1、监听
1.1、监听队列
如订单系统和库存系统
订单系统下订单之后将消息存放在消息队列中
库存系统需要时刻进行监听消息队列的内容,有新的订单就需要进行库存相关的操作
此时模拟监听消息队列中的Book信息
编写监听类:
@RabbitListener监听相关的消息队列(这里只是做测试,所以方法里的参数直接写的是Book类型,消息接收后,直接把消息的内容转为了Book类型)
@Service public class BookService { //queues:监听哪些队列 @RabbitListener(queues = {"atguigu.news"}) public void receive(Book book){ System.out.println("atguigu.news队列收到消息"+book); } }
在配置类中开启基于注解的RabbitMQ模式
@EnableRabbit //开启基于注解的RabbitMQ模式 @SpringBootApplication public class Springboot02AmqpApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Springboot02AmqpApplication.class, args); } }
开启服务之后只要atguigu.news队列中有消息,receive方法就会执行
测试:
1、开启服务
2、在测试方法中给atguigu.news队列发送消息
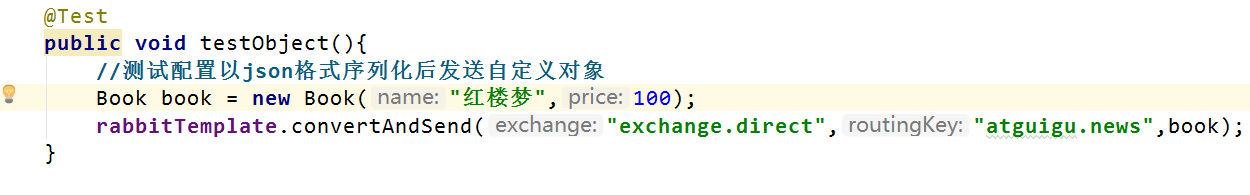
3、运行测试方法,发送消息
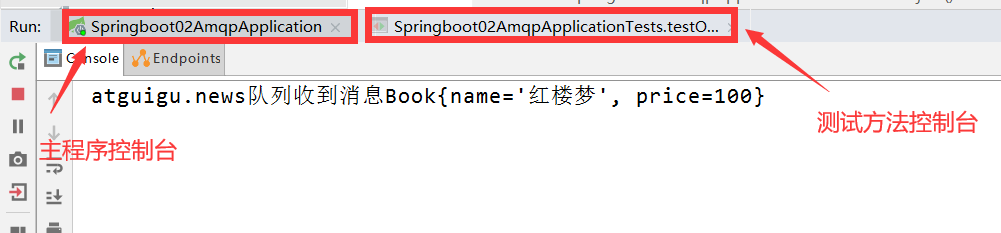
4、在主程序控制台中可以看到receive方法执行了
1.2、监听方法中获取消息头、消息体相关的参数(直接把消息封装成Message对象,注意别导错包)
//import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message; //监听atguigu消息队列,获取消息头和消息体相关参数 @RabbitListener(queues = "atguigu") public void receive02(Message message){ System.out.println(message.getBody()); System.out.println(message.getMessageProperties()); }
消息如下:

监听后的打印信息如下:
![]()
2、AmqpAdmin创建或删除exchange、queue、binding
假设有些信道活着队列不存在的情况
可以使用AmqpAdmin进行创建交换器,转换规则、队列(Queue、Exchange、Binding)

2.1创建exchange
交换器的类型如下

@Autowired AmqpAdmin amqpAdmin; /** * 测试通过amqpAdmin创建exchange */ @Test public void creatExchange(){ //这里以创建direct类型的exchange为例 amqpAdmin.declareExchange(new DirectExchange("amqpadmin.exchange")); System.out.println("创建交换器完成"); }
创建成功

2.2创建queue
/** * 测试通过amqpAdmin创建queue */ @Test public void creatQueue(){ amqpAdmin.declareQueue(new Queue("amqpadmin.queue",true)); System.out.println("创建队列完成"); }
创建成功

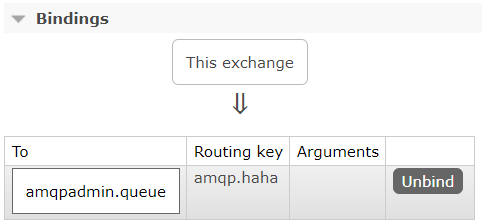
2.3创建binding
/** * 测试通过amqpAdmin创建binding */ @Test public void creatBinding(){ /** *创建Binding的参数解释: * 1、目的队列名称 * 2、绑定的类型 * 3、exchange的名称 * 4、绑定的路由键 * 5、一个map,需要是传必要的参数,不需要是写null就行 */ amqpAdmin.declareBinding(new Binding("amqpadmin.queue",Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,"amqpadmin.exchange","amqp.haha",null)); System.out.println("创建绑定规则完成"); }
绑定成功