup.p.string 'No longer bold' >>>type(soup.p.string) bs4.element.NavigableString
4.Tag与遍历文档树
tag 对象可以说是BeautifulSoup 中最为重要的对象,通过beautifulSoup来提取数据基本都围绕着这个对象来进行操作.
contents和children:
通过contents 可以获取某个节点的所有的子节点,包括里面的NavigableString对象,获取的是列表格式.###[<title>?</title>]###
而通过children同样的是获取某个节点的所有子节点,返回的是一个迭代器,这种方式会比列表格式更加节省内存.###<title>?</title>###
>>>soup.head.contents [<title>The Dormouse;s story</title>] >>>tags = soup.head.children >>>tags <list_iterator at 0x110f76940> >>> for tag in tags: >>> print(tag) <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
descendants:
上面的contents和children获取是某个节点的直接子节点,而无法获得子孙节点,通过descendants可以获得所有子孙节点,返回的结果跟children一样,需要迭代或者转类型使用.
>>>len(list(soup.body.descendants)) 19 >>>len(list(soup.body.children)) 6
string 和 strings:
string 获取1个字符串, strings 获取所有字符串,返回的是列表类型.
>>>soup.title.string "The Dormouse's story" >>>list(soup.body.strings) ["","","",""....]##多个,懒得打字##
父节点parent 和parents:
parent 获取某个节点的父节点,也就是包裹当前节点的节点
parents 获取当前节点递归到顶层的所有父辈元素
>>>soup.b.parent <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> >>>[i.name for i in soup.b.parents] ['p','body','html','[document]']
兄弟节点: 是指父节点相同的节点.
next_sibling 和 previous_sibling(加s同上取所有):
next_sibling是获取当前节点的下一个兄弟节点,previous_sibling 是获取当前节点的上一个兄弟节点.
##兄弟节点中排第一个的节点没有上一个节点(previous),最后一个节点没有下一个节点(next)##
>>>soup.head.next_sibling ' ' >>>soup.body.previous_sibling ' '
find_all(): find_all()方法基本所有节点对象都调用.
1. 通过name搜索
>>>soup.find_all('b')
[<b>The Dormouse's story</b>]
>>>soup.find_all(["a","b"])
[<b>...</b>,<a>...</a>....]#懒得打字#
2. 通过属性搜索
>>>soup.find_all(attrs={'class':'sister'})
[<a class="sister">.......</a>,<a class="sister">......</a>,.....]
3. 限制查找范围为子节点
>>>soup.html.find_all('title') [<title>The Dormouse's story</title>] #recursive 参数设置为False,可以将搜索范围限制在直接子节点中 >>>soup.html.find_all("title", recursive=False) []
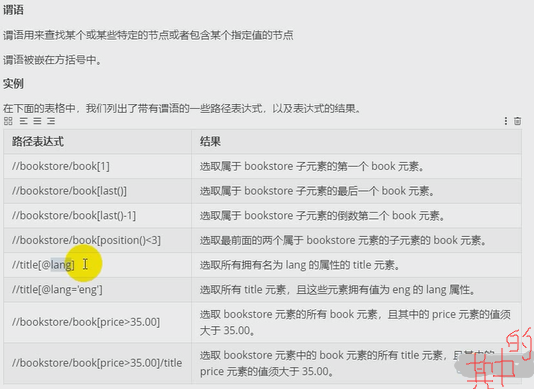
5. XPath
XPath 是一门在XML文档中查找信息的语言,XPath可用来在XML文档中对元素和属性进行遍历.相比于BeautifulSoup, XPath在提取数据时会更有效率.
XPath 使用路径表达式来选取XML文档中的节点或节点集,节点是通过沿着路径(path)或者步(steps)来选取的.
from lxml import etree page = etree.HTML(html_doc) #返回HTML节点 #html_doc 是html页面
选取节点:
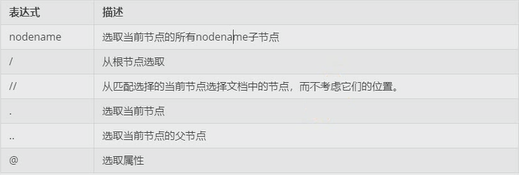
1. 查找当前节点的所有子节点
print(page.xpath('head')) [<Element head at 0x7fd65143ef88>]
2. 从跟节点进行查找
print(page.xpath('/html'))
3. 从整个文档中查找,不考虑位置
print(page.xpath('//book'))
4. 选取当前节点的父节点
print(page.xpath('//book')[0].xpath('..'))
5. 选取当前节点名为category属性的所有值
print(page.xpath('//book')[0].xpath('@category'))
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
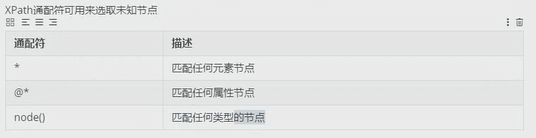
选取未知节点:
获取节点中的文本:
1. 用text()获取某个节点下的文本
print(page.xpath('//book[1]/author/text()'))
2. 用string()获取某个节点下所有的文本
print(page.xpath('string(//book[1])'))
MAX.小说爬取案例1:
利用requests+re爬取一篇小说

1 #爬取一篇小说 2 3 #导入相应库 4 import requests 5 import re 6 7 #小说主页的url 地址 8 novel_url='http://www.quanshuwang.com/book/0/567' 9 #1. 下载小说的信息 10 response = requests.get(novel_url) 11 #2. 设置html编码 12 response.encoding='gbk' 13 novel_html=response.text 14 #3. 解析小说的名称 15 novel_title = re.findall(r'class="article_title">(.*?)<',novel_html)[0] 16 #4. 解析章节名称 和 url 17 #[(url1,第一章),(url2,第二章)......] re.S 可匹配不可监测字符,空,换行,取章节DIV 18 div_html = re.findall(r'class="clearfix dirconone">(.*?)</DIV>',novel_html,re.S)[0] 19 chapter_info= re.findall(r'<a href="(.*?)" title="(.*?)">',div_html) 20 #下载每一章的内容,存为一个txt文档 21 with open(r'C:UsersluoweDesktop\%s.txt'%novel_title , 'w' , encoding='utf-8') as f: 22 #chapter_info是列表,[(1,2),(3,4)....]格式,url接收第一个(1),title接收第二个(2) 23 for chapter_url ,chapter_title in chapter_info: 24 #在文档中写入标题,并换行 25 f.write(chapter_title+' ') 26 #下载章节内容,打开了新url 27 response = requests.get(chapter_url) 28 response.encoding='gbk' #设置编码,防止乱码 29 #接收页面html,并解析 30 novel_html = response.text 31 #因为内容中有回车换行,所有要加re.S验证,返回的列表,只取第一个[0] 32 novel_content = re.findall(r'style5();</script>(.*?)<script',novel_html, re.S)[0] 33 #清洗数据 34 novel_content = novel_content.replace(' ',' ') #去空格 35 novel_content = novel_content.replace('<br />',' ') #去标签 36 novel_content = novel_content.replace(' ','') #去空去换行 37 #写入文档,每写入一章,换一行 38 f.write( novel_content + ' ') 39 print(chapter_title, chapter_url)
MAX.小说爬取案例2:
利用BeautifulSoup爬取一篇小说

1 #爬取一篇小说 2 3 #导入相应库 4 import requests 5 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as be 6 7 #小说主页的url 地址 8 novel_url='http://www.quanshuwang.com/book/9/9006' 9 10 #1. 下载小说的信息 11 response = requests.get(novel_url) 12 #2. 设置html编码 13 response.encoding='gbk' 14 novel_html=response.text 15 #3. 利用BeautifulSoup解析网页,,小说的名称 16 novel_soup = be(novel_html, 'lxml') 17 novel_title_a = novel_soup.find_all('a',attrs={'class':'article_title'})[0] 18 novel_title=novel_title_a.string 19 20 #4. 解析出所有的章节a标签 21 div = novel_soup.find_all('div',attrs={"class":"chapterNum"})[0] 22 chapter_tag_a = div.find_all('a') 23 24 #5. 构造 章节信息 25 chapter_info=[] 26 for tag_a in chapter_tag_a: 27 chapter_info.append((tag_a['href'],tag_a.string)) 28 29 #6. 去下载每一章的内容,存为一个txt文档 30 with open(r'C:UsersluoweDesktop\%s.txt'% novel_title,'w' , encoding='utf-8') as f: 31 #6.1 循环下载每一章的内容,并写入到text文档中 32 for chap_url, chap_title in chapter_info: 33 #6.2 在文档中写入章节标题 34 f.write(chap_title + ' ') 35 #6.3 下载章节的内容 36 chap_response = requests.get(chap_url) 37 chap_response.encoding='gbk' 38 chap_html=chap_response.text 39 #6.4 解析小说内容 40 chap_soup =be(chap_html,'lxml') 41 42 chap_text=''.join(chap_soup.find(attrs={'id':'content'}).strings) 43 #6.5 清洗数据 44 chap_text = chap_text.replace(' ','') 45 chap_text = chap_text.replace('<br />','') 46 chap_text = chap_text.replace(' ','') 47 chap_text = chap_text.replace('style5();','') 48 #6.6 写入文档 49 f.write(chap_text + ' ') 50 print(chap_title,chap_url)
MAX. 小说爬取案例3:
利用xpath爬取一篇小说

1 #爬取一篇小说 2 #导入相应库 3 import requests 4 import re 5 from lxml import etree 6 7 #小说主页的url 地址 8 novel_url='http://www.quanshuwang.com/book/0/437' 9 #1. 下载小说的信息 10 response = requests.get(novel_url) 11 #2. 设置html编码 12 response.encoding='gbk' 13 novel_html=response.text 14 15 #3. 利用XPath解析网页 16 page = etree.HTML(novel_html) 17 18 #4. 解析小说的名称 19 chapter_title = page.xpath('//a[@class="article_title"]/text()')[0] 20 #4. 解析章节标签 21 chapter_tag_a = page.xpath('//div[@class="chapterNum"]//li/a') 22 23 #5. 构造章节信息 24 chapter_info = [] 25 for tag_a in chapter_tag_a: 26 chapter_info.append((tag_a.xpath('@href')[0],tag_a.xpath('text()')[0])) 27 28 #6. 下载每一章的内容,存为一个txt文档 29 with open(r'C:UsersluoweDesktop\%s.txt'%chapter_title , 'w' , encoding='utf-8') as f: 30 #6.1 循环下载每一章节内容,写入text文档中 31 for chapter_url ,chapter_title in chapter_info: 32 #6.2 在文档中写入标题,并换行 33 f.write(chapter_title+' ') 34 #6.3 下载章节的详细内容 35 response = requests.get(chapter_url) 36 response.encoding='gbk' #设置编码,防止乱码 37 novel_html = response.text 38 #6.4 解析小说内容 39 chapter_page = etree.HTML(novel_html) 40 novel_content = chapter_page.xpath('string(//div[@id="content"])') 41 #6.5 清洗数据 42 novel_content = novel_content.replace(' ',' ') #去空格 43 novel_content = novel_content.replace('<br />',' ') #去标签 44 novel_content = novel_content.replace(' ','') #去空去换行 45 #6.6 写入文档,每写入一章,换一行 46 f.write( novel_content + ' ') 47 print(chapter_title, chapter_url)
