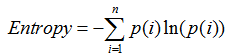一、原理:
决策树:能够利用一些决策结点,使数据根据决策属性进行路径选择,达到分类的目的。
一般决策树常用于DFS配合剪枝,被用于处理一些单一算法问题,但也能进行分类 。
也就是通过每一个结点的决策进行分类,那么关于如何设置这些结点的决策方式:
熵:描述一个集合内元素混乱程度的因素。
熵的衡量公式:
公式中的熵值 Entropy 会随着集合中类别数量增加而快速增加,也就是说一个集合中类别越少,那么它的熵就小,整体就越稳定。
对于一个标记数据集,要合理的建立一棵决策树,就需要合理的决定决策结点来使决策树尽快的降低熵值。
如何选择合适的决策:
(1)信息增溢
对于当前的集合,对每一个决策属性都尝试设置为决策结点的目标,计算决策分类前的熵值 与 分类后的所有子集的熵值 的差。选择最大的,作为当前的决策目标。
此方式有一些确定,就是当面对一些决策变量的分类子集很多,而子集却很小的情况。这次办法虽然会很快的降低熵,但这并不是我们想要的。
(2)信息增溢率
这是对熵增溢的一种改进,把原本的前后熵值的差,增加:
决策分类前属性的熵和 与 决策分类后的的熵 的比值,如果比值很小,说明分类分很多,损失值就会很大。
(3)gini系数:
gini系数和信息增溢率比较像
决策树的剪枝 :
预剪枝:设置max_depth来达到建树过程中的剪枝,表示树的最大深度
后剪枝:通过min_sample_split与min_sample_leaf来对已经建成的决策树进行剪枝,分别是结点的元素个数与子树的叶子结点个数
随机森林 :
构建多个决策树,从而得到更加符合期望的一些决策结果。以森林的结果众数来表示结果。
往往采用生成子数据集,取60%随机生成数据集
交叉验证:
几折交叉验证方式为,将训练数据进行几次对折,取一部分作为测试集,其他作为训练集。并将每个部分轮流作为测试集,最后得到一个平均评分。
网格超参数调优:
对分类器的参数进行调优评价,最后得到一个最优的参数组,并作为最终的分类器的参数。
二、实现 :
数据集:威斯康辛州乳腺癌数据集
数据标签分布较为均衡
'''交叉验证''' ''' sklearn.model_selection.cross_val_score(estimator, X,yscoring=None, cv=None, n_jobs=1,verbose=0,fit_params=None,pre_dispatch='2*n_jobs') estimator:估计方法对象(分类器) X:数据特征(Featrues) y:数据标签(Labels) soring:调用方法(包括accuracy和mean_squared_error等等) cv:几折交叉验证(样本等分成几个部分,轮流作为验证集来验证模型) n_jobs:同时工作的cpu个数(-1 代表全部) ''' #两种分类器的比较 #决策树 clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=None,min_samples_split=2,random_state=0) scores = cross_val_score(clf, xtrain, ytrain) print(scores.mean()) #0.932157394843962 #随机森林 clf = RandomForestClassifier() scores = cross_val_score(clf, xtrain, ytrain) print(scores.mean()) #0.9471958389868838
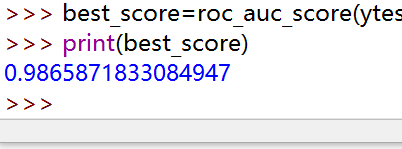
参数调优过程: