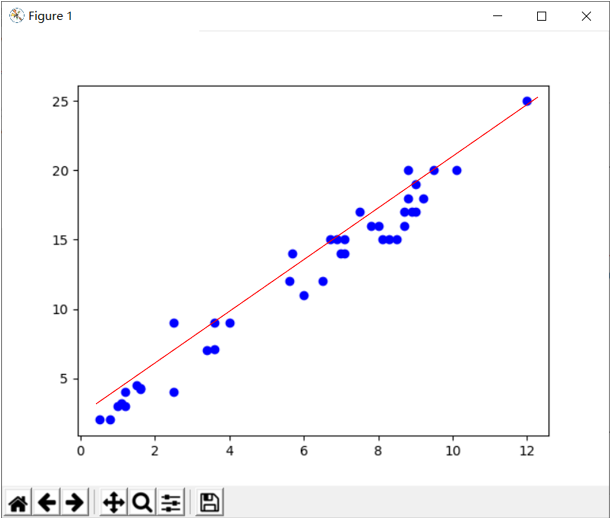
【1.总结】
线性回归可以理解为:在N维空间中找一个形式像直线方程(y=ax+b)一样的函数来拟合数据。
因此,线性回归包括:
单元(单因素)线性回归
多元(多因素)线性回归
而在构建线性回归模型的过程中,我们需要选择最合适的那条线,即预测结果与真实结果误差最小,这里就涉及到一个概念:损失函数(最小二乘法)。
损失函数是模型输出和观测结果间概率分布差异的量化

其实质为欧式距离加和。
李航-《统计学习方法》中总结了“算法-策略-优化”模型,以下归纳线性回归算法的思想。

(1)所谓正规方程,

(2)所谓梯度下降,是对自变量进行不断的更新(针对w和b求偏导),使得目标函数不断逼近最小值的过程

【2.思考线性回归算法可以用来做什么?】
线性回归算法主要是学习已有数据集,预测后续发展。如可以根据气候条件等因素预测某地区日出时间。
【3.自主编写线性回归算法 ,数据可以自己造,或者从网上获取。(加分题)】
1)获取数据
1 import pandas as pd 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 4 5 points = pd.read_csv("E:/机器学习/机器学习及其算法/data/data.csv") 6 # points 7 # 提取points中的两列数据,分别作为x,y 8 x = points.iloc[:, 0] 9 y = points.iloc[:, 1] 10 x = x.values.reshape(1, -1) 11 y = y.values.reshape(1, -1) 12 13 14 # 用plt画出散点图 15 plt.scatter(x, y) 16 plt.show()
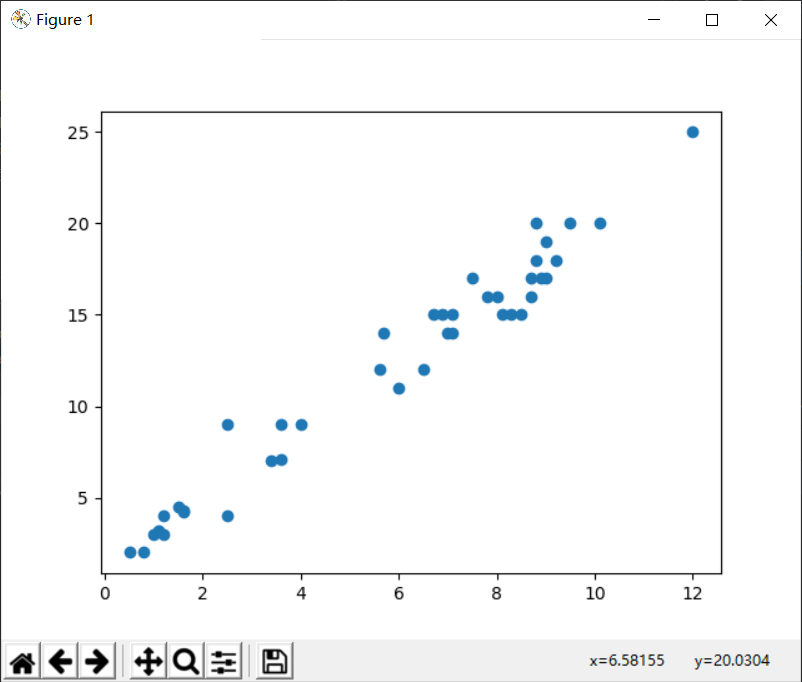
2)构造函数
· 损失函数
# 损失函数是系数的函数,另外还要传入数据的x,y def compute_cost(w, b, points): total_cost = 0 m = float(len(points)) for i in range(len(points)): x = points.iloc[i, 0] y = points.iloc[i, 1] total_cost += (y - w * x - b) ** 2 return total_cost / m # 一除都是浮点
· 优化器——梯度下降
1 def grad_desc(points, initial_w, initial_b, alpha, num_iter): 2 # alpha为学习率,num_iter为迭代次数 3 w = initial_w 4 b = initial_b 5 # 定义一个list保存所有的损失函数值,用来显示下降过程。 6 cost_list = [] 7 for i in range(num_iter): 8 cost_list.append(compute_cost(w, b, points)) 9 w, b = step_grad_desc(w, b, alpha, points) 10 return [w, b, cost_list]
· 参数更新——计算梯度
1 def step_grad_desc(current_w, current_b, alpha, points): 2 sum_grad_w = 0 3 sum_grad_b = 0 4 m = float(len(points)) 5 # 对每个点代入公式求和 6 for i in range(len(points)): 7 x = points.iloc[i, 0] 8 y = points.iloc[i, 1] 9 sum_grad_w += (current_w * x + current_b - y) * x 10 sum_grad_b += current_w * x + current_b - y 11 # 用公式求当前梯度 12 grad_w = 2 / m * sum_grad_w 13 grad_b = 2 / m * sum_grad_b 14 15 # 梯度下降,更新当前的w和b 16 updated_w = current_w - alpha * grad_w 17 updated_b = current_b - alpha * grad_b 18 return updated_w, updated_b
· 初始化数据
1 alpha = 0.0000001 2 initial_w = 0 3 initial_b = 0 4 num_iter = 20
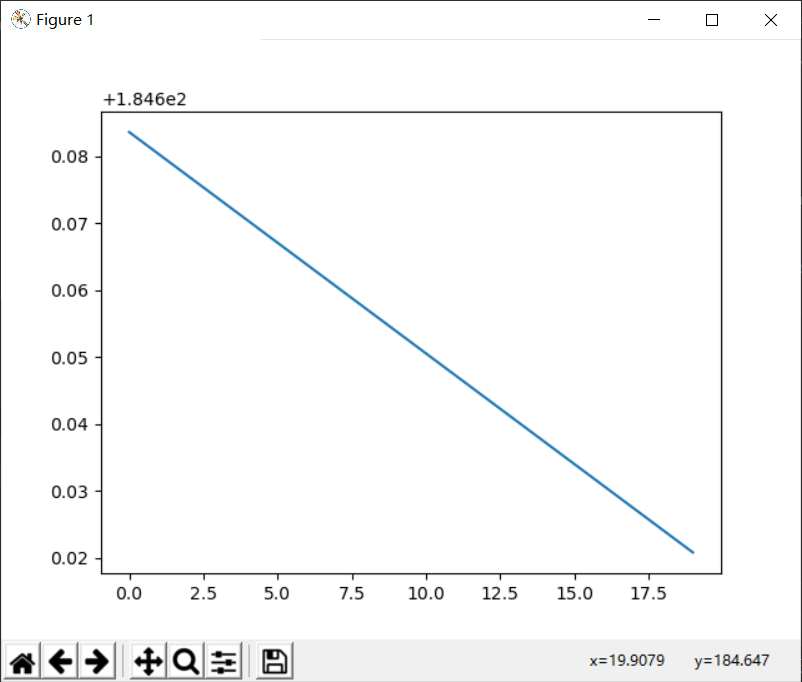
· 调用函数——计算w、b和损失值
1 w, b, cost_list = grad_desc(points, initial_w, initial_b, alpha, num_iter) 2 print("w is :", w) 3 print("b is :", b) 4 5 cost = compute_cost(w, b, points) 6 7 print("cost_list:", cost_list) 8 print("cost is:", cost) 9 pred_y = w * x + b 10 plt.plot(cost_list)

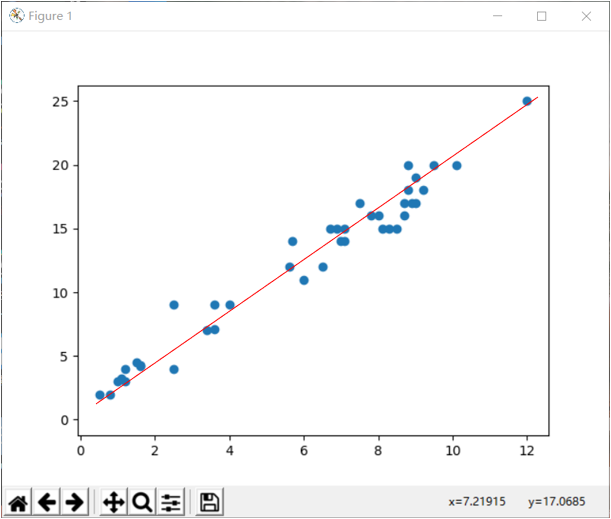
· 可视化——预测值与原始值
1 plt.scatter(x, y) 2 plt.plot(x, pred_y, c='r') 3 plt.show()
3)对比sklearn.LinearRegression
1 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 2 3 model = LinearRegression() 4 model.fit(x, y) 5 pre = model.predict(x) 6 plt.scatter(x, y, c='b') 7 plt.plot(x, pre, c='r') 8 plt.show()