一、公平锁与非公平锁
1.1 概述
公平锁:是指多个线程按照申请锁的顺序来获取锁。
非公平锁:是指在多线程获取锁的顺序并不是按照申请锁的顺序,有可能后申请的线程比先申请的线程优先获取到锁,在高并发的情况下,有可能造成优先级反转或者饥饿现象。饥饿现象就是低优先级的线程可能一直拿不到锁,而一直处于等待状态。
1.2 区别
公平锁:Threads acquire a fair lock in the order in which they requested it.
公平锁,就是很公平,在并发环境中,每个线程在获取锁时会先查看此锁维护的等待队列,如果为空,或者当前线程是等待队列的第一个,就占有锁,否则就会加入到等待队列中,以后会按照 FIFO 的规则从队列中取到自己。
非公平锁:a nonfair lock permits barging: threads requesting a lock can jump ahead of the queue of waiting threads if the lock
happens to be available when it is requested.
非公平锁比较粗鲁,上来就直接尝试占有锁,如果尝试失败,就再采用类似公平锁那种方式。而且,非公平锁比公平锁的吞吐量大。
1.3 Java 中的一些公平锁和非公平锁
1. java 中的 ReentrantLock,默认是非公平锁,当参数 fair 为 true 时,就是公平锁。
1 /** 2 * Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}. 3 * This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}. 4 */ 5 public ReentrantLock() { 6 sync = new NonfairSync(); 7 } 8 9 /** 10 * Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the 11 * given fairness policy. 12 * 13 * @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy 14 */ 15 public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) { 16 sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync(); 17 }
2. synchronized 也是一种非公平锁。
二、可重入锁与不可重入锁
2.1 概述
可重入锁(也叫做递归锁): 指的是同一线程外层函数获得锁之后,内层递归函数仍然能获取该锁的代码,在同一个线程在外层方法获取锁的时候,在进入内层方法会自动获取锁,也就是说,线程可以进入任何一个它已经拥有的锁所同步着的代码块。可重入锁最大的作用就是避免死锁。
不可重入锁,即若当前线程执行某个方法已经获取了该锁,那么在方法中尝试再次获取锁时,就会获取不到被阻塞。
2.2 java 中的可重入锁
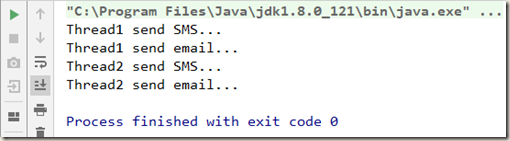
2.2.1 synchronized 锁
1 class Phone { 2 public synchronized void sendSMS() { 3 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " send SMS..."); 4 sendEmail(); 5 } 6 7 public synchronized void sendEmail() { 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " send email..."); 9 } 10 } 11 12 public class ReentrantLockDemo { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 Phone phone = new Phone(); 16 17 new Thread(() -> { 18 phone.sendSMS(); 19 }, "Thread1").start(); 20 21 new Thread(() -> { 22 phone.sendSMS(); 23 }, "Thread2").start(); 24 } 25 }
2.2.2 ReentrantLock
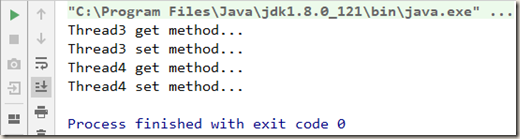
1 class Phone implements Runnable { 2 Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 3 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 get(); 7 } 8 9 public void get() { 10 lock.lock(); 11 try { 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get method..."); 13 set(); 14 } finally { 15 lock.unlock(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 public void set() { 20 lock.lock(); 21 try { 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " set method..."); 23 } finally { 24 lock.unlock(); 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 29 public class ReentrantLockDemo { 30 31 public static void main(String[] args) { 32 Phone phone = new Phone(); 33 34 Thread thread3 = new Thread(phone, "Thread3"); 35 Thread thread4 = new Thread(phone, "Thread4"); 36 thread3.start(); 37 thread4.start(); 38 } 39 }
2.3 面试题
使用 ReentrantLock 时,如果加入两层锁呢,程序是直接报编译错误,还是正常运行,正常运行的话,能得到预期的结果吗?
1 class Phone implements Runnable { 2 3 // ... 4 5 public void get() { 6 lock.lock(); 7 lock.lock(); 8 try { 9 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get method..."); 10 set(); 11 } finally { 12 lock.unlock(); 13 lock.unlock(); 14 } 15 } 16 17 // ... 18 }
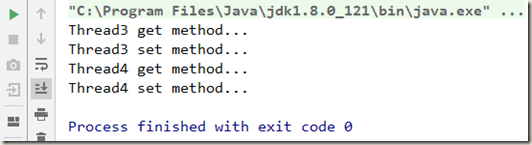
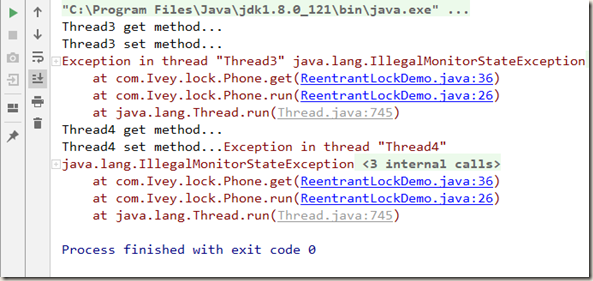
当缺少 unlock() 时(也就是,lock 和 unlock不是一一对应,lock 比 unlock 多 ),程序不会报编译错误,但得不到预期的结果,从下面可以看出,程序一直处于运行的状态:
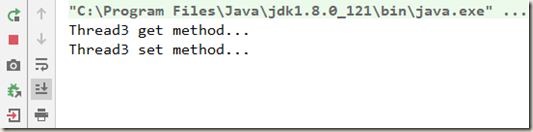
当缺少 lock() 时(也就是,unlock 比 lock 多 ),此时,程序也不会报编译错误,控制台也输出了结果,但是抛出了 IllegalMonitorStateException 异常。
三、自旋锁
3.1 概述
自旋锁是指尝试获取锁的线程不会立即阻塞,而是采用循环的方式去尝试获取锁,这样的好处是减少线程上下文切换的消耗,缺点是循环会消耗CPU。
3.2 java 中的自旋锁
1 // Unsafe.java 2 public final int getAndAddInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4) { 3 int var5; 4 do { 5 var5 = this.getIntVolatile(var1, var2); 6 } while(!this.compareAndSwapInt(var1, var2, var5, var5 + var4)); 7 8 return var5; 9 }
3.3 手写一个自旋锁
1 public class SpinLockDemo { 2 3 AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>(); 4 5 public void myLock() { 6 Thread thread = Thread.currentThread(); 7 System.out.println(thread.getName() + " come in..."); 8 while (!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null, thread)) { 9 10 } 11 } 12 13 public void myUnLock() { 14 Thread thread = Thread.currentThread(); 15 atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread, null); 16 System.out.println(thread.getName() + " come out..."); 17 } 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 21 SpinLockDemo spinLockDemo = new SpinLockDemo(); 22 23 new Thread(() -> { 24 spinLockDemo.myLock(); 25 try { 26 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); 27 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 spinLockDemo.myUnLock(); 31 }, "Thread1").start(); 32 33 try { 34 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 35 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 39 new Thread(() -> { 40 spinLockDemo.myLock(); 41 try { 42 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 43 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 spinLockDemo.myUnLock(); 47 }, "Thread2").start(); 48 } 49 }
四、写锁(独占锁)、读锁(共享锁)和互斥锁
4.1 概述
独占锁:指该锁一次只能被一个线程所持有。对 ReentrantLock 和 Synchronized 而言都是独占锁。
共享锁:指该锁可被多个线程所持有。
对 ReentrantReadWriteLock 其读锁是共享锁,其写锁是独占锁。
读锁的共享锁可保证并发读是非常高效的,读写,写读,写写的过程是互斥的。
4.2 示例(模拟缓存)
4.2.1 加锁前:
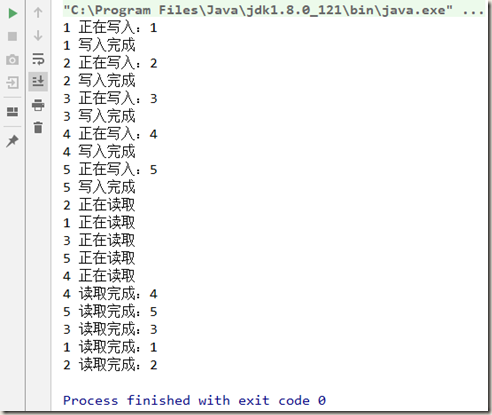
数据写入的时候,被打断:
1 class MyCache { 2 3 private volatile Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); 4 5 public void put(String key, Object value) { 6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在写入:" + key); 7 try { 8 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); 9 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 } 12 map.put(key, value); 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 写入完成"); 14 } 15 16 public void get(String key) { 17 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在读取"); 18 try { 19 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 Object result = map.get(key); 24 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 读取完成:" + result); 25 } 26 } 27 28 public class ReadWriteLockDemo { 29 30 public static void main(String[] args) { 31 MyCache myCache = new MyCache(); 32 33 for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { 34 final int temp = i; 35 new Thread(() -> { 36 myCache.put(temp + "", temp + ""); 37 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 38 } 39 40 for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { 41 final int temp = i; 42 new Thread(() -> { 43 myCache.get(temp + ""); 44 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 45 } 46 } 47 }
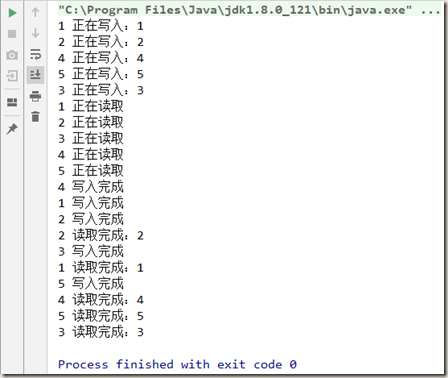
4.2.2 加锁后:
写入时正常,不会中断;读取时,可以共享锁。
1 class MyCache { 2 3 private volatile Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); 4 private ReentrantReadWriteLock rwLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); 5 6 public void put(String key, Object value) { 7 rwLock.writeLock().lock(); 8 try { 9 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在写入:" + key); 10 try { 11 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 map.put(key, value); 16 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 写入完成"); 17 } catch (Exception e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } finally { 20 rwLock.writeLock().unlock(); 21 } 22 } 23 24 public void get(String key) { 25 rwLock.readLock().lock(); 26 try { 27 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在读取"); 28 try { 29 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); 30 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } 33 Object result = map.get(key); 34 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 读取完成:" + result); 35 } catch (Exception e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } finally { 38 rwLock.readLock().unlock(); 39 } 40 } 41 }