Consider all the leaves of a binary tree. From left to right order, the values of those leaves form a leaf value sequence.
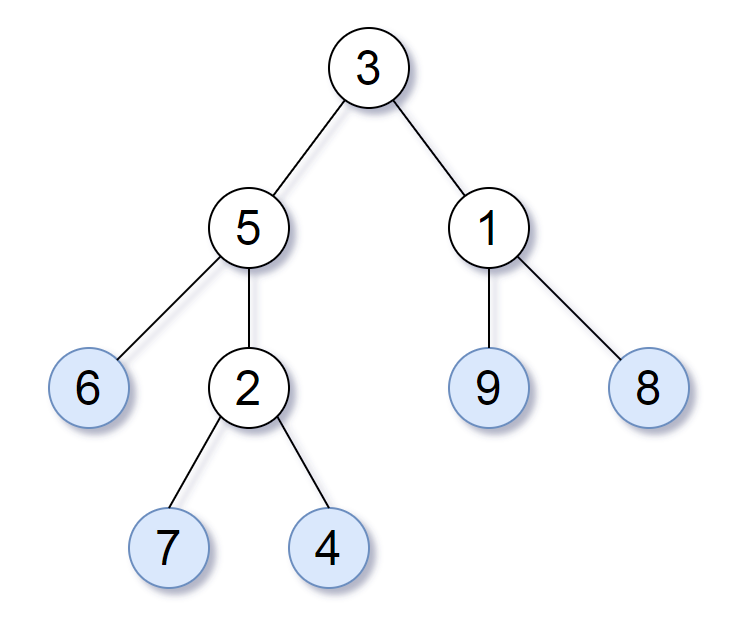
For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is (6, 7, 4, 9, 8).
Two binary trees are considered leaf-similar if their leaf value sequence is the same.
Return true if and only if the two given trees with head nodes root1 and root2 are leaf-similar.
Note:
- Both of the given trees will have between
1and100nodes.
The straightforward solution is to use DFS to get both the leaf sequence first then compare them. An even better solution is to compare one leaf node at a time, providing the possiblity of early traverse termination. To return leaf node value one at a time and keep track unvisited leaf nodes, we use a stack. Since stack is LIFO and we need to visit left leaf nodes first, we push a node's right child into the stack first, then left child.
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { Stack<TreeNode> s1 = new Stack<>(); Stack<TreeNode> s2 = new Stack<>(); s1.push(root1); s2.push(root2); while(!s1.isEmpty() && !s2.isEmpty()) { if(dfs(s1) != dfs(s2)) { return false; } } return s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty(); } private int dfs(Stack<TreeNode> stack) { while(true) { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if(node.right != null) stack.push(node.right); if(node.left != null) stack.push(node.left); if(node.left == null && node.right == null) return node.val; } } }
Related Topics
How to traverse a binary tree in pre-order, in-order and post-order iteratively?(not using recursion)