Spring注解 @Configuration
一.注解作用.
标注在类上,该类会被CGLIB动态代理生成子类,可以达到这样的效果:在某@Bean方法下调用另一个标注了@Bean的方法,得到的会是同一个Bean对象;
@Configuration注解注意点:
1.可以作为Component标签使用;
2.标注的类不能是final类型的(final类无法动态代理生成子类);
3.注解类里的@Bean对象的id默认是方法名,如果设置了@Bean的name或者value属性,取第一个作为beanId,name中其他的作为别名使用;
4. 标注了@Configuration的类不能是普通内部类,如果非要是个内部类,那就静态内部类也是可以的; 因为普通内部类依赖于外部类的存在;
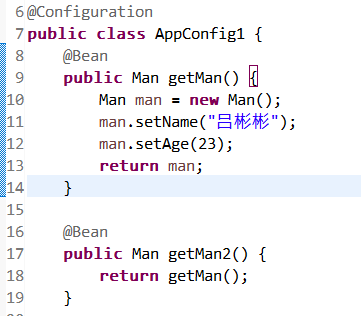
达到的效果就是这样: 回到解析@Configuration的地方四
 获取bean会发现getMan和getMan2对象是同一个对象,去掉Configuration的话就是两个不同的对象
获取bean会发现getMan和getMan2对象是同一个对象,去掉Configuration的话就是两个不同的对象 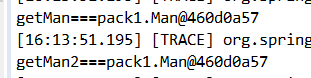
二. 注解形式的Spring容器的启动方式(非Web项目)
方式1. 启动时候将配置类作为参数传入容器,多个配置类也可以一起传入,参数是可变参数类型可以接收多个;
public class AppConfig1 {
@Bean
public Man getMan() {
Man man = new Man();
man.setName("吕彬彬");
man.setAge(23);
return man;
}
@Bean
public Man getMan2() {
return getMan();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig1.class);
//传入的AppConfig1就是配置类,可以不标注@Configuration也能使用
String[] names = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String string : names) {
System.out.println(string+"==="+ac.getBean(string));
}
ac.close();
}
方式2. 空的构造器,之后手动注册配置类,但是记得要调用其refresh方法启动容器;
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ac.register(AppConfig1.class);
ac.refresh();
String[] names = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String string : names) {
System.out.println(string+"==="+ac.getBean(string));
}
ac.close();
三. 分析不加@Configuration 只是一个启动类就可以解析@Bean注解
3.1 简单绘制下我理解的Spring容器bean的初始化流程:1-2是Spring容器初始化经历的过程,而3-9则是每一个bean创建必经的过程;InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor这些特殊的bean处理器如果有就会执行相应的方法;
如果没有 也不影响Bean初始化流程 ;这也是Spring可以丰富扩展的一个点,Spring很多功能Aop、Tx底层就为我们添加了很多这种BFPP、BPP;
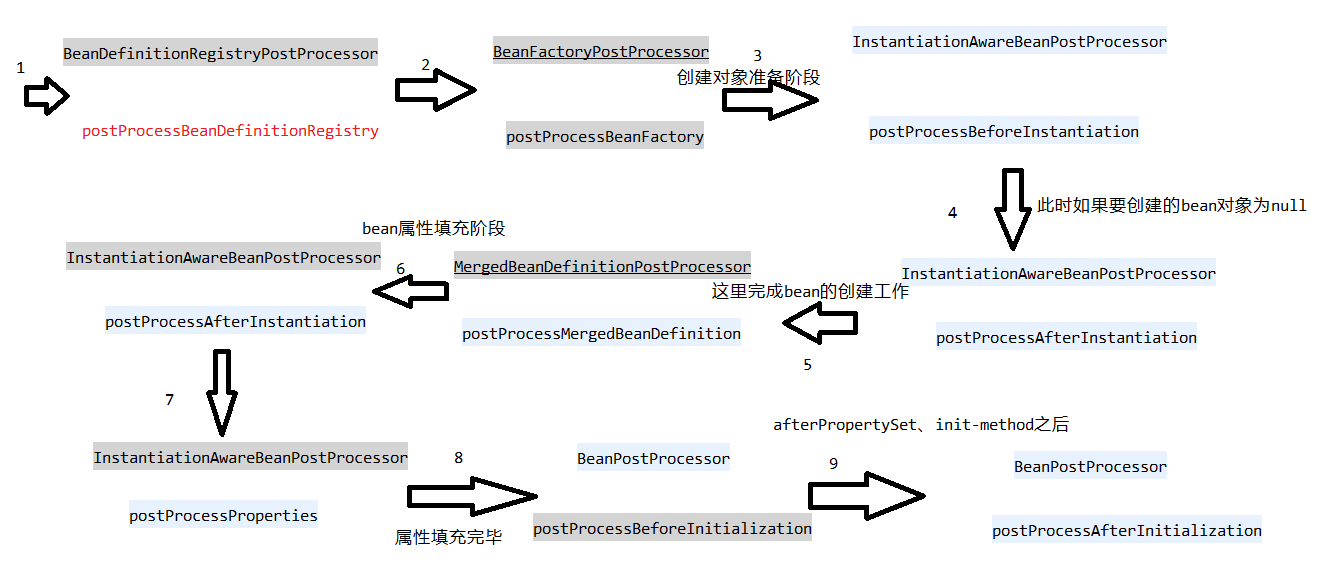
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext就为我们添加了这样一个BFPP ConfigurationClassPostProcessor;同样还有很多其他的BFPP、BPP,方法位于AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的类结构图如下,我们只需要看生命周期1、2中的方法即可;
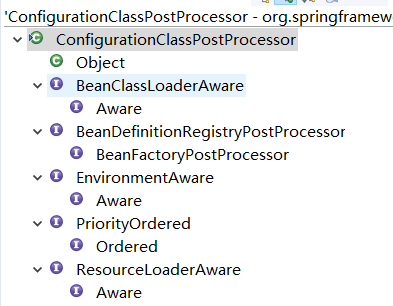
3.2.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法干了什么呢?
1 public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { //registry就是传入的Spring的基本容器BeanFactory对象,最常见的是DefaultListableBeanFactory
2 int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
3 if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
4 throw new IllegalStateException(
5 "postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
6 }
7 if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
8 throw new IllegalStateException(
9 "postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
10 }
11 this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
12
13 processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
//Spring给的解释该方法是Build and validate a configuration model based on the registry of Configuration classes.
14 }
查看processConfigBeanDefinitions方法
1 public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
2 List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
3 String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); //遍历现有注册的所有bean, 包括了之前的配置类AppConfig1,类型是AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
4
5 for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
6 BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
7 if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
8 ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
//判断beanDef有没有CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL属性(代表有Configuration注解) CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE属性代表有@Bean注解
//只有解析过的beanDef才会有这两种属性
9 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
10 logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
11 }
12 }
13 else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
//checkConfigurationClassCandidate方法做了以下操作:
// 有@Configuration注解我就给beanDef添加属性CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL
// 有@Bean注解我就给beanDef添加属性CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE
// 如果两种注解都没有直接返回false,相反有一种都能为true, 就会添加到config候选集合中
14 configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
15 }
16 }
17
18 // config候选集合为空直接返回
19 if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
20 return;
21 } 46 ....省略代码
47 // Configuration类解析器
48 ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
49 this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
50 this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
51
52 Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates); // config候选集合candidates
53 Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
54 do {
55 parser.parse(candidates);
// 开始解析Configuration类,解析过程较为复杂, 简单的针对@Bean对象, parser的configurationClasses集合中添加的ConfigurationClass中持有BeanMethod对象,就是含有@Bean标签的方法
56 parser.validate(); //验证config配置类不能为final类型,还有@Bean方法如果是static的也无需验证
57
58 Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
59 configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
60
62 if (this.reader == null) {
63 this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
64 registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
65 this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
66 }
67 this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
//读取ConfigurationClass的集合,根据BeanMethod来创建ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition,也是一种BeanDefinition对象,不同之处是创建的使用的是factory-method工厂方式创建的
//每个ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition的工厂名就是配置类的ID,工厂方法就是@Bean得方法名;
//同样还有很多处理,比如@Bean的属性设置、init-Method、destroy-Method ; Lazy 、DependsOn等注解的解析 , 还有很多额外的注解的解析就不介绍了;最后解析完成会注册到registry中
68 alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
69
70 candidates.clear();
71 if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
72 String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
73 Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
74 Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
75 for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
76 alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
77 }
78 for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
79 if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
80 BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
81 if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
82 !alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
83 candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
84 }
85 }
86 }
87 candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
88 }
89 }
90 while (!candidates.isEmpty());
93 if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
94 sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
95 }
97 if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
100 ((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
101 }
102 }
到这里postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法就解析完毕,可以看到没有@Configuration注解的AppConfig1类的@Bean注解的@Bean也注册到Spring容器中了;
结束postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法时候打印下已经注册的BeanDefinition,可以看到最后两个Bean定义 主要是factoryBeanName以及factoryMethodName属性设置上了

3.3 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法干了什么呢?
Spring初始化流程图步骤2执行postProcessBeanFactory方法: 其中enhanceConfigurationClasses方法会遍历所有的bean发现没有Configuration注解的bean就结束方法了,所以在这里不分析该方法,后面也会分析的 :)
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
int factoryId = System.identityHashCode(beanFactory);
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + beanFactory);
}
this.factoriesPostProcessed.add(factoryId);
if (!this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
// BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor hook apparently not supported...
// Simply call processConfigurationClasses lazily at this point then.
processConfigBeanDefinitions((BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory);
}
enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory);
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor(beanFactory));
}
下面叙述下这种@Bean转换的ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition怎么实例化: AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的doCreateBean方法 ===> 调用createBeanInstance ===> 发现factoryMethodName不为空,调用instantiateUsingFactoryMethod ===> 最后调用SimpleInstantiationStrategy的instantiate方法;
3.4 没有@Configuration注解下@Bean的实例化
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner,
@Nullable Object factoryBean, final Method factoryMethod, Object... args) {
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(factoryMethod);
return null;
});
}
else {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(factoryMethod);
}
Method priorInvokedFactoryMethod = currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod.get(); //currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod为ThreadLocal对象,实例化Bean的时候会记录当前的factoryMethod
try {
currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod.set(factoryMethod);
Object result = factoryMethod.invoke(factoryBean, args); //调用反射实例化该@Bean对象
if (result == null) {
result = new NullBean();
}
return result;
}
finally { //实例化完成后恢复currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod为之前的值
if (priorInvokedFactoryMethod != null) {
currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod.set(priorInvokedFactoryMethod);
}
else {
currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod.remove();
}
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(factoryMethod,
"Illegal arguments to factory method '" + factoryMethod.getName() + "'; " +
"args: " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(args), ex);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(factoryMethod,
"Cannot access factory method '" + factoryMethod.getName() + "'; is it public?", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
String msg = "Factory method '" + factoryMethod.getName() + "' threw exception";
if (bd.getFactoryBeanName() != null && owner instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory &&
((ConfigurableBeanFactory) owner).isCurrentlyInCreation(bd.getFactoryBeanName())) {
msg = "Circular reference involving containing bean '" + bd.getFactoryBeanName() + "' - consider " +
"declaring the factory method as static for independence from its containing instance. " + msg;
}
throw new BeanInstantiationException(factoryMethod, msg, ex.getTargetException());
}
}
到这里@Bean最简单的创建过程已经分析完成。
四.@Configuration注解下为啥 一 里面得到的@Bean就是同一个对象呢? 回到效果图地方
前面帮助:其中3.2processConfigBeanDefinitions给标注了@Configuration的配置类设置了属性CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL
4.1 查看3.3中没有解析的postProcessBeanFactory的enhanceConfigurationClasses方法
public void enhanceConfigurationClasses(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> configBeanDefs = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (String beanName : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
//遍历了所有的BeanDefinition对象,没有CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL就是空的configBeanDefs,方法之前直接返回了;
if (!(beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" +
beanName + "' since it is not stored in an AbstractBeanDefinition subclass");
}
else if (logger.isInfoEnabled() && beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) {
logger.info("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName +
"' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause " +
"is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor " +
"return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'.");
}
configBeanDefs.put(beanName, (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef); //存放标注了Configuration注解的beanDefinition
}
}
if (configBeanDefs.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ConfigurationClassEnhancer enhancer = new ConfigurationClassEnhancer();
for (Map.Entry<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> entry : configBeanDefs.entrySet()) {
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDef = entry.getValue();
// If a @Configuration class gets proxied, always proxy the target class
beanDef.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
try {
Class<?> configClass = beanDef.resolveBeanClass(this.beanClassLoader);
if (configClass != null) {
Class<?> enhancedClass = enhancer.enhance(configClass, this.beanClassLoader);
//生成AppConfig1的子类CGLIB代理Class 并且在下面将beanDef类型更改为了该CGLIB class
if (configClass != enhancedClass) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(String.format("Replacing bean definition '%s' existing class '%s' with " +
"enhanced class '%s'", entry.getKey(), configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName()));
}
beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot load configuration class: " + beanDef.getBeanClassName(), ex);
}
}
}
4.2 既然知道了是采用CGLIB动态代理,那有很多属性需要设置,代理哪些接口,代理的父类类型已经知道了,回调函数、回调函数过滤器设置了哪些?
1 private Enhancer newEnhancer(Class<?> configSuperClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
2 Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
3 enhancer.setSuperclass(configSuperClass); //被代理的父类类型设置上去就是AppConfig1
4 enhancer.setInterfaces(new Class<?>[] {EnhancedConfiguration.class});
//被代理的接口只设置了EnhancedConfiguration,只是为了给CGLIB子类能够设置上BeanFactory属性
5 enhancer.setUseFactory(false);
6 enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
7 enhancer.setStrategy(new BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
8 enhancer.setCallbackFilter(CALLBACK_FILTER);
9 enhancer.setCallbackTypes(CALLBACK_FILTER.getCallbackTypes());
10 return enhancer;
11 }
CALLBACK_FILTER对象如下:
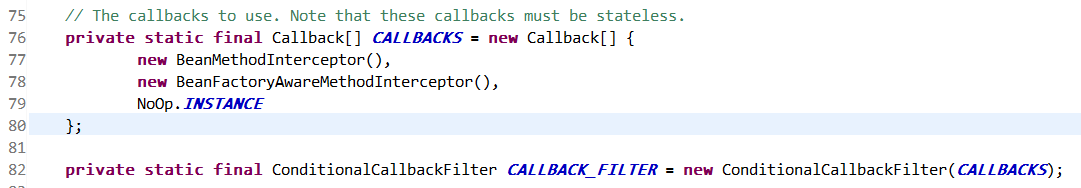
接着利用enhancer对象生成代理子类
1 private Class<?> createClass(Enhancer enhancer) {
2 Class<?> subclass = enhancer.createClass();
3 // Registering callbacks statically (as opposed to thread-local)
4 // is critical for usage in an OSGi environment (SPR-5932)...
5 Enhancer.registerStaticCallbacks(subclass, CALLBACKS); //CALLBACKS对象在上面图片里
6 return subclass;
7 }
4.3 这样就生成的CGLIB代理的AppConfig对象,相当于AOP增强了该对象,本来AOP增强内的方法调用自身的方法是不能直接增强自身的,那Spring是怎么做的呢?
简单介绍下,Spring CGLIB CallBackFilter的作用; Callback我们都知道是回调方法,CGLIB对象调用方法就会调用回调方法,但是添加了CallBackFilter,他有个方法accpet(Method method)方法用来判断调用的方法,返回值为int类型,代表着走哪个Callback的下标,传入的是个Callback的数组嘛 :)
1 public int accept(Method method) {
2 for (int i = 0; i < this.callbacks.length; i++) {
3 Callback callback = this.callbacks[i];
4 if (!(callback instanceof ConditionalCallback) || ((ConditionalCallback) callback).isMatch(method)) {
5 return i;
6 }
7 }
8 throw new IllegalStateException("No callback available for method " + method.getName());
9 }
4.3.1先查看第一个Callback BeanMethodInterceptor
查看其isMatch方法
@Override
public boolean isMatch(Method candidateMethod) {
return (candidateMethod.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class &&
!BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor.isSetBeanFactory(candidateMethod) &&
BeanAnnotationHelper.isBeanAnnotated(candidateMethod));
//方法不是Object中定义的,且不是setBeanFactory方法,且该方法包含@Bean注解就返回true
}
可以发现,只要调用自身的@Bean注解的方法都会走这个BeanMethodInterceptor回调,那我们就不看剩下两个回调函数了,另外一个不做任何操作,一个只是负责给CGLIB对象设置上BeanFactory对象,你说怎么设置,之前CGLIB中就添加了一个实现的接口EnhancedConfiguration,这个接口实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,可以注入BeanFactory对象;
4.3.2 查看 BeanMethodInterceptor的intercept方法
什么时候调用getMan、getMan2方法呢?看到3.4 这样一行 Object result = factoryMethod.invoke(factoryBean, args) 调用反射实例化Bean对象,这个时候不就会走回调方法了吗 :)
1 public Object intercept(Object enhancedConfigInstance, Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs,
2 MethodProxy cglibMethodProxy) throws Throwable {
3
4 ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(enhancedConfigInstance);
// 通过反射从CGLIB增强的对象获取beanFactory对象
5 String beanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(beanMethod); // 得到beanName值,默认为方法名字,可以通过@Bean注解指定
6
8 if (BeanAnnotationHelper.isScopedProxy(beanMethod)) { // 解析Scope注解
9 String scopedBeanName = ScopedProxyCreator.getTargetBeanName(beanName);
10 if (beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(scopedBeanName)) {
11 beanName = scopedBeanName;
12 }
13 }
//FactoryBean类型的Bean解析方式,暂不分析
22 if (factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName) &&
23 factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, beanName)) {
24 Object factoryBean = beanFactory.getBean(BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
25 if (factoryBean instanceof ScopedProxyFactoryBean) {
26 // Scoped proxy factory beans are a special case and should not be further proxied
27 }
28 else {
29 // It is a candidate FactoryBean - go ahead with enhancement
30 return enhanceFactoryBean(factoryBean, beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanFactory, beanName);
31 }
32 }
33
34 if (isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(beanMethod)) {
//判断当前执行的方法是否是正在执行的@Bean的方法,getMan2中调用getMan方法,getMan含有@Bean 这时候就返回false
38 if (logger.isInfoEnabled() &&
39 BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanMethod.getReturnType())) {
40 logger.info(String.format("@Bean method %s.%s is non-static and returns an object " +
41 "assignable to Spring's BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. This will " +
42 "result in a failure to process annotations such as @Autowired, " +
43 "@Resource and @PostConstruct within the method's declaring " +
44 "@Configuration class. Add the 'static' modifier to this method to avoid " +
45 "these container lifecycle issues; see @Bean javadoc for complete details.",
46 beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName()));
47 }
48 return cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(enhancedConfigInstance, beanMethodArgs); //getMan方法直接反射可以得到对象
49 }
50
51 return resolveBeanReference(beanMethod, beanMethodArgs, beanFactory, beanName); //在getMan2中调用getMan方法就会执行这段逻辑
52
通常情况下,比如getMan方法下,会返回true,然后调用反射直接得到Bean对象;而getMan2方法执行的时候调用getMan方法,this对象就是CGLIB对象,就会在走一次这个方法,ThreadLocal对象里存储的是getMan2,当前方法是getMan,就会返回false了,执行resolveBeanReference方法;
1 private boolean isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(Method method) { 2 Method currentlyInvoked = SimpleInstantiationStrategy.getCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod();
//获取ThreadLocalcurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod对象currentlyInvokedFactoryMethod中当前的Method 3 return (currentlyInvoked != null && method.getName().equals(currentlyInvoked.getName()) && 4 Arrays.equals(method.getParameterTypes(), currentlyInvoked.getParameterTypes())); 5 }
4.3.3 查看resolveBeanReference方法
1 private Object resolveBeanReference(Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs,
2 ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory, String beanName) {
3
8 boolean alreadyInCreation = beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(beanName); //getMan并不是正在创建的bean,false
9 try {
10 if (alreadyInCreation) {
11 beanFactory.setCurrentlyInCreation(beanName, false);
12 }
13 boolean useArgs = !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(beanMethodArgs);
14 if (useArgs && beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
18 for (Object arg : beanMethodArgs) {
19 if (arg == null) {
20 useArgs = false;
21 break;
22 }
23 }
24 }
25 Object beanInstance = (useArgs ? beanFactory.getBean(beanName, beanMethodArgs) :
26 beanFactory.getBean(beanName)); //没有参数的情况下,直接getBean获取就可以了
27 if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanInstance)) {
28 if (beanInstance.equals(null)) {
29 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
30 logger.debug(String.format("@Bean method %s.%s called as bean reference " +
31 "for type [%s] returned null bean; resolving to null value.",
32 beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName(),
33 beanMethod.getReturnType().getName()));
34 }
35 beanInstance = null;
36 }
37 else {
38 String msg = String.format("@Bean method %s.%s called as bean reference " +
39 "for type [%s] but overridden by non-compatible bean instance of type [%s].",
40 beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName(),
41 beanMethod.getReturnType().getName(), beanInstance.getClass().getName());
42 try {
43 BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName);
44 msg += " Overriding bean of same name declared in: " + beanDefinition.getResourceDescription();
45 }
46 catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
47 // Ignore - simply no detailed message then.
48 }
49 throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
50 }
51 }
52 Method currentlyInvoked = SimpleInstantiationStrategy.getCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(); //当前ThreadLocal中的是getMan2
53 if (currentlyInvoked != null) {
54 String outerBeanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(currentlyInvoked);
55 beanFactory.registerDependentBean(beanName, outerBeanName); //设置依赖关系
56 }
57 return beanInstance;
58 }
59 finally {
60 if (alreadyInCreation) {
61 beanFactory.setCurrentlyInCreation(beanName, true);
62 }
63 }
64 }
五.总结与疑问
查看CGLIB代理的AppConfig1对象
1 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig1.class);
2 AppConfig1 config = ac.getBean(AppConfig1.class);
3 Field[] fs = config.getClass().getFields();
4 for (Field field : fs) {
5 System.out.println(field.getName());
6 }
查看输出:)

总结:@Configuration 可以使 该配置类中 @Bean下方法中如果调用同类的方法 返回的是同一个对象!
疑问? 突然之间懵逼了,测试一下,会发现@Configuration标注的情况下,this对象指代的是CGLIB代理对象, 我记得Spring Aop的代理对象的this对象不是CGLIB代理对象啊?
所以望知悉的人告知,是this就是CGLIB代理对象还是 SpringAop 作了不透明的封装,this方法调用的时候走父类的方法呢?
解决方法,也算找到问题出在哪里,搞明白其中的道道了 ; 点我查看解决