1.单线程实例:
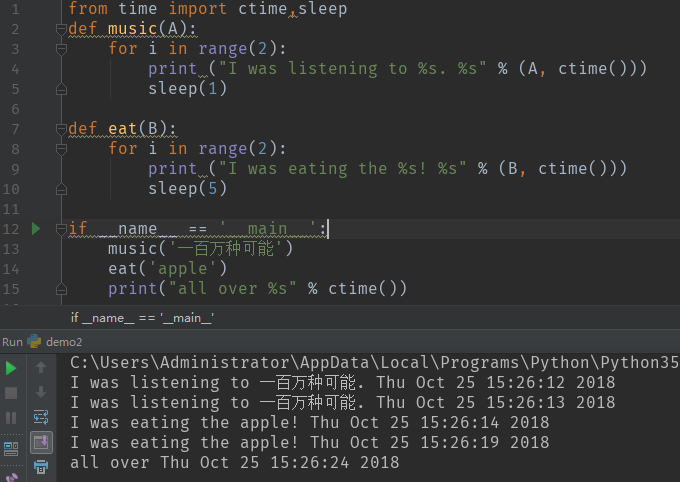
代码如下: from time import ctime,sleep def music(A): for i in range(2): print ("I was listening to %s. %s" % (A, ctime())) sleep(1) def eat(B): for i in range(2): print ("I was eating the %s! %s" % (B, ctime())) sleep(5) if __name__ == '__main__': music('一百万种可能') eat('apple') print("all over %s" % ctime())
2.多线程实例:
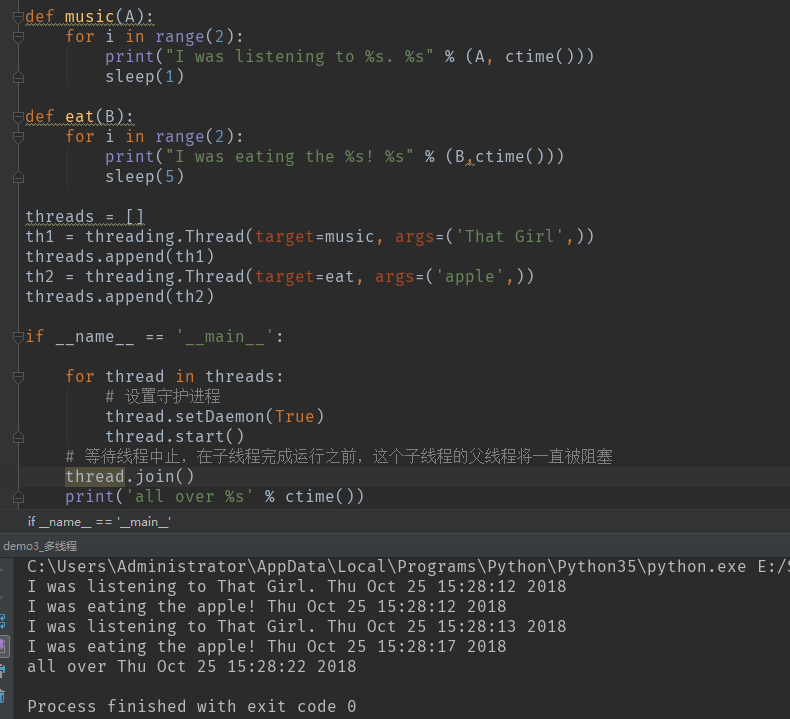
代码如下: from time import ctime,sleep import threading def music(A): for i in range(2): print("I was listening to %s. %s" % (A, ctime())) sleep(1) def eat(B): for i in range(2): print("I was eating the %s! %s" % (B,ctime())) sleep(5) threads = [] th1 = threading.Thread(target=music, args=('That Girl',)) threads.append(th1) th2 = threading.Thread(target=eat, args=('apple',)) threads.append(th2) if __name__ == '__main__': for thread in threads: # 设置守护进程 thread.setDaemon(True) thread.start() # 等待线程中止,在子线程完成运行之前,这个子线程的父线程将一直被阻塞 thread.join() print('all over %s' % ctime())