一、什么是阻塞队列
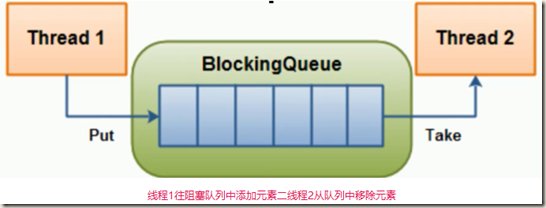
阻塞队列,顾名思义,首先它是一个队列,而一个阻塞队列在数据结构中所起的作用大致如图所示:
当阻塞队列是空时,从队列中获取元素的操作将会被阻塞。
当阻塞队列是满时,往队列中添加元素的操作将会被阻塞。
同样,试图往已满的阻塞队列中添加新元素的线程同样也会被阻塞,直到其他线程从队列中移除一个或者多个元素或者全清空队列后,使队列重新变得空闲起来并后续新增。
二、阻塞队列有什么好处
在多线程领域:所谓阻塞,在某些情况下会挂起线程(即线程阻塞),一旦条件满足,被挂起的线程又会被自动唤醒。
使用阻塞队列的好处是我们不需要关心什么时候需要阻塞线程,什么时候需要唤醒线程,因为BlockingQueue 都一手包办好了。
在 concurrent 包发布以前,在多线程环境下,每个程序员都必须自己去控制这些细节,尤其还要兼顾效率和线程安全,而这会给我们的程序带来不小的复杂度。
三、java 中的阻塞队列
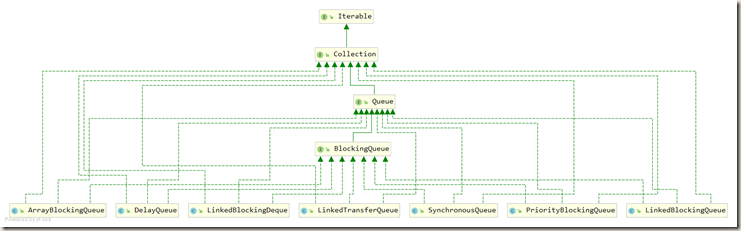
3.1 架构介绍
3.2 种类分析
- ArrayBlockingQueue:由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列。
- LinkedBlockingQueue:由链表结构组成的有界(但大小默认值是Integer.MAX_VALUE)阻塞队列。
- PriorityBlockingQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。
- DelayQueue:使用优先级队列实现的延迟无界阻塞队列。
- SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即是单个元素的队列。(与其他BlcokingQueue不同,synchronousQueue 是一个不存储元素的 BlcokingQueue。每个 put 操作必须要等待一个take操作,否则不能继续添加元素,反之亦然。)
- LinkedTransferQueue:由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列。
- LinkedBlockingDeque:由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列。
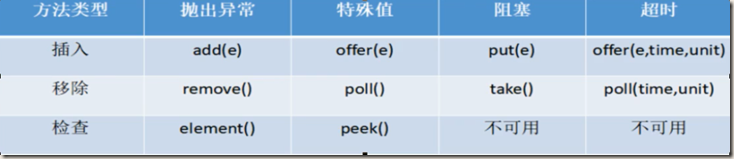
3.3 BlockingQueue 的核心方法
抛出异常 | 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里面add插入元素会抛出 IllegalStateException:Queue full |
特殊值 | 插入方法,成功返回true,失败返回 false |
一直阻塞 | 当阻塞队列满时,生产者继续往队列里面 put 元素,队列会一直阻塞,直到put数据或者响应中断退出。 |
超时退出 | 当阻塞队列满时,队列会阻塞生产者线程一定时间,超过后限时后生产者线程就会退出。 |
四、生产者-消费者问题
4.1 传统的使用 await() 和 signal()
1 class ShareData { 2 private int number = 0; 3 private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 4 private Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 5 6 public void increment() { 7 lock.lock(); 8 try { 9 while (number != 0) { 10 condition.await(); 11 } 12 number++; 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + number); 14 condition.signalAll(); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } finally { 18 lock.unlock(); 19 } 20 } 21 22 public void decrement() { 23 lock.lock(); 24 try { 25 while (number == 0) { 26 condition.await(); 27 } 28 number--; 29 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + number); 30 condition.signalAll(); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } finally { 34 lock.unlock(); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 39 public class ProdConsumer_traditionDemo { 40 41 public static void main(String[] args) { 42 ShareData shareData = new ShareData(); 43 44 new Thread(() -> { 45 for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { 46 shareData.increment(); 47 } 48 }, "Thread-A").start(); 49 50 new Thread(() -> { 51 for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { 52 shareData.decrement(); 53 } 54 }, "Thread-B").start(); 55 } 56 }
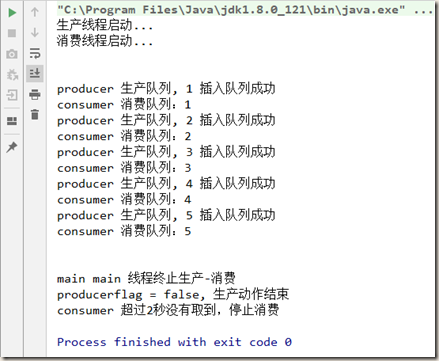
4.2 使用阻塞队列
1 class MyResource { 2 private volatile boolean flag = true; 3 private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(); 4 5 private BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = null; 6 7 public MyResource(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) { 8 this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue; 9 } 10 11 public void producer() throws InterruptedException { 12 String data = null; 13 boolean resFlag; 14 15 while (flag) { 16 data = atomicInteger.incrementAndGet() + ""; 17 resFlag = blockingQueue.offer(data, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 18 if (resFlag) { 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 生产队列, " + data + " 插入队列成功"); 20 } else { 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 生产队列, " + data + " 插入队列失败"); 22 } 23 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 24 } 25 26 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "flag = false, 生产动作结束"); 27 } 28 29 public void consumer() throws InterruptedException { 30 String result = null; 31 32 while (flag) { 33 result = blockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 34 35 if (result == null || result.equalsIgnoreCase("")) { 36 flag = false; 37 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 超过2秒没有取到,停止消费"); 38 return; 39 } 40 41 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 消费队列:" + result); 42 } 43 } 44 45 public void stop() { 46 this.flag = false; 47 } 48 } 49 50 public class ProdConsumer_BlockQueueDemo { 51 52 public static void main(String[] args) { 53 MyResource myResource = new MyResource(new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10)); 54 55 new Thread(() -> { 56 System.out.println("生产线程启动..."); 57 try { 58 myResource.producer(); 59 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 60 e.printStackTrace(); 61 } 62 }, "producer").start(); 63 64 new Thread(() -> { 65 System.out.println("消费线程启动..."); 66 try { 67 myResource.consumer(); 68 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 69 e.printStackTrace(); 70 } 71 }, "consumer").start(); 72 73 try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } 74 75 myResource.stop(); 76 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " main 线程终止生产-消费"); 77 } 78 }