Given the array houses and an integer k. where houses[i] is the location of the ith house along a street, your task is to allocate k mailboxes in the street.
Return the minimum total distance between each house and its nearest mailbox.
The answer is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
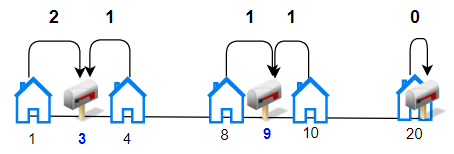
Input: houses = [1,4,8,10,20], k = 3
Output: 5
Explanation: Allocate mailboxes in position 3, 9 and 20.
Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is |3-1| + |4-3| + |9-8| + |10-9| + |20-20| = 5
Example 2:
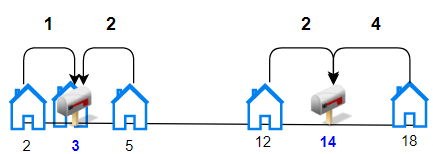
Input: houses = [2,3,5,12,18], k = 2
Output: 9
Explanation: Allocate mailboxes in position 3 and 14.
Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is |2-3| + |3-3| + |5-3| + |12-14| + |18-14| = 9.
Example 3:
Input: houses = [7,4,6,1], k = 1
Output: 8
Example 4:
Input: houses = [3,6,14,10], k = 4
Output: 0
Constraints:
n == houses.length1 <= n <= 1001 <= houses[i] <= 10^41 <= k <= n- Array
housescontain unique integers.
Given the input constraint, we know that any solution with runtime O(N^3) or better is efficient enough. There are at most N mailboxes as there is no point of having more mailboxes than the total number of houses. (Assigning one different mailbox to each house already gives a total cost of 0). So we should try to compute the result of all houses with fewer available mailboxes first, then try to add 1 more mailbox at a time to get closer to the final result.
Let's start with solving this using recursion. To solve f(N, k), we need to solve the following and pick the minimum:
f(N - 1, k - 1) + min cost of serving kth mailbox to the last house;
f(N - 2, k - 1) + min cost of serving kth mailbox to the last 2 houses;
f(N - 3, k - 1) + min cost of serving kth mailbox to the last 3 houses;
..........
f(k - 1, k - 1) + min cost of serving kth mailbox to the last N - k + 1 houses; we need at least k - 1 houses to use k - 1 mailboxes.
Similarly, to solve f(N - 1, k - 1), we first need to solve f(N - 2, k - 2), f(N - 3, k - 2)........; to solve f(N - 2, k - 1), we first need to solve f(N - 3, k -2).......
We see the overlapping subproblems! This is a hint for a dynamic programming solution.
State: dp[i][j]: the min total distance of houses[0, i] with j mailboxes serving to them.
Optimal substructure: dp[i][j] = Min of {dp[i'][j - 1] + min total distance of houses[i' + 1, i] with 1 mailbox serving to them}, for all i' in [j - 2, i). We need to have at least j - 1 houses to use j - 1 mailboxes, so the starting index for i' is j - 2 (0 index).
Initialization: if there is only 1 mailbox, we achieve the min total distance by putting this mailbox in the median house position of its serving range. To speed up this computation, we first sort all houses' positions then build a prefix sum array. This allows us to compute the cost of 1 mailbox serving to a range house[i, j] in O(1) time.
The runtime is O(N^3), space complexity is O(N^2). To compute dp[i][j], we only need the results of dp[*][j - 1], this means we can reduce the space from O(N^2) to O(N).
class Solution { public int minDistance(int[] houses, int k) { int n = houses.length; Arrays.sort(houses); int[][] dp = new int[n][k + 1]; for(int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) { Arrays.fill(dp[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE); } int[] ps = new int[n]; ps[0] = houses[0]; for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) { ps[i] = ps[i - 1] + houses[i]; } for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(i % 2 == 0) { dp[i][1] = ps[i] - (i > 0 ? ps[i / 2 - 1] : 0) - ps[i / 2]; } else { dp[i][1] = ps[i] - ps[i / 2] - ps[i / 2]; } } for(int j = 2; j <= k; j++) { for(int i = j - 1; i < n; i++) { for(int t = j - 2; t < i; t++) { if((i - t) % 2 == 0) { dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[t][j - 1] + ps[i] - ps[t + (i - t) / 2] - ps[t + (i - t) / 2] + ps[t]); } else { dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[t][j - 1] + ps[i] - ps[t + (i - t) / 2 + 1] - ps[t + (i - t) / 2] + ps[t]); } } } } return dp[n - 1][k]; } }