Hibernate相关概念
一、事物概念
Hibernate的任何对数据有改动的操作,都应该被放在事务里面。
hibernate中的事务由s.beginTransaction();开始由s.getTransaction().commit();结束
本例子,执行了两个操作
第一个,删除id=1的产品,这个是会成功的
第二个,修改id=2的产品,使得其产品名称超过了数据库中设置的长度30,这个是会失败的。
因为这两个操作都是在一个事务中,而且第二个操作失败了,所以最后的结果是两个操作都没有生效
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import org.hibernate.Session; 4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 5 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 6 7 import hibernate.pojo.Product; 8 9 public class testTransaction { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 14 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 15 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 16 session.beginTransaction(); 17 18 Product product = (Product) session.get(Product.class, 1); 19 session.delete(product); 20 21 Product product2 = (Product) session.get(Product.class, 2); 22 product2.setName("iphoneiphoneiphoneiphoneiphoneiphoneiphoneiphoneiphone"); 23 session.update(product2); 24 25 session.getTransaction().commit(); 26 session.close(); 27 sFactory.close(); 28 } 29 30 }
二、属性延迟加载
属性的延迟加载: 当使用load的方式来获取对象的时候,只有访问了这个对象的属性,hibernate才会到数据库中进行查询,否则不会访问数据库。
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import org.hibernate.Session; 4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 5 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 6 7 import hibernate.pojo.Product; 8 9 public class testDelayProperty { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 14 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 15 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 16 session.beginTransaction(); 17 18 Product product = (Product) session.load(Product.class, 1); 19 System.out.println("log1"); 20 System.out.println(product.getName()); 21 System.out.println("log2"); 22 23 session.getTransaction().commit(); 24 session.close(); 25 sFactory.close(); 26 } 27 28 }
三、关系延迟加载
延迟加载又叫lazyload,在one-many many-many的时候都可以使用关系的延迟加载。
<set name="products" lazy="false">改为<set name="products" lazy="true">表示通过Category获取产品是延迟加载的。
1 <?xml version="1.0"?> 2 <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC 3 "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" 4 "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> 5 6 <hibernate-mapping package="hibernate.pojo"> 7 <class name="Category" table="category"> 8 <id name="id" column="id"> 9 <generator class="native"> 10 </generator> 11 </id> 12 <property name="name" /> 13 14 <set name="products" lazy="true"> 15 <key column="cid" not-null="false" /> 16 <one-to-many class="Product" /> 17 </set> 18 </class> 19 </hibernate-mapping>
测试:
执行22行的时候,只会查询Category表的信息,不会查询product表。只有在执行24行,通过category取products的时候,才会进行对product表的查询。
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 6 import org.hibernate.Session; 7 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 8 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 9 10 import hibernate.pojo.Category; 11 import hibernate.pojo.Product; 12 13 public class testDelayRelation { 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 17 18 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 19 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 20 session.beginTransaction(); 21 22 Category category = (Category) session.get(Category.class, 4); 23 System.out.println("log1"); 24 Set<Product> products = category.getProducts(); 25 Iterator<Product> iterator = products.iterator(); 26 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 27 System.out.println(iterator.next().getName()); 28 29 } 30 System.out.println("log2"); 31 32 session.getTransaction().commit(); 33 session.close(); 34 sFactory.close(); 35 } 36 37 }
四、级联
什么是级联? 简单的说,就是没有配置级联的时候,删除分类,其对应的产品不会被删除。 但是如果配置了恰当的级联,那么删除分类的时候,其对应的产品都会被删除掉。
级联有4种类型:
all:所有操作都执行级联操作;
none:所有操作都不执行级联操作;
delete:删除时执行级联操作;
save-update:保存和更新时执行级联操作;
级联通常用在one-many和many-to-many上,几乎不用在many-one上。
1.delete级联
在Category.hbm.xml 加上 <set name="products" cascade="delete" lazy="false">
在删除分类的时候,会把分类下对应的产品都删除掉,否则只会把产品对应的cid设置为空。
2.save-update级联
运行代码就会发现,这3个瞬时状态的产品对象虽然没有添加到数据库里,但是在事务提交的时候,会把他们3个持久化。 如果没有cascade="save-update",就会报错。
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import org.hibernate.Session; 4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 5 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 6 7 import hibernate.pojo.Category; 8 import hibernate.pojo.Product; 9 10 public class testCascadeSaveUpdate { 11 /* 12 * 级联有4种类型: all:所有操作都执行级联操作; none:所有操作都不执行级联操作; delete:删除时执行级联操作; 13 * save-update:保存和更新时执行级联操作; 14 */ 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 17 18 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 19 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 20 session.beginTransaction(); 21 22 Category category = (Category) session.get(Category.class, 5); 23 Product product = new Product(); 24 product.setName("xiaomi_note"); 25 Product product2 = new Product(); 26 product2.setName("xiaomi_max"); 27 Product product3 = new Product(); 28 product3.setName("xiaomi_8"); 29 30 category.getProducts().add(product); 31 category.getProducts().add(product2); 32 category.getProducts().add(product3); 33 34 session.getTransaction().commit(); 35 session.close(); 36 sFactory.close(); 37 } 38 39 }
五、一级缓存
hibernate默认是开启一级缓存的,一级缓存存放在session上。
例子:
第一次通过id=1获取对象的时候,session中是没有对应缓存对象的,所以会在"log1"后出现sql查询语句。
第二次通过id=1获取对象的时候,session中有对应的缓存对象,所以在"log2"后不会出现sql查询语句。
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import org.hibernate.Session; 4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 5 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 6 7 import hibernate.pojo.Category; 8 9 public class testCacheL1 { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 14 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 15 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 16 session.beginTransaction(); 17 18 System.out.println("log1"); 19 Category category = (Category) session.get(Category.class, 1); 20 System.out.println("log2"); 21 Category category2 = (Category) session.get(Category.class, 1); 22 System.out.println("log3"); 23 24 session.getTransaction().commit(); 25 session.close(); 26 sFactory.close(); 27 } 28 29 }
六、二级缓存
Hibernate的一级缓存是在Session上,二级缓存是在SessionFactory上。
创建了两个Session:
在第一个Session里
第一次获取id=1的Category 会执行SQL语句
第二次获取id=1的Category,不会执行SQL语句,因为有一级缓存
在第二个Session里
获取id=1的Category,如果没有设置二级缓存时,会执行SQL语句,因为在第二个Session,没有缓存该对象。 所以总共会看到两条SQL语句。
如果设置了二级缓存就使用不同的session,都去获取id=1的category,只会访问一次数据库。因为第二次获取虽然没有从第二个session中拿到缓存,但是从sessionfactory中拿到了Category缓存对象。
1.在hibernate.cfg.xml 中增加对二级缓存的配置
1 <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> 2 <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC 3 "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" 4 "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> 5 6 <hibernate-configuration> 7 8 <session-factory> 9 <!-- Database connection settings --> 10 <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> 11 <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tests?characterEncoding=UTF-8</property> 12 <property name="connection.username">root</property> 13 <property name="connection.password">123456</property> 14 <!-- SQL dialect --> 15 <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> 16 <property name="current_session_context_class">thread</property> 17 <property name="show_sql">true</property> 18 <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> 19 <property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property> 20 <property name="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider</property> 21 <mapping resource="hibernate/pojo/Product.hbm.xml" /> 22 <mapping resource="hibernate/pojo/Category.hbm.xml" /> 23 <mapping resource="hibernate/pojo/User.hbm.xml" /> 24 </session-factory> 25 26 </hibernate-configuration>
2.在src目录下,创建一个ehcache.xml用于EHCache的缓存配置。
1 <ehcache> 2 <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> 3 <defaultCache 4 maxElementsInMemory="10000" 5 eternal="false" 6 timeToIdleSeconds="120" 7 timeToLiveSeconds="120" 8 overflowToDisk="true" 9 /> 10 </ehcache>
3.对于要进行二级缓存的实体类,进行配置,增加<cache usage="read-only" />
4.测试
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import org.hibernate.Session; 4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 5 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 6 7 import hibernate.pojo.Category; 8 9 public class testCacheL2 { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 14 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 15 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 16 session.beginTransaction(); 17 18 Category category = (Category) session.get(Category.class, 1); 19 System.out.println("log1"); 20 Category category2 = (Category) session.get(Category.class, 1); 21 System.out.println("log2"); 22 session.getTransaction().commit(); 23 session.close(); 24 25 Session session2 = sFactory.openSession(); 26 session2.beginTransaction(); 27 Category category3 = (Category) session2.get(Category.class, 1); 28 System.out.println("log3"); 29 30 session2.getTransaction().commit(); 31 session2.close(); 32 33 sFactory.close(); 34 } 35 36 }
七、分页
使用Criteria进行分页查询Hibernate使用Criteria 来进行分页查询c.setFirstResult(2); 表示从第2条数据开始c.setMaxResults(5); 表示一共查询5条数据
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import java.util.List; 4 5 import org.hibernate.Criteria; 6 import org.hibernate.Session; 7 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 8 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 9 import org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions; 10 11 import hibernate.pojo.Product; 12 13 public class testPaging { 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 17 18 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 19 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 20 session.beginTransaction(); 21 22 String name = "iphone"; 23 24 Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Product.class); 25 criteria.add(Restrictions.like("name", "%" + name + "%")); 26 criteria.setFirstResult(2); 27 criteria.setMaxResults(5); 28 29 List<Product> products = criteria.list(); 30 for (Product p : products) { 31 System.out.println(p.getName()); 32 } 33 34 session.getTransaction().commit(); 35 session.close(); 36 sFactory.close(); 37 } 38 39 }
八、两种获取方式
Hibernate中根据Id单条查询获取对象的方式有两种,分别是get()和load(),来看一下这两种方式的区别。
1.当get()方法被调用的时候就会立即发出SQL语句。
2.当调用load()方法的时候会返回一个目标对象的代理对象,在这个代理对象中只存储了目标对象的ID值,只有当调用除ID值以外的属性值的时候才会发出SQL查询的。
3.Exception
<1>当使用get获取数据库中不存在的数据时会抛出空指针异常NullPointerException
<2>当使用load获取数据库中不存在的数据时会发生一个ObjectNotFoundException异常。
这个是因为使用load()的时候返回的是一个代理对象,因为这个时候还没有进行查询,所以我们并没有办法确定要查询的对象到底存在不存在,所以使用load()查询的返回值是永远不会为空的,但是呢,当我们试图访问被代理的真实对象的时候,因为这个对象并不存在,所以就抛出了一个ObjectNotFoundException。
还有一种说法是get()是用于不确定对象是否真的存在的情况,所以在查询出来后可以先进行一个空指针判断,而load()方法用于对象一定存在的情况下,不然等会儿使用的时候就可能会抛出ObjectNotFoundException了。
4.缓存
get()和load()都会使用缓存,都是首先从一级缓存Session中查找,当找不到的时候再去二级缓存中查找,当查询不到的时候get()返回的是null,而load()则返回代理对象。
如果使用这两种方式访问同一个id数据,会发现两个返回的都是真实对象,连load()返回的也是真实对象,并且它们引用的还是同一块对象。这个是因为get()查询出来的对象后会将其放入到缓存中,而load()再去查询的时候它会先去缓存中查找,如果缓存中没有的话才会返回代理对象,但是当缓存中已经存在的话就直接将真实对象返回来了。
5.小结
返回值:
get()返回的是查询出来的实体对象,而load()查询出来的是一个目标实体的代理对象。
查询时机:
get()在调用的时候就立即发出SQL语句查询,而load()在访问非ID属性的时候才会发出查询语句并且将被代理对象target填充上,但是如果这个动作发生在Session被关闭后的话就会抛出LazyInitializationException。
查询结果为空时:
get()抛出NullPointerException
load()抛出ObjectNotFoundException
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import org.hibernate.Session; 4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 5 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 6 7 import hibernate.pojo.Product; 8 9 public class testLoadAndGet { 10 11 /* 12 * load方式是延迟加载,只有属性被访问的时候才会调用sql语句 ;get方式是非延迟加载,无论后面的代码是否会访问到属性,马上执行sql语句 13 */ 14 @SuppressWarnings("unused") 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 17 18 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 19 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 20 session.beginTransaction(); 21 System.out.println("log1"); 22 Product product = (Product) session.get(Product.class, 1); 23 System.out.println("log2"); 24 Product product2 = (Product) session.load(Product.class, 2); 25 // Product product2 = (Product) session.load(Product.class, 200); 26 System.out.println("log3"); 27 // System.out.println(product2.getName()); 28 System.out.println("log4"); 29 30 // Product p3 = (Product) session.get(Product.class, 500); 31 // System.out.println("p3=" + p3.getName()); 32 33 // Product p4 = (Product) session.load(Product.class, 500); 34 // System.out.println("p4=" + p4.getName()); 35 36 Product product3 = (Product) session.load(Product.class, 5); 37 System.out.println(product3.getName()); 38 Product product4 = (Product) session.load(Product.class, 5); 39 System.out.println(product4.getName()); 40 session.getTransaction().commit(); 41 session.close(); 42 System.out.println(product.getName()); 43 sFactory.close(); 44 } 45 46 }
九、两种Session方式
Hibernate有两种方式获得session,分别是:openSession和getCurrentSession
区别在于
1. 获取的是否是同一个session对象
openSession每次都会得到一个新的Session对象
getCurrentSession在同一个线程中,每次都是获取相同的Session对象,但是在不同的线程中获取的是不同的Session对象
2. 事务提交的必要性
openSession只有在增加,删除,修改的时候需要事务,查询时不需要的
getCurrentSession是所有操作都必须放在事务中进行,并且提交事务后,session就自动关闭,不能够再进行关闭
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import org.hibernate.Session; 4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 5 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 6 7 import hibernate.pojo.Product; 8 9 public class testSession { 10 11 static Session session; 12 static Session session2; 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 15 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 16 17 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 18 // Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 19 // Session session2 = sFactory.openSession(); 20 21 // Session session = sFactory.getCurrentSession(); 22 // Session session2 = sFactory.getCurrentSession(); 23 // 24 // System.out.println(session == session2); 25 26 // session.close(); 27 // session2.close(); 28 29 Thread thread = new Thread() { 30 public void run() { 31 session = sFactory.getCurrentSession(); 32 } 33 }; 34 thread.start(); 35 36 Thread thread2 = new Thread() { 37 public void run() { 38 session2 = sFactory.getCurrentSession(); 39 } 40 }; 41 thread2.start(); 42 43 thread.join(); 44 thread2.join(); 45 46 System.out.println(session == session2); 47 48 Session session3 = sFactory.openSession(); 49 System.out.println(((Product) session3.get(Product.class, 2)).getName()); 50 51 // Session session4 = sFactory.getCurrentSession(); 52 // session4.get(Product.class, 2); 53 54 session.close(); 55 session2.close(); 56 57 Session session5 = sFactory.getCurrentSession(); 58 session5.beginTransaction(); 59 session5.get(Product.class, 3); 60 session5.getTransaction().commit(); 61 // session5.close(); 62 63 sFactory.close(); 64 } 65 66 }
十、N+1
Hibernate有缓存机制,可以通过用id作为key把product对象保存在缓存中 同时hibernate也提供Query的查询方式。假设数据库中有100条记录,其中有30条记录在缓存中,但是使用Query的list方法,就会所有的100条数据都从数据库中查询,而无视这30条缓存中的记录。 N+1是什么意思呢,首先执行一条sql语句,去查询这100条记录,但是,只返回这100条记录的ID 然后再根据id,进行进一步查询。如果id在缓存中,就从缓存中获取product对象了,否则再从数据库中获取。
Hibernate使用Iterator实现N+1。
首先通过Query的iterator把所有满足条件的Product的id查出来然后再通过it.next()查询每一个对象如果这个对象在缓存中,就直接从缓存中取了否则就从数据库中获取N+1中的1,就是指只返回id的SQL语句,N指的是如果在缓存中找不到对应的数据,就到数据库中去查。
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 5 import org.hibernate.Query; 6 import org.hibernate.Session; 7 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 8 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 9 10 import hibernate.pojo.Product; 11 12 public class testN1 { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 16 17 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 18 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 19 session.beginTransaction(); 20 21 String name = "iphone"; 22 Query query = session.createQuery("from Product p where p.name like ?"); 23 query.setString(0, "%" + name + "%"); 24 25 Iterator<Product> iterator = query.iterate(); 26 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 27 Product product = (Product) iterator.next(); 28 System.out.println(product.getName()); 29 30 } 31 32 Query query2 = session.createQuery("select count(*) from Product p where p.name like ?"); 33 query2.setString(0, "%" + name + "%"); 34 35 long total = (Long) query2.uniqueResult(); 36 System.out.println(total); 37 38 session.getTransaction().commit(); 39 session.close(); 40 sFactory.close(); 41 } 42 43 }
十一、乐观锁
乐观锁(Optimistic Lock), 顾名思义,就是很乐观,每次去拿数据的时候都认为别人不会修改,所以不会上锁,但是在更新的时候会判断一下在此期间别人有没有去更新这个数据。
1.场景描述:
<1>. 通过session1得到id=1的对象 product1
<2>. 在product1原来价格的基础上增加1000
<3>. 更新product1之前,通过session2得到id=1的对象product2
<4>. 在product2原来价格的基础上增加1000
<5>. 更新product1
<6>. 更新product2
最后结果是product的价格只增加了1000,而不是2000
代码:
1 package hibernate.test; 2 3 import org.hibernate.Session; 4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 5 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 6 7 import hibernate.pojo.Product; 8 9 public class testOptimisticLock { 10 /* 11 * 场景描述 1. 通过session1得到id=1的对象 product1 2. 在product1原来价格的基础上增加1000 12 * 3.更新product1之前,通过session2得到id=1的对象product2 4. 在product2原来价格的基础上增加1000 13 * 5.更新product1 6. 更新product2 14 */ 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 17 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 18 19 SessionFactory sFactory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); 20 Session session = sFactory.openSession(); 21 Session session2 = sFactory.openSession(); 22 23 session.beginTransaction(); 24 session2.beginTransaction(); 25 26 Product product = (Product) session.get(Product.class, 1); 27 System.out.println("产品原价为:" + product.getPrice()); 28 product.setPrice(product.getPrice() + 1000); 29 30 Product product2 = (Product) session2.get(Product.class, 1); 31 product2.setPrice(product2.getPrice() + 1000); 32 33 session.update(product); 34 session2.update(product2); 35 36 session.getTransaction().commit(); 37 session2.getTransaction().commit(); 38 39 Product product3 = (Product) session.get(Product.class, 1); 40 System.out.println("最终的价格:" + product3.getPrice()); 41 42 session.close(); 43 session2.close(); 44 sFactory.close(); 45 } 46 47 }
2.修改配置文件 Product.hbm.xml
<version name="version" column="ver" type="int"></version>增加一个version字段,用于版本信息控制。这就是乐观锁的核心机制。
比如session1获取product1的时候,version=1。 那么session1更新product1的时候,就需要确保version还是1才可以进行更新,并且更新结束后,把version改为2。
注意: version元素必须紧跟着id后面,否则会出错。
1 <?xml version="1.0"?> 2 <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC 3 "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" 4 "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> 5 6 <hibernate-mapping package="hibernate.pojo"> 7 <class name="Product" table="product"> 8 <id name="id" column="id"> 9 <generator class="native"> 10 </generator> 11 </id> 12 <!--version元素必须紧挨着id后面 --> 13 <version name="version" column="ver" type="int"></version> 14 <property name="name" /> 15 <property name="price" /> 16 <many-to-one name="category" class="Category" column="cid"></many-to-one> 17 <set name="users" table="user_product" lazy="false" > 18 <key column="pid"></key> 19 <many-to-many column="uid" class="User"></many-to-many> 20 </set> 21 </class> 22 23 </hibernate-mapping>
3.修改 Product.java
增加version属性
1 package hibernate.pojo; 2 3 import java.util.Set; 4 5 public class Product { 6 int id; 7 String name; 8 float price; 9 Category category; 10 Set<User> users; 11 int version; 12 int cid; 13 14 public int getId() { 15 return id; 16 } 17 18 public void setId(int id) { 19 this.id = id; 20 } 21 22 public String getName() { 23 return name; 24 } 25 26 public void setName(String name) { 27 this.name = name; 28 } 29 30 public float getPrice() { 31 return price; 32 } 33 34 public void setPrice(float price) { 35 this.price = price; 36 } 37 38 public Category getCategory() { 39 return category; 40 } 41 42 public void setCategory(Category category) { 43 this.category = category; 44 } 45 46 public Set<User> getUsers() { 47 return users; 48 } 49 50 public void setUsers(Set<User> users) { 51 this.users = users; 52 } 53 54 public int getCid() { 55 return cid; 56 } 57 58 public void setCid(int cid) { 59 this.cid = cid; 60 } 61 62 public int getVersion() { 63 return version; 64 } 65 66 public void setVersion(int version) { 67 this.version = version; 68 } 69 70 }
4.再次运行代码
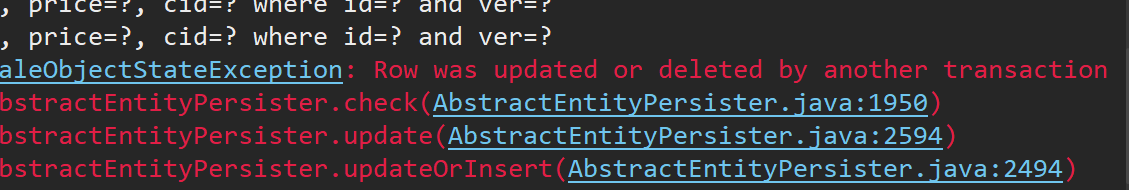
5.原理
<1>. 假设数据库中产品的价格是10000,version是10
<2>. session1,session2分别获取了该对象
<3>. 都修改了对象的价格
<4>. session1试图保存到数据库,检测version依旧=10,成功保存,并把version修改为11
<5>. session2试图保存到数据库,检测version=11,说明该数据已经被其他人动过了。 保存失败,抛出异常
