(1) evaluate _lenet5中的导入数据部分
1 # 导入数据集,该函数定义在logistic_sgd中,返回的是一个list 2 datasets = load_data(dataset) 3 4 # 从list中提取三个元素,每个元素都是一个tuple(每个tuple含有2个元素,分别为images数据和label数据) 5 train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0] #训练集 6 valid_set_x, valid_set_y = datasets[1] #校验集 7 test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2] #测试集 8 9 10 # 训练集、校验集、测试集分别含有的样本个数 11 n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] 12 n_valid_batches = valid_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] 13 n_test_batches = test_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] 14 # 训练集、校验集、测试集中包含的minibatch个数(每个iter,只给一个minibatch,而不是整个数据集) 15 n_train_batches /= batch_size 16 n_valid_batches /= batch_size 17 n_test_batches /= batch_size

(2)evaluate _lenet5中的building model部分
1 # 首先,定义一些building model用到的符号变量 2 index = T.lscalar() # 用于指定具体哪个minibatch的指标 3 4 # start-snippet-1 5 x = T.matrix('x') # 存储图像的像素数据 6 y = T.ivector('y') # 存储每幅图像对应的label 7 8 # 开始build model 9 print '... building the model' 10 11 # 将输入的数据(batch_size, 28 * 28)reshape为4D tensor(batch_size是每个mini-batch包含的image个数) 12 layer0_input = x.reshape((batch_size, 1, 28, 28)) 13 14 # 构造第一个卷积层 15 # (1)卷积核大小为5*5、个数为nkerns[0]、striding =1,padding=0 16 # 输出的feature map大小为:(28-5+1 , 28-5+1) = (24, 24) 17 # (2)含有max-pooling,pooling的大小为2*2、striding =1,padding=0 18 # 输出的map大小为:(24/2, 24/2) = (12, 12) 19 # (3)综上,第一个卷积层输出的feature map为一个4D tensor,形状为:(batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12) 20 layer0 = LeNetConvPoolLayer( 21 rng, 22 input=layer0_input, 23 image_shape=(batch_size, 1, 28, 28), 24 filter_shape=(nkerns[0], 1, 5, 5), 25 poolsize=(2, 2) 26 ) 27 28 # 构造第二个卷积层,卷积核大小为5*5 29 # (1)卷积核大小为5*5、个数为nkerns[0]、striding =1,padding=0 30 # 输出的feature map大小为:(12-5+1, 12-5+1) = (8, 8) 31 # (2)含有max-pooling,pooling的大小为2*2、striding =1,padding=0 32 # 输出的map大小为:(8/2, 8/2) = (4, 4) 33 # (3)综上,第二个卷积层输出的feature map为一个4D tensor,形状为:(batch_size, nkerns[1], 4, 4) 34 layer1 = LeNetConvPoolLayer( 35 rng, 36 input=layer0.output, 37 image_shape=(batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12), 38 filter_shape=(nkerns[1], nkerns[0], 5, 5), 39 poolsize=(2, 2) 40 ) 41 42 # 将第二个卷积层的输出map(形状为(batch_size, nkerns[1], 4, 4))转化为一个matrix的形式 43 # 该矩阵的形状为:(batch_size, nkerns[1] * 4 * 4),每一行为一个图形对应的feature map 44 layer2_input = layer1.output.flatten(2) 45 46 # 第一个全链接层 47 # (1)输入的大小固定,即第二个卷积层的输出 48 # (2)输出大小自己选的,这里选定为500 49 # (3)sigmoid函数为tan函数 50 layer2 = HiddenLayer( 51 rng, 52 input=layer2_input, 53 n_in=nkerns[1] * 4 * 4, 54 n_out=500, 55 activation=T.tanh 56 ) 57 58 # 输出层,即逻辑回归层 59 layer3 = LogisticRegression(input=layer2.output, n_in=500, n_out=10) 60 61 # 代价函数的计算 62 cost = layer3.negative_log_likelihood(y) 63 64 # 测试model,输入为具体要测试的test集中的某个mini-batch 65 # 输出为训练得到的model在该mini-batch上的error 66 test_model = theano.function( 67 [index], 68 layer3.errors(y), 69 givens={ 70 x: test_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size], 71 y: test_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size] 72 } 73 ) 74 75 # 校验model,输入为具体要测试的校验集中的某个mini-batch 76 # 输出为训练得到的model在该mini-batch上的error 77 validate_model = theano.function( 78 [index], 79 layer3.errors(y), 80 givens={ 81 x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size], 82 y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size] 83 } 84 ) 85 86 # 创建一个list,该list存放的是该CNN网络的所有待利用梯度下降法优化的参数 87 params = layer3.params + layer2.params + layer1.params + layer0.params 88 89 # 创建一个list,该list存放的是代价函数对该CNN网络的所有待利用梯度下降法优化的参数的梯度 90 grads = T.grad(cost, params) 91 92 # 为train模型创建更新规则,即创建一个list,自动更新params、grads中每一组值 93 updates = [ 94 (param_i, param_i - learning_rate * grad_i) 95 for param_i, grad_i in zip(params, grads) 96 ] 97 98 # 训练model,输入为具体要训练集中的某个mini-batch 99 # 输出为训练得到的model在该mini-batch上的error 100 train_model = theano.function( 101 [index], 102 cost, 103 updates=updates, 104 givens={ 105 x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size], 106 y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size] 107 } 108 )
(3)Lenet-5中的training model部分
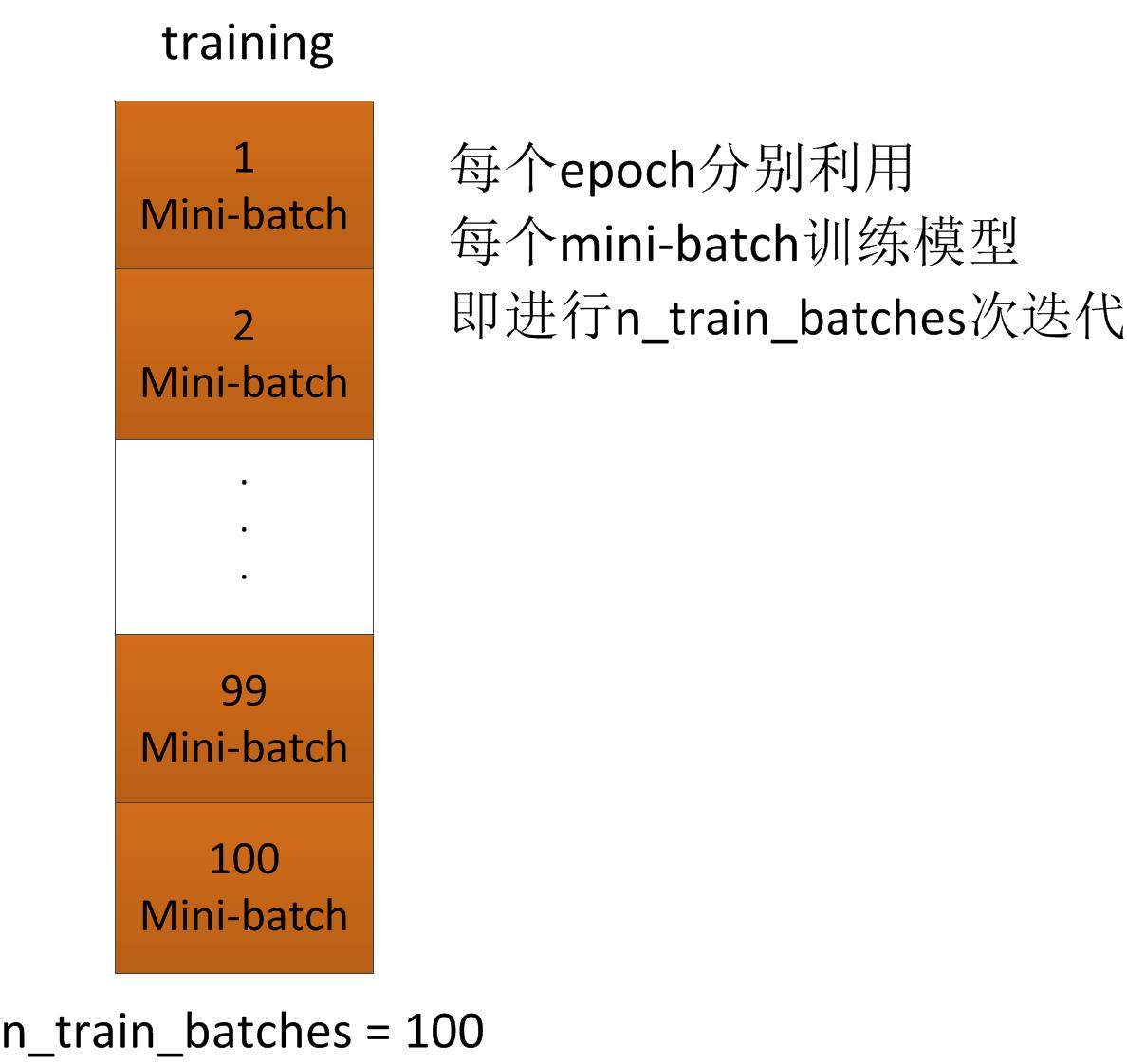
1 # 开始训练模型 2 print '... training' 3 4 # 定义一些进行early-stopping的相关参数 5 # look as this many examples regardless 6 patience = 10000 7 # wait this much longer when a new best is found 8 patience_increase = 2 9 # a relative improvement of this much is considered significant 10 improvement_threshold = 0.995 11 # go through this many minibatche before checking the network on the validation set; in this case we check every epoch 12 validation_frequency = min(n_train_batches, patience / 2) 13 14 # 训练过程中需要的其他参数 15 best_validation_loss = numpy.inf 16 best_iter = 0 17 test_score = 0. 18 start_time = timeit.default_timer() 19 20 epoch = 0 21 done_looping = False 22 23 while (epoch < n_epochs) and (not done_looping): 24 25 #epoch次数增加1,每轮epoch,利用所有组mini-batch进行一次模型训练 26 # 每轮epoch,整体的迭代次数iter增加n_train_batches次 27 epoch = epoch + 1 28 29 # 对于整个训练集中的第minibatch_index 个mini-batch 30 # minibatch_index=0,1,...,n_train_batches-1 31 for minibatch_index in xrange(n_train_batches): 32 33 # 总的iter次数(每一轮epoch,iter个数都增加n_train_batches) 34 # 即每一个iter,只利用一个mini-batch进行训练 35 # 而每一个epoch,利用了所有的mini-batch进行训练 36 iter = (epoch - 1) * n_train_batches + minibatch_index 37 38 # 整体的迭代次数可以被100整除时,显示一次迭代次数 39 if iter % 100 == 0: 40 print 'training @ iter = ', iter 41 42 # 利用第minibatch_index个mini-batch训练model,得到model的代价函数 43 cost_ij = train_model(minibatch_index) 44 45 # 如果整体的迭代次数满足需要进行校验的条件,则对该次iter对应的model进行校验 46 if (iter + 1) % validation_frequency == 0: 47 48 # 计算该model在校验集上的loss函数值 49 validation_losses = [validate_model(i) for i 50 in xrange(n_valid_batches)] 51 this_validation_loss = numpy.mean(validation_losses) 52 print('epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, validation error %f %%' % 53 (epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, 54 this_validation_loss * 100.)) 55 56 # 如果该model在校验集的loss值小于之前的值 57 if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss: 58 59 # 增加patience的值,目的是为了进行更多次的iter 60 # 也就是说,如果在测试集上的性能不如之前好,证明模型开始恶化,那么,不再进行那么多次的training了 61 if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss * 62 improvement_threshold: 63 patience = max(patience, iter * patience_increase) 64 65 # save best validation score and iteration number 66 best_validation_loss = this_validation_loss 67 best_iter = iter 68 69 # 利用测试集测试该模型 70 test_losses = [ 71 test_model(i) 72 for i in xrange(n_test_batches) 73 ] 74 # 计算测试集的loss值 75 test_score = numpy.mean(test_losses) 76 print((' epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, test error of ' 77 'best model %f %%') % 78 (epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, 79 test_score * 100.)) 80 81 if patience <= iter: 82 done_looping = True 83 break 84 85 # 整个训练过程结束,记录training时间 86 end_time = timeit.default_timer() 87 print('Optimization complete.') 88 print('Best validation score of %f %% obtained at iteration %i, ' 89 'with test performance %f %%' % 90 (best_validation_loss * 100., best_iter + 1, test_score * 100.)) 91 print >> sys.stderr, ('The code for file ' + 92 os.path.split(__file__)[1] + 93 ' ran for %.2fm' % ((end_time - start_time) / 60.))
(4)真个convolutional_mlp的原始代码

1 """This tutorial introduces the LeNet5 neural network architecture 2 using Theano. LeNet5 is a convolutional neural network, good for 3 classifying images. This tutorial shows how to build the architecture, 4 and comes with all the hyper-parameters you need to reproduce the 5 paper's MNIST results. 6 7 8 9 This implementation simplifies the model in the following ways: 10 11 - LeNetConvPool doesn't implement location-specific gain and bias parameters 12 - LeNetConvPool doesn't implement pooling by average, it implements pooling 13 by max. 14 - Digit classification is implemented with a logistic regression rather than 15 an RBF network 16 - LeNet5 was not fully-connected convolutions at second layer 17 18 References: 19 - Y. LeCun, L. Bottou, Y. Bengio and P. Haffner: 20 Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document 21 Recognition, Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(11):2278-2324, November 1998. 22 http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/publis/pdf/lecun-98.pdf 23 24 """ 25 import os 26 import sys 27 import timeit 28 29 import numpy 30 31 import theano 32 import theano.tensor as T 33 from theano.tensor.signal import downsample 34 from theano.tensor.nnet import conv 35 36 from logistic_sgd import LogisticRegression, load_data 37 from mlp import HiddenLayer 38 39 40 class LeNetConvPoolLayer(object): 41 """Pool Layer of a convolutional network """ 42 43 def __init__(self, rng, input, filter_shape, image_shape, poolsize=(2, 2)): 44 """ 45 Allocate a LeNetConvPoolLayer with shared variable internal parameters. 46 47 :type rng: numpy.random.RandomState 48 :param rng: a random number generator used to initialize weights 49 50 :type input: theano.tensor.dtensor4 51 :param input: symbolic image tensor, of shape image_shape 52 53 :type filter_shape: tuple or list of length 4 54 :param filter_shape: (number of filters, num input feature maps, 55 filter height, filter width) 56 57 :type image_shape: tuple or list of length 4 58 :param image_shape: (batch size, num input feature maps, 59 image height, image width) 60 61 :type poolsize: tuple or list of length 2 62 :param poolsize: the downsampling (pooling) factor (#rows, #cols) 63 """ 64 65 assert image_shape[1] == filter_shape[1] 66 self.input = input 67 68 # there are "num input feature maps * filter height * filter width" 69 # inputs to each hidden unit 70 fan_in = numpy.prod(filter_shape[1:]) 71 # each unit in the lower layer receives a gradient from: 72 # "num output feature maps * filter height * filter width" / 73 # pooling size 74 fan_out = (filter_shape[0] * numpy.prod(filter_shape[2:]) / 75 numpy.prod(poolsize)) 76 # initialize weights with random weights 77 W_bound = numpy.sqrt(6. / (fan_in + fan_out)) 78 self.W = theano.shared( 79 numpy.asarray( 80 rng.uniform(low=-W_bound, high=W_bound, size=filter_shape), 81 dtype=theano.config.floatX 82 ), 83 borrow=True 84 ) 85 86 # the bias is a 1D tensor -- one bias per output feature map 87 b_values = numpy.zeros((filter_shape[0],), dtype=theano.config.floatX) 88 self.b = theano.shared(value=b_values, borrow=True) 89 90 # convolve input feature maps with filters 91 conv_out = conv.conv2d( 92 input=input, 93 filters=self.W, 94 filter_shape=filter_shape, 95 image_shape=image_shape 96 ) 97 98 # downsample each feature map individually, using maxpooling 99 pooled_out = downsample.max_pool_2d( 100 input=conv_out, 101 ds=poolsize, 102 ignore_border=True 103 ) 104 105 # add the bias term. Since the bias is a vector (1D array), we first 106 # reshape it to a tensor of shape (1, n_filters, 1, 1). Each bias will 107 # thus be broadcasted across mini-batches and feature map 108 # width & height 109 self.output = T.tanh(pooled_out + self.b.dimshuffle('x', 0, 'x', 'x')) 110 111 # store parameters of this layer 112 self.params = [self.W, self.b] 113 114 # keep track of model input 115 self.input = input 116 117 118 def evaluate_lenet5(learning_rate=0.1, n_epochs=200, 119 dataset='mnist.pkl.gz', 120 nkerns=[20, 50], batch_size=500): 121 """ Demonstrates lenet on MNIST dataset 122 123 :type learning_rate: float 124 :param learning_rate: learning rate used (factor for the stochastic 125 gradient) 126 127 :type n_epochs: int 128 :param n_epochs: maximal number of epochs to run the optimizer 129 130 :type dataset: string 131 :param dataset: path to the dataset used for training /testing (MNIST here) 132 133 :type nkerns: list of ints 134 :param nkerns: number of kernels on each layer 135 """ 136 137 rng = numpy.random.RandomState(23455) 138 139 datasets = load_data(dataset) 140 141 train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0] 142 valid_set_x, valid_set_y = datasets[1] 143 test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2] 144 145 # compute number of minibatches for training, validation and testing 146 n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] 147 n_valid_batches = valid_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] 148 n_test_batches = test_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] 149 n_train_batches /= batch_size 150 n_valid_batches /= batch_size 151 n_test_batches /= batch_size 152 153 # allocate symbolic variables for the data 154 index = T.lscalar() # index to a [mini]batch 155 156 # start-snippet-1 157 x = T.matrix('x') # the data is presented as rasterized images 158 y = T.ivector('y') # the labels are presented as 1D vector of 159 # [int] labels 160 161 ###################### 162 # BUILD ACTUAL MODEL # 163 ###################### 164 print '... building the model' 165 166 # Reshape matrix of rasterized images of shape (batch_size, 28 * 28) 167 # to a 4D tensor, compatible with our LeNetConvPoolLayer 168 # (28, 28) is the size of MNIST images. 169 layer0_input = x.reshape((batch_size, 1, 28, 28)) 170 171 # Construct the first convolutional pooling layer: 172 # filtering reduces the image size to (28-5+1 , 28-5+1) = (24, 24) 173 # maxpooling reduces this further to (24/2, 24/2) = (12, 12) 174 # 4D output tensor is thus of shape (batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12) 175 layer0 = LeNetConvPoolLayer( 176 rng, 177 input=layer0_input, 178 image_shape=(batch_size, 1, 28, 28), 179 filter_shape=(nkerns[0], 1, 5, 5), 180 poolsize=(2, 2) 181 ) 182 183 # Construct the second convolutional pooling layer 184 # filtering reduces the image size to (12-5+1, 12-5+1) = (8, 8) 185 # maxpooling reduces this further to (8/2, 8/2) = (4, 4) 186 # 4D output tensor is thus of shape (batch_size, nkerns[1], 4, 4) 187 layer1 = LeNetConvPoolLayer( 188 rng, 189 input=layer0.output, 190 image_shape=(batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12), 191 filter_shape=(nkerns[1], nkerns[0], 5, 5), 192 poolsize=(2, 2) 193 ) 194 195 # the HiddenLayer being fully-connected, it operates on 2D matrices of 196 # shape (batch_size, num_pixels) (i.e matrix of rasterized images). 197 # This will generate a matrix of shape (batch_size, nkerns[1] * 4 * 4), 198 # or (500, 50 * 4 * 4) = (500, 800) with the default values. 199 layer2_input = layer1.output.flatten(2) 200 201 # construct a fully-connected sigmoidal layer 202 layer2 = HiddenLayer( 203 rng, 204 input=layer2_input, 205 n_in=nkerns[1] * 4 * 4, 206 n_out=500, 207 activation=T.tanh 208 ) 209 210 # classify the values of the fully-connected sigmoidal layer 211 layer3 = LogisticRegression(input=layer2.output, n_in=500, n_out=10) 212 213 # the cost we minimize during training is the NLL of the model 214 cost = layer3.negative_log_likelihood(y) 215 216 # create a function to compute the mistakes that are made by the model 217 test_model = theano.function( 218 [index], 219 layer3.errors(y), 220 givens={ 221 x: test_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size], 222 y: test_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size] 223 } 224 ) 225 226 validate_model = theano.function( 227 [index], 228 layer3.errors(y), 229 givens={ 230 x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size], 231 y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size] 232 } 233 ) 234 235 # create a list of all model parameters to be fit by gradient descent 236 params = layer3.params + layer2.params + layer1.params + layer0.params 237 238 # create a list of gradients for all model parameters 239 grads = T.grad(cost, params) 240 241 # train_model is a function that updates the model parameters by 242 # SGD Since this model has many parameters, it would be tedious to 243 # manually create an update rule for each model parameter. We thus 244 # create the updates list by automatically looping over all 245 # (params[i], grads[i]) pairs. 246 updates = [ 247 (param_i, param_i - learning_rate * grad_i) 248 for param_i, grad_i in zip(params, grads) 249 ] 250 251 train_model = theano.function( 252 [index], 253 cost, 254 updates=updates, 255 givens={ 256 x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size], 257 y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size] 258 } 259 ) 260 # end-snippet-1 261 262 ############### 263 # TRAIN MODEL # 264 ############### 265 print '... training' 266 # early-stopping parameters 267 patience = 10000 # look as this many examples regardless 268 patience_increase = 2 # wait this much longer when a new best is 269 # found 270 improvement_threshold = 0.995 # a relative improvement of this much is 271 # considered significant 272 validation_frequency = min(n_train_batches, patience / 2) 273 # go through this many 274 # minibatche before checking the network 275 # on the validation set; in this case we 276 # check every epoch 277 278 best_validation_loss = numpy.inf 279 best_iter = 0 280 test_score = 0. 281 start_time = timeit.default_timer() 282 283 epoch = 0 284 done_looping = False 285 286 while (epoch < n_epochs) and (not done_looping): 287 epoch = epoch + 1 288 for minibatch_index in xrange(n_train_batches): 289 290 iter = (epoch - 1) * n_train_batches + minibatch_index 291 292 if iter % 100 == 0: 293 print 'training @ iter = ', iter 294 cost_ij = train_model(minibatch_index) 295 296 if (iter + 1) % validation_frequency == 0: 297 298 # compute zero-one loss on validation set 299 validation_losses = [validate_model(i) for i 300 in xrange(n_valid_batches)] 301 this_validation_loss = numpy.mean(validation_losses) 302 print('epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, validation error %f %%' % 303 (epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, 304 this_validation_loss * 100.)) 305 306 # if we got the best validation score until now 307 if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss: 308 309 #improve patience if loss improvement is good enough 310 if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss * 311 improvement_threshold: 312 patience = max(patience, iter * patience_increase) 313 314 # save best validation score and iteration number 315 best_validation_loss = this_validation_loss 316 best_iter = iter 317 318 # test it on the test set 319 test_losses = [ 320 test_model(i) 321 for i in xrange(n_test_batches) 322 ] 323 test_score = numpy.mean(test_losses) 324 print((' epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, test error of ' 325 'best model %f %%') % 326 (epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, 327 test_score * 100.)) 328 329 if patience <= iter: 330 done_looping = True 331 break 332 333 end_time = timeit.default_timer() 334 print('Optimization complete.') 335 print('Best validation score of %f %% obtained at iteration %i, ' 336 'with test performance %f %%' % 337 (best_validation_loss * 100., best_iter + 1, test_score * 100.)) 338 print >> sys.stderr, ('The code for file ' + 339 os.path.split(__file__)[1] + 340 ' ran for %.2fm' % ((end_time - start_time) / 60.)) 341 342 if __name__ == '__main__': 343 evaluate_lenet5() 344 345 346 def experiment(state, channel): 347 evaluate_lenet5(state.learning_rate, dataset=state.dataset)
