集合框架
-
啥是集合?集合框架有什么特点
所谓集合,就是把若干个对象放到一起的容器。 -
当我们讨论集合框架的特点时,首先我们来想一想数组的特点:
- No.1,数组中存的都是相同类型的数据;
- No.2,数组的长度,一旦定义好了之后长度无法改变;
- No.3,数组是有序的,使用下标来取值
-
根据数组的特点,我们对比集合框架的特点:
- 1.不限长度;
- 2.不限类型;
-
在系统层面,集合框架包含以下内容:
- 1.接口
- 2.(接口的)实现类
- 3.算法(搜索,排序)
Collection (接口)
注:collection接口中没有获取元素的操作。
当创建对象后——
Collection collection = new ArrayList(); //ArrayList是升级版数组
1.collection.add(); //添加
ex:collection.add("张三"); //添加“张三”
collection.add(22); //添加“22”
collection.add("刘子博"); //添加“刘子博”
System.out.println(collection);
输出: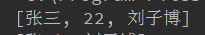
2.collection.remove(); //移除
ex:collection.remove(22); //移除22
System.out.println(collection);
输出: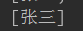
注:当collection.remove();括号中的参数是对象时,移除第一个与参数相等的
ex:Student student = new Student(); //自己新建学生类(已省略),创建对象1,属性有姓名和年龄
student.setName("王六"); //给对象1赋值
student.setAge(20);
Student student1 = new Student(); //创建对象2
student1.setName("王五"); //给对象2赋值
student1.setAge(14);
collection.add(student); //add对象1
collection.add(student1); //add两次对象2作为测试
collection.add(student1);
System.out.println(collection);
collection.remove(student1);
System.out.println(collection);
输出:
3.collection.size(); //计算长度
ex:System.out.println(collection.size()); //因为上个操作将“22”移除,所以此时只有两个数据
输出:
4.collection.contains(); //看括号中的参数是否在集合中存在,返回布尔值
//即看集合中是否包含某个元素
ex:System.out.println(collection.contains("张三"));
输出:
5.collection.isEmpty(); //判断集合是否为空,返回布尔值
ex:System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
输出: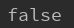
6.collection.addAll(); //把另一个集合中所有的元素加入自己这里
ex:Collection newC = new ArrayList(); //新建一个对象并赋值
newC.add("李四");
newC.add(100);
collection.addAll(newC);
System.out.println(collection);
输出: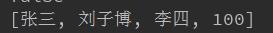
7.collection.removeAll(); //移除和参数给定数组中一样的元素
ex:collection.removeAll(newC);
8.collection.clear(); //清除集合中所有元素
ex:collection.clear();
System.out.println(collection);
输出:
下面我们了解关于Collection的子接口(Map不是子接口)
List
当创建对象后——
List list = new ArrayList();
1.list.add(); //在某个位置加入新元素 格式(下标,要加的东西)
ex:list.add("赵六");
list.add("王八");
list.add("钱七");
System.out.println(list);
list.add(1,"周九"); //在1号位置添加“周九”
System.out.println(list);
输出: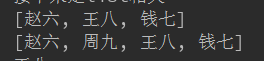
2.list.get(); //按下标有序取值 括号中填下标
ex:System.out.println(list.get(2)); //取2号下标的数据
输出: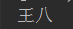
3.list.set(); //按下标修改 括号中填下标
ex:list.set(2,"王久"); //将2号下标数据更改为“王久”
System.out.println(list);
输出: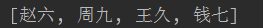
4.list.remove(); //按下标删除 括号中填下标
ex:list.remove(2);
System.out.println(list);
输出: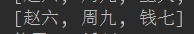
5.三种方法遍历list
(1)使用for循环——有下标的传统遍历
ex:for (int i = 0;i < list.size();i++){
System.out.println("下标为" + i + "的元素是" + list.get(i));
}
输出:
(2)使用foreach方法——只想遍历元素不关心下标(快捷键list.for回车)
注:此处Object o = list.get(i)
ex:for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
输出:
(3)使用迭代器——1.使用集合对象创建迭代器,迭代器不关心顺序
2.如果需要在遍历过程中对list的元素个数进行修改,只能使用迭代器
ex:Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Object o = iterator.next();
System.out.println(o);
}
输出: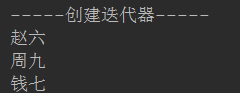
Set
set的特点:1.无序
2.元素不能重复
所以,set接口经常用于去重
当创建对象后——
Set set = new HashSet();
1.set.add();
ex:set.add("张三");
set.add("张三");
set.add("张三");
set.add("李四");
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println(set.size());
输出: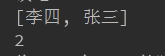
练习:将1000个0-29的随机数添加到set中
解答:System.out.println("将1000个0-29的随机数添加到set中");
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
int a = random.nextInt(30);
set.add(a);
}
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println(set.size());
输出:
2.遍历set
(1)用foreach遍历set
ex:System.out.println("用foreach遍历set");
for (Object o : set) {
System.out.println(o);
}
输出: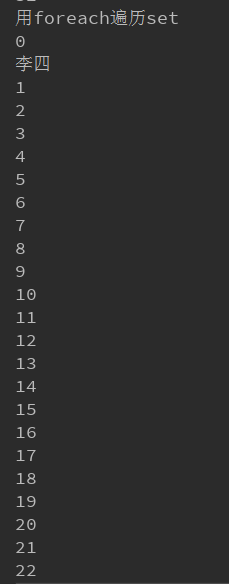
图太长了就截一半了
(2)用迭代器遍历set
ex:System.out.println("用迭代器遍历set");
Iterator iterator1 = set.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()){
Object o = iterator1.next();
System.out.println(o);
}
输出: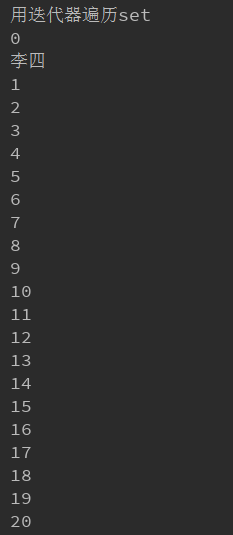
图太长了就截一半了
Map
Map的特点:
1.Map是 用来储存“键值对(key - value)”的集合。
2.存储数据无序。
3.每个key对应一个value,key不能重复,如果重复后来的值会覆盖之前的值。
4.可以通过key来描述value的作用。
当创建对象后——
Map map = new HashMap();
1.map.put(key,value); //添加数据 修改数据
ex:map.put("name","张三");
map.put("name","李四");
map.put("address","大连");
map.put("age",44);
map.put("hobby","跑步");
**2.map.get(key); //根据key来获取值
注:如果前一个key和后一个key相等,前一个key-value中的value会被覆盖。
ex:System.out.println(map.get("name"));
输出: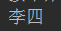
3.map.isEmpty(); //看是否为空,返回布尔值
ex:System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
输出: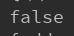
4.map.remove(key); //根据key移除
ex:map.remove("name");
System.out.println(map);
输出:
5.map.containsKey(key);和map.containsValue(value); //判断key或者value是否存在,返回布尔值
ex:System.out.println(map.containsKey("address"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue("张三"));
输出: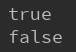
6.map.size(); //获取map的大小
ex:System.out.println(map.size());
输出:
7.map.keySet();和map.values(); //获取所有的key或value
ex:System.out.println(map.keySet()); //key
System.out.println(map.values()); //value
输出: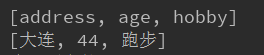
8.遍历map
(1)遍历所有的key和value——相当于遍历所有的key
ex:Set allkeys = map.keySet();
for (Object key : allkeys) {
System.out.println(key + "---" + map.get(key));
}
输出:
(2)遍历所有的value
ex:Collection values = map.values();
for (Object value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
输出:
泛型
- 啥是泛型?
泛型<尖括号里面的东西叫泛型>。 - 泛型有啥用?
有时候在集合中需要限制对象的类型。
新建对象——
List
Student stu = new Student();
stuList.add(stu);
for (Student student2 : stuList) {
System.out.println(student2);
}
//map的泛型
Map<String,Student> map1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<String,List<String>> map2 = new HashMap<>();
代码及工程
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1_M-cp3AgEUfg0XK9mjCmpw
提取码:i8ft