基本类型包装类概述:
在实际程序使用中,程序界面上用户输入的数据都是以字符串类型进行存储的。
而程序开发中,我们需要把字符串数据,根据需求转换成指定的基本数据类型。
想实现字符串与基本数据之间转换,需要使用基本数据类型对象包装类:java将基本数据类型值封装成了对象。
封装成对象有什么好处?可以提供更多的操作基本数值的功能。
8种基本类型对应的包装类如下:
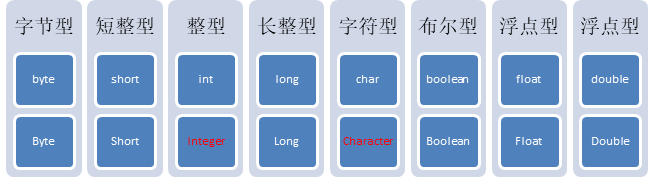
基本数据类型对象包装类特点:用于在基本数据和字符串之间进行转换。
将字符串转成基本类型:

parseXXX(String s);其中XXX表示基本类型,参数为可以转成基本类型的字符串,如果字符串无法转成基本类型,将会发生数字转换的问题 NumberFormatException
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("123") + 2);
//打印结果为 125
l 将基本数值转成字符串有3种方式:
n 基本类型直接与””相连接即可;34+""
n 调用String的valueOf方法;String.valueOf(34) ;

|调用包装类中的toString方法;Integer.toString(34) ;

public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=Integer.parseInt("12");
double b=Double.parseDouble("2.5");
System.out.println(b+1);
//将基本数据类型装转化字符串:
//1.基本类型+””相连接即可;34+""
int c=3;
System.out.println((c+"")+1);
//2.String类型中的valueof方法,调用String的valueOf方法;String.valueOf(34)
int d=7;
System.out.println(String.valueOf(d)+1);
System.out.println(String.valueOf(true)+1);
//3.包装类中的带参的toString(基本类型 变量)
int e=8;
System.out.println(Integer.toString(e)+1);
}
}
基本类型和对象转换:
l 基本数值---->包装对象
方法1:

Integer i = new Integer(4);//使用构造函数函数
Integer ii = new Integer("4");//构造函数中可以传递一个数字字符串
方法2:

Integer iii = Integer.valueOf(4);//使用包装类中的valueOf方法
Integer iiii = Integer.valueOf("4");//使用包装类中的valueOf方法
l 包装对象---->基本数值

int num = i.intValue();
自动装箱拆箱:
l 自动拆箱:对象自动直接转成基本数值
l 自动装箱:基本数值自动直接转成对象
Integer i = 4;//自动装箱。相当于Integer i = Integer.valueOf(4); i = i + 5;//等号右边:将i对象转成基本数值(自动拆箱) i.intValue() + 5; 加法运算完成后,再次装箱,把基本数值转成对象。
l 自动装箱(byte常量池)细节的演示
当数值在byte范围之内时,进行自动装箱,不会新创建对象空间而是使用已有的空间,byte范围内(-128——127)。
Integer a = new Integer(3);
Integer b = new Integer(3);
System.out.println(a==b);//false
System.out.println(a.equals(b));//true
System.out.println("---------------------");
Integer x = 127;
Integer y = 127;
//在jdk1.5自动装箱时,如果数值在byte范围之内,不会新创建对象空间而是使用原来已有的空间。
System.out.println(x==y); //true
System.out.println(x.equals(y)); //true