1. 字符串补充
1.1 首字母大写
name = "alex"
name1 = name.capitalize()
print(name1)
1.2 每个单词首字母大写
name = "alex wusir"
print(name.title())
1.3 大小写反转
name = "Alex"
print(name.swapcase())
1.4 居中,填充
name = "Alex"
print(name.center(20,"_")) #后边的可以不写,只写20,后边最多可以写一个一个字符长度,可以是一个数字,一个字母,一个符号,一个汉字
1.5 查找 从左向右,只查找一个
name = "alex"
print(name.find("b")) #find 查找不存在的返回-1
print(name.index('b')) #index查找不存在就报错
1.6 拼接
name = "a23x"
print("_".join(name)) ***a_l_3_x 每个字符之间拼接
# 1.请将列表中的每个元素通过 "_" 链接起来。
# users = ['大黑哥','龚明阳','渣渣辉']
# print("_".join(users))
# "添加的元素".join(列表)
#
# users = ['大黑哥','龚明阳',666,'渣渣辉']
# s = ""
# for i in users: #(users中每个元素都要可以叠代)
# s = s + str(i) + "_"
# print(s[:-1])
1. %s
2. f{}
3. name.format()
name = "alex{},{},{}" #逗号隔开
print(name.format(1,2,3)) #按照顺序位置进行填充 alex1,2,3
name = "alex{2},{0},{1}"
print(name.format("a","b","c")) #按照索引进行添加 alexc,a,b
name = "alex{a},{b},{c}"
print(name.format(b=11,c=67,a=22)) #按照关键字进行填充 alex22,11,67
1.8 字符串的 - + * 都是开辟了新的空间
a = "alex"
b = a + a
c = a * 3
print(a,b,c) #alex alexalex alexalexalex
print(id(a),id(b),id(c)) #108006909408 108007759792 108007788592
a = "alex"
b = a.strip("a")
print(a,b) #alex lex
print(id(a),id(b)) #880907429344 880908272672
2. 列表 list
2.1 创建
lst = []
list()
2.2 排序 (默认升序) sort()
lst = [1,2,23,234,456,23,2123,432,234,2,23]
lst.sort()
print(lst) #[1, 2, 2, 23, 23, 23, 234, 234, 432, 456, 2123]
lst = ["你好","我好","大家好"]
lst.sort()
print(lst) #['你好', '大家好', '我好'] #['你好', '大家好', '我好']
print(id(lst[0]),id(lst[1]),id(lst[2])) #51193388176 51193428176 51193388088
2.3 降序 sort(reverse=True)
lst = [1,2,23,234,456,23,2123,432,234,2,23]
lst.sort(reverse = True)
print(lst) #[2123, 456, 432, 234, 234, 23, 23, 23, 2, 2, 1]
2.4 反转
2.4.1 通过切片
lst = [1,2,23,234,456,23,2123,432,234,2,23]
print(lst[::-1]) #[23, 2, 234, 432, 2123, 23, 456, 234, 23, 2, 1]
2.4.2 reverse()
lst = [1,2,23,234,456,23,2123,432,234,2,23]
lst.reverse()
print(lst) #[23, 2, 234, 432, 2123, 23, 456, 234, 23, 2, 1]
2.5 面试题
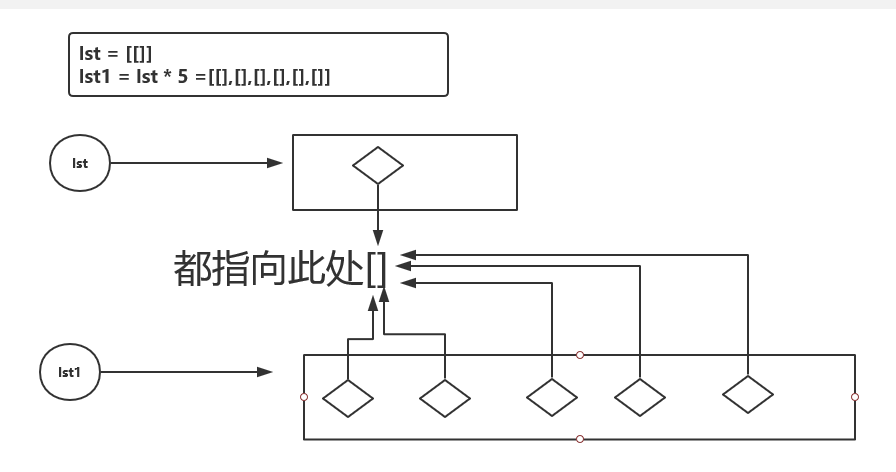
2.51
lst = [[]]
new_lst = lst * 5
new_lst[0].append(10)
print(lst) #[[10]]
print(new_lst) #[[10],[10],[10],[10],[10]]
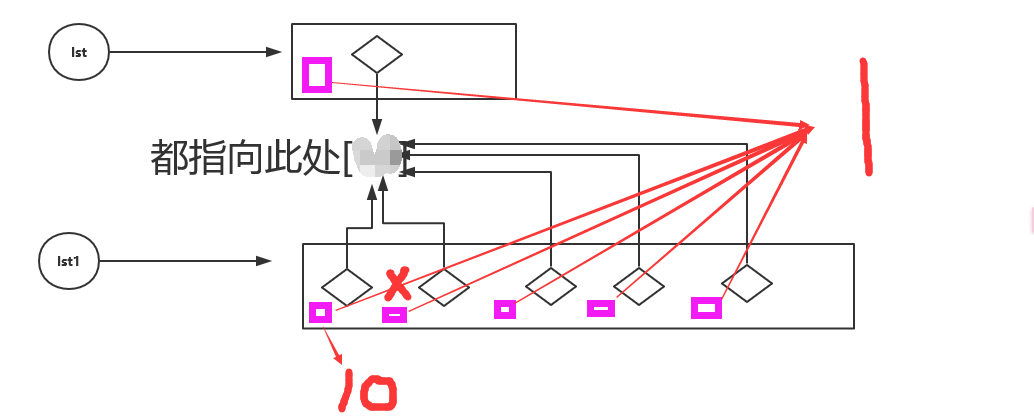
2.5.2
lst = [1,[]]
new_lst = lst *5
new_lst[0] = 10
print(lst) # [1,[]]
print(new_lst) # [10,[],1,[],1,[],1,[],1,[]] #相当于浅拷贝,开辟新的空间,里边内容共用
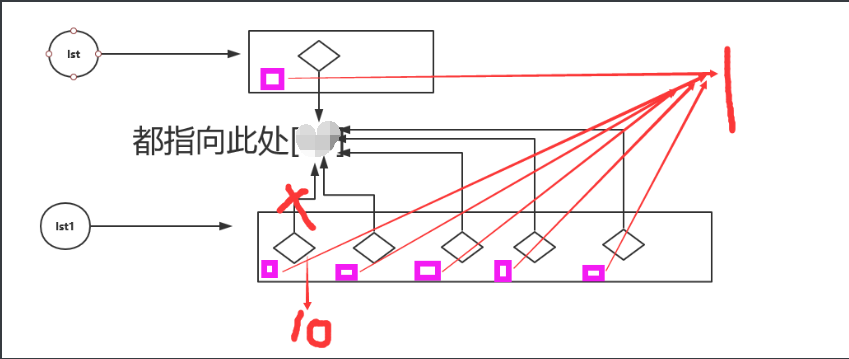
2.5.3
lst = [1,[]]
new_lst = lst *5
new_lst[1] = 10
print(lst) # [1,[]]
print(new_lst) # [1,10,1,[],1,[],1,[],1,[]
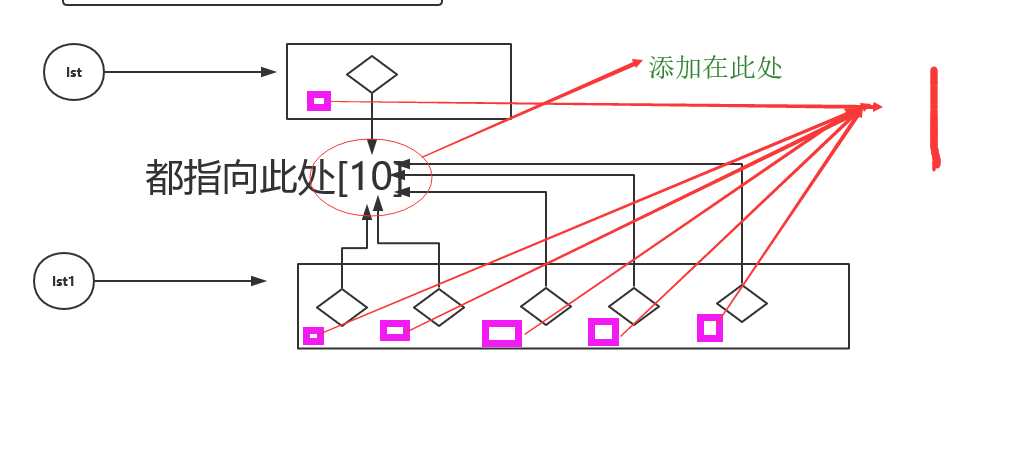
2.5.4
lst = [1,[]]
new_lst = lst *5
new_lst[1].append(10)
print(lst) # [1,[10]]
print(new_lst) # [1,[10],1,[10],1,[10],1,[10],1,[10]]
2.5.6 实现方式
lst = [1,[]]
lst1 = []
lst1.extend(lst*5) #迭代添加
print(lst1)
3. 元组 tuple()
3.1 数据类型是()中数据本身的数据类型
tu = (12)
print(type(tu)) #<class 'int'>
tu = ("12")
print(type(tu)) # <class 'str'>
tu = (12,) # (12,)是元组
print(type(tu)) #<class 'tuple'>
tu = (True)
print(type(tu)) #<class 'bool'>
tu = ({"你好"})
print(type(tu)) #<class 'set'>
tu = ({"你好":666})
print(type(tu)) #<class 'dict'>
***3.2 元组 - + * 不可变共用,可变也共用,只有最外层不同
tu = (1,2,3,(4,5,6))
tu1 = tu + tu
print(tu1)
print(id(tu),id(tu1)) #id 不相同1081022870296 1081021967160
print(tu[-1] is tu1[-1]) #id 相同844223886104 844223886104
4. 字典 dict
4.1 创建字典
dic = {}
print(dict(k=1,k1=2)) #{'k': 1, 'k1': 2}
4.2 随机删除 popitem()
dic = {"key1":1,"key2":2,"key3":56}
print(dic.popitem()) #默认删除最后一个,返回值为删除的键值对('key3', 56) 为元组
print(dic) #{'key1': 1, 'key2': 2}
print(type(('key3', 56))) #<class 'tuple'>
3 3.5 批量添加键值对 需要dic去接收
dic = {}
dic = dic.fromkeys("123",[23]) # 批量添加键值对{"1":[23],"2":[23],"3":[23]}
print(dic)
dic = dict.fromkeys("123456789",1) # 批量添加键值对"键是可迭代对象",值 -- 会被共用
dic["1"] = 18
print(dic) #{'1': 18, '2': 1, '3': 1, '4': 1, '5': 1, '6': 1, '7': 1, '8': 1, '9': 1}
5. 集合 set () 无序的
set:
set() -- 空集合
{} -- 空字典
定义集合:
set = set("alex") # **迭代****无序**添加的
print(set) #{'x', 'a', 'l', 'e'}
6.为False的一些数据类型
bool: False
数字: 0
字符串: ""
列表:[]
元组:() #<class 'tuple'>
字典:{}
集合: set()
其他: None
机智:3 > 5
print(bool()) 添加要判断的元素
7. 数据类型之间转换
7.1 列表和元组转换
lst = [1,2,3]
tu = (4,5,6)
lst1 = list(tu)
tu1 = tuple(lst)
print(tuple(lst)) #(1, 2, 3)
print(list(tu)) #[4, 5, 6]
7.2 字符串转换为列表
name = '"alex","你好",888'
print(name.split(",")) #['"alex"', '"你好"', '888']
7.3 列表转换为字符串
lst = ["1","2","3"]
print(''.join(lst)) #123
7.4 字典转换为字符串
dic = {"1":2}
print(str(dic),type(str(dic))) #{'1': 2} <class 'str'>
7.5 集合和列表互换
s = {1,2,3}
lst = [4,5,6]
s1 = set(lst)
lst1 = list(s)
print(s1) #{4, 5, 6}
print(lst1) #[1, 2, 3]
8. python 数据类型分类
可变:
list ,dict ,set
不可变:
int bool str tuple
有序:
list,tuple,str,int,bool
无序:
dict,set
取值方式:
索引: str list tuple
直接: set ,int ,bool
键: dict
9. 会遇到的坑
lst = [] #没有数据,无法进行 for 循环
for i in range(len(lst)):
lst.append(3)
print(lst) #[]
lst = [] ##没有数据,无法进行 for 循环
for i in lst:
lst.append(3)
print(lst) #[]
lst = [1,2]
for i in range(len(lst)): #len(lst)不会变
lst.append(3)
print(lst) #[1, 2, 3, 3]
解释:
lst = [1,2]
s = len(lst) #2
lst.append(3)
s1 = len(lst) #3
print(s,s1)
lst = [1,2]
for i in lst: #lst一直在变
lst.append(3)
print(lst) # 死循环,不会打印
解释:
lst = [1,2]
lst.append(3)
s1 = len(lst) #3
print(s,s1)
10.删除列表的坑*** 循环lst是可变的,range(len(lst))是不变的
lst = [1,2,3,4]
for i in lst: #lst是可变的,range(len(lst))是不变的
lst.pop() #从后向前删除
print(lst) #[1,2] #从后往前删,第一次循环删除4,第二次删除3,此时len(lst)为2,不循环了
lst = [1,2,3,4]
for i in lst:
lst.pop(0) #从前向后删除,当前边没数时,后边的自动向前移动,第一次删除1,/2会挪到1的位置,
print(lst) #第二次循环删除时会删除2,现在lst就两个数,也就循环两次
结果:[3,4]
lst = [1,2,3,4]
for i in lst:
lst.remove(i) #通过索引删除第一次删除1,第二次3的索引为1,删除3,循环停止
print(lst) #[2, 4]
10.1 看看到底循环了几次
lst = [1,2,3,4]
for i in lst:
lst.remove(i) #通过索引删除第一次删除1,第二次3的索引为1,删除3,循环停止
print(lst) #[2, 4]
结果:
[2, 3, 4] #第一次循环结果
[2, 4] #第二次循环结果,没有第三次
11. 列表成功删除
lst = [1,2,3]
for i in lst:
lst.clear()
print(lst) #[]
lst = [1,2,3]
for i in range(len(lst)):
lst.pop()
print(lst) #[]
lst = [1,2,3,4,6]
for i in range(len(lst)-1,-1,-1):
del lst[i] #通过索引删除
print(lst)
lst = [1,2,3,4,6]
for i in range(len(lst)):
del lst[-1] #通过索引删除
print(lst) #[]
**** 重点删除方法
lst = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
lst1 = lst.copy() #取得与lst相同长度的列表lst1
for i in lst1: #lst1是不会变的,借用其中的相同元素和长度来循环
lst.remove(i) #通过元素删除
print(lst) #[]
12. 删除字典的坑字典的迭代的时候改变了原来的大小*(不能加不能删,但可以改)
dic = dict.fromkeys("12345",1)
for i in dic:
dic[i] = "123"
print(dic)
dic = dict.fromkeys("12345",1)
dic1 = dic.copy()
for i in dic1:
dic.pop(i)
print(dic)
集合和字典都是迭代的时候不能改变原来的大小
13. 二次编码
密码本:
ascii -- 没有中文
gbk -- 英文 8b(位) 1B(字节) 中文 16b 2B
unicode -- 英文16b 2B 中文32b 4B
utf-8 -- 英文8b 1B 欧洲16b 2B 亚洲24b 3B
name = "你好啊"
s1 = name.encode("utf-8") # 编码
s2 = name.encode("gbk") # 编码
s2 = s1.decode("utf-8") # 解码
print(s2.encode("gbk")) #解码
以什么编码集(密码本)进行编码就要用什么编码集(密码本)解码



