Dreamoon wants to climb up a stair of n steps. He can climb 1 or 2 steps at each move. Dreamoon wants the number of moves to be a multiple of an integer m.
What is the minimal number of moves making him climb to the top of the stairs that satisfies his condition?
The single line contains two space separated integers n, m (0 < n ≤ 10000, 1 < m ≤ 10).
Print a single integer — the minimal number of moves being a multiple of m. If there is no way he can climb satisfying condition print - 1 instead.
10 2
6
3 5
-1
For the first sample, Dreamoon could climb in 6 moves with following sequence of steps: {2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1}.
For the second sample, there are only three valid sequence of steps {2, 1}, {1, 2}, {1, 1, 1} with 2, 2, and 3 steps respectively. All these numbers are not multiples of 5.
简单题:暴力枚举
import java.util.*;
public class CF467A{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=in.nextInt(),m=in.nextInt();
int low=n/2;
int high=n;
if(n%2==1) low++;
int ans=-1;
for(int i=low;i<=high;i++){
if(i%m==0){
ans=i; break;
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}Dreamoon is standing at the position 0 on a number line. Drazil is sending a list of commands through Wi-Fi to Dreamoon's smartphone and Dreamoon follows them.
Each command is one of the following two types:
- Go 1 unit towards the positive direction, denoted as '+'
- Go 1 unit towards the negative direction, denoted as '-'
But the Wi-Fi condition is so poor that Dreamoon's smartphone reports some of the commands can't be recognized and Dreamoon knows that some of them might even be wrong though successfully recognized. Dreamoon decides to follow every recognized command and toss a fair coin to decide those unrecognized ones (that means, he moves to the 1 unit to the negative or positive direction with the same probability 0.5).
You are given an original list of commands sent by Drazil and list received by Dreamoon. What is the probability that Dreamoon ends in the position originally supposed to be final by Drazil's commands?
The first line contains a string s1 — the commands Drazil sends to Dreamoon, this string consists of only the characters in the set {'+', '-'}.
The second line contains a string s2 — the commands Dreamoon's smartphone recognizes, this string consists of only the characters in the set {'+','-', '?'}. '?
' denotes an unrecognized command.
Lengths of two strings are equal and do not exceed 10.
Output a single real number corresponding to the probability. The answer will be considered correct if its relative or absolute error doesn't exceed 10 - 9.
++-+- +-+-+
1.000000000000
+-+- +-??
0.500000000000
+++ ??-
0.000000000000
For the first sample, both s1 and s2 will lead Dreamoon to finish at the same position + 1.
For the second sample, s1 will lead Dreamoon to finish at position 0, while there are four possibilites for s2: {"+-++", "+-+-", "+--+", "+---"} with ending position {+2, 0, 0, -2} respectively. So there are 2 correct cases out of 4, so the probability of finishing at the correct position is 0.5.
For the third sample, s2 could only lead us to finish at positions {+1, -1, -3}, so the probability to finish at the correct position + 3 is 0.
简单题:
/**
* Created by ckboss on 14-10-16.
*/
import java.util.*;
public class CF476B {
static double Calu(int deta,int c){
double ret=1;
for(int i=c;i>=c-deta+1;i--){
ret=ret*i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=deta;i++){
ret=ret/i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=c;i++){
ret=ret*0.5;
}
return ret;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String cmd1=in.next();
String cmd2=in.next();
int a1=0,b1=0,a2=0,b2=0,c=0;
for(int i=0,sz=cmd1.length();i<sz;i++){
if(cmd1.charAt(i)=='+') a1++;
else b1++;
}
for(int i=0,sz=cmd2.length();i<sz;i++){
if(cmd2.charAt(i)=='+') a2++;
else if(cmd2.charAt(i)=='-') b2++;
else c++;
}
double ans=0.0;
if(a2<=a1&&b2<=b1){
ans = Calu(a1-a2,c);
}
System.out.print(ans);
}
}
Dreamoon loves summing up something for no reason. One day he obtains two integers a and b occasionally.
He wants to calculate the sum of all niceintegers. Positive integer x is called nice if 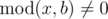 and
and 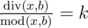 ,
where k is some integer number in range [1, a].
,
where k is some integer number in range [1, a].
By 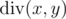 we
denote the quotient of integer division of x and y.
By
we
denote the quotient of integer division of x and y.
By 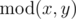 we
denote the remainder of integer division of x and y.
You can read more about these operations here: http://goo.gl/AcsXhT.
we
denote the remainder of integer division of x and y.
You can read more about these operations here: http://goo.gl/AcsXhT.
The answer may be large, so please print its remainder modulo 1 000 000 007 (109 + 7). Can you compute it faster than Dreamoon?
The single line of the input contains two integers a, b (1 ≤ a, b ≤ 107).
Print a single integer representing the answer modulo 1 000 000 007 (109 + 7).
1 1
0
2 2
8
For the first sample, there are no nice integers because 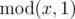 is
always zero.
is
always zero.
For the second sample, the set of nice integers is {3, 5}.
化简一下式子。
。。
。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int LL;
const LL MOD=1000000007LL;
LL a,b;
LL bl()
{
LL ret=0;
LL bbb=(b*(b-1)/2)%MOD;
for(int i=1;i<=a;i++)
ret=(ret+((i*bbb)%MOD*b)%MOD+bbb)%MOD;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<bl()<<endl;
return 0;
}
Dreamoon likes to play with sets, integers and 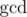 .
. 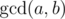 is
defined as the largest positive integer that divides both a and b.
is
defined as the largest positive integer that divides both a and b.
Let S be a set of exactly four distinct integers greater than 0.
Define S to be of rank k if and only if for all
pairs of distinct elements si, sj from S, 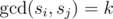 .
.
Given k and n, Dreamoon wants to make up n sets of rank k using integers from 1 to m such that no integer is used in two different sets (of course you can leave some integers without use). Calculate the minimum m that makes it possible and print one possible solution.
The single line of the input contains two space separated integers n, k (1 ≤ n ≤ 10 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ 100).
On the first line print a single integer — the minimal possible m.
On each of the next n lines print four space separated integers representing the i-th set.
Neither the order of the sets nor the order of integers within a set is important. If there are multiple possible solutions with minimal m, print any one of them.
1 1
5 1 2 3 5
2 2
22 2 4 6 22 14 18 10 16
For the first example it's easy to see that set {1, 2, 3, 4} isn't a valid set of rank 1 since 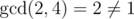 .
.
规律,6×i+1 。 6×i+2 , 6×i+3 , 6×i+5
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,k;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
printf("%d
",(6*(n-1)+5)*k);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%d %d %d %d
",k*(6*i+1),k*(6*i+2),k*(6*i+3),k*(6*i+5));
}
return 0;
}
Dreamoon has a string s and a pattern string p. He
first removes exactly x characters from s obtaining
string s' as a result. Then he calculates 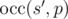 that
is defined as the maximal number of non-overlapping substrings equal to p that can be found in s'.
He wants to make this number as big as possible.
that
is defined as the maximal number of non-overlapping substrings equal to p that can be found in s'.
He wants to make this number as big as possible.
More formally, let's define 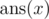 as
maximum value of
as
maximum value of 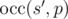 over
all s' that can be obtained by removing exactly x characters
from s. Dreamoon wants to know
over
all s' that can be obtained by removing exactly x characters
from s. Dreamoon wants to know 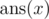 for
all x from 0 to |s| where |s| denotes
the length of string s.
for
all x from 0 to |s| where |s| denotes
the length of string s.
The first line of the input contains the string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 2 000).
The second line of the input contains the string p (1 ≤ |p| ≤ 500).
Both strings will only consist of lower case English letters.
Print |s| + 1 space-separated integers in a single line representing the 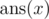 for
all x from 0 to |s|.
for
all x from 0 to |s|.
aaaaa aa
2 2 1 1 0 0
axbaxxb ab
0 1 1 2 1 1 0 0
For the first sample, the corresponding optimal values of s' after removal 0 through |s| = 5 characters from s are {"aaaaa", "aaaa", "aaa", "aa","a", ""}.
For the second sample, possible corresponding optimal values of s' are {"axbaxxb", "abaxxb", "axbab", "abab", "aba", "ab", "a", ""}.
DP[i][j]再第一个串中前i个字符里删j个能得到的最大匹配数
cal(i)从第一个串第i个字符往前删至少删几个能够和第二个串匹配
dp[i][j]=max( dp[i-1][j],dp[i-cal(i)-len2][j-cal(i)] );
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
char s[2200],p[550];
int dp[2200][2200],len1,len2;
int cal(int x)
{
if(x<len2) return INF;
int ans=0,p1=len2,q=x;
while(p1&&q)
{
if(s[q]==p[p1]) p1--,q--;
else ans++,q--;
}
if(p1==0) return ans;
return INF;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%s%s",s+1,p+1);
len1=strlen(s+1),len2=strlen(p+1);
for(int i=0;i<=len1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<=len1;j++)
{
if(i<j) dp[i][j]=-INF;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++)
{
int x=cal(i);
for(int j=0;j<=len1;j++)
{
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j]);
if(j-x>=0) dp[i][j]=max(dp[i][j],dp[i-x-len2][j-x]+1);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<=len1;i++)
printf("%d ",dp[len1][i]);
putchar(10);
return 0;
}