使用数据结构 栈(Stack)来实现一种低级的迷宫寻路的功能。
低级是因为无法判断路径是不是最短的。
这里使用的栈结构如图 (这图我选择死亡...)

注意结构体里DataType的实际含义,是另外一个结构体,用于储存二维位置x,y
地图使用一个10x10的二维数组来表示,数字1表示该点是墙壁,0表示可以行走,2表示已经走过的地方。
我们用栈来储存走过的位置,比如我们从起点(4,0)出发,就把(4,0)压入栈,并把该点数值改为2,意为已经来过了。
如果遇到死路,那就不停地出栈,直到栈顶的这个点周围有路可走为止。
逻辑部分伪代码如下
while(没有到达终点)
{
if(上下左右四个方向有路可走)
{
将可以走的那个位置(不是当前位置!)压入栈
}
else
{
出栈
}
}
1 #include <stack> 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 using std::stack; 7 8 const int MAZEWIDTH = 10; 9 const int MAZEHEIGHT = 10; 10 11 //0可走 12 //1墙 13 //2走过 14 //3走过又退回来了 15 int Maze[MAZEWIDTH][MAZEHEIGHT] = { 16 //0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 17 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,//0 18 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,//1 19 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,//2 20 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1,//3 21 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,//4 22 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,//5 23 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1,//6 24 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,//7 25 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,//8 26 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1//9 27 }; 28 29 struct _XY { 30 int x, y; 31 32 _XY() { 33 x = y = 0; 34 } 35 36 _XY(int a, int b) : x(a), y(b) { } 37 38 int operator==(const struct _XY &a) { 39 return (a.x == x) && (a.y == y); 40 } 41 }; 42 43 typedef _XY XY; 44 45 class MazeBreaker { 46 private: 47 int MazeMap[MAZEWIDTH][MAZEHEIGHT]; 48 stack<XY> path; 49 XY start, end; 50 51 52 void push(XY xy) { 53 path.push(xy); 54 MazeMap[xy.x][xy.y] = 2; 55 } 56 57 void push(int x, int y) { 58 path.push(XY(x, y)); 59 MazeMap[x][y] = 2; 60 } 61 62 void pop() { 63 if (!(path.top() == start)) { 64 XY &loc = path.top(); 65 MazeMap[loc.x][loc.y] = 3; 66 path.pop(); 67 } 68 } 69 70 int End() { 71 return path.top() == end; 72 } 73 74 void ThereIsAWay() { 75 XY &loc = path.top(); 76 //UP 77 if (MazeMap[loc.x - 1][loc.y] == 0) { 78 push(loc.x - 1, loc.y); 79 return; 80 } 81 //RIGHT 82 if (MazeMap[loc.x][loc.y - 1] == 0) { 83 push(loc.x, loc.y - 1); 84 return; 85 } 86 //DOWN 87 if (MazeMap[loc.x + 1][loc.y] == 0) { 88 push(loc.x + 1, loc.y); 89 return; 90 } 91 //LEFT 92 if (MazeMap[loc.x][loc.y + 1] == 0) { 93 push(loc.x, loc.y + 1); 94 return; 95 } 96 pop(); 97 return; 98 } 99 100 public: 101 102 void GenerateMap() { 103 for (int lop = 0; lop < MAZEWIDTH; lop++) { 104 for (int lop2 = 0; lop2 < MAZEHEIGHT; lop2++) { 105 MazeMap[lop][lop2] = Maze[lop][lop2]; 106 } 107 } 108 push(start); 109 } 110 111 MazeBreaker() { 112 start.x = 5; 113 start.y = 0; 114 end.x = 1; 115 end.y = 9; 116 } 117 118 void FindPath() { 119 while (!End()) { 120 ThereIsAWay(); 121 } 122 123 for (int lop = 0; lop < MAZEWIDTH; lop++) { 124 for (int lop2 = 0; lop2 < MAZEHEIGHT; lop2++) { 125 if (MazeMap[lop][lop2] == 2) { 126 cout << "O"; 127 } else if (MazeMap[lop][lop2] == 3) { 128 cout << "X"; 129 } else { 130 cout << " "; 131 } 132 } 133 cout << endl; 134 } 135 } 136 137 }; 138 139 int main() { 140 MazeBreaker mb; 141 mb.GenerateMap(); 142 mb.FindPath(); 143 return 0; 144 }
///////////以下是老版本////////////
首先是栈的头文件,注意栈结构体内容的具体定义
Stack.h
1 #ifndef _STACK_H_ 2 #define _STACK_H_ 3 4 #include<stdio.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 7 //以下两个数据大小视实际情况而定 8 //初始栈容量 9 #define STACK_INIT_SIZE 20 10 //每次扩容的增量 11 #define STACKINCREMENT 10 12 13 //迷宫地图 14 int Maze[10][10]; 15 16 //表示位置 17 struct xy 18 { 19 int x, y; 20 }; 21 typedef struct xy XY; 22 typedef XY DataType; 23 24 struct stack 25 { 26 //指向栈最顶上的元素的接下来一个位置 27 //表示新入栈的值可以放在指向的地方 28 DataType *Top; 29 //指向栈底部,最里面的元素 30 DataType *Bottom; 31 //表示了当前栈的容量 32 int stacksize; 33 }; 34 typedef struct stack STACK; 35 36 //新建栈 37 int InitStack(STACK *S); 38 39 //销毁栈 40 int DestroyStack(STACK *S); 41 42 //返回顶层元素 43 int GetTop(STACK S,int *x,int *y); 44 45 //Push操作,入栈,压栈 46 int Push(STACK *S, int x,int y); 47 48 //Pop操作,出栈 49 int Pop(STACK *S); 50 51 #endif
然后是定义
Stack.c
1 #include"Stack.h" 2 3 int InitStack(STACK *S) 4 { 5 //创建出设定长度的顺序表,地址赋给bottom指针 6 S->Bottom = (DataType*)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE*sizeof(DataType)); 7 if (!S->Bottom) 8 { 9 return 0; 10 } 11 S->stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE; 12 S->Top = S->Bottom; 13 return 1; 14 } 15 16 int DestroyStack(STACK *S) 17 { 18 S->Top = NULL; 19 free(S->Bottom); 20 S->Bottom = NULL; 21 return 1; 22 } 23 24 int GetTop(STACK S, int *x, int *y) 25 { 26 if (S.Bottom != S.Top) 27 { 28 //由于top指向的是最顶上元素的下一个位置 29 //所以取出最顶上元素的时候 30 //要把top减去1 31 *x = ((S.Top - 1)->x); 32 *y = ((S.Top - 1)->y); 33 return 1; 34 } 35 return 0; 36 } 37 38 int Push(STACK *S, int x,int y) 39 { 40 //当超出当前栈的容量时 41 //这里应该只有等于的情况 42 //而不会大于 43 if ((S->Top - S->Bottom) >= S->stacksize) 44 { 45 //realloc函数将开辟指定的储存空间 46 //并将原来的数据全部移到这个新的储存空间 47 S->Bottom = (DataType*)realloc(S->Bottom, (S->stacksize + STACKINCREMENT)*sizeof(DataType)); 48 if (!S->Bottom) 49 { 50 return 0; 51 } 52 //由于重新开辟了空间 53 //需要重新根据bottom指针的位置指定top 54 S->Top = S->Bottom + S->stacksize; 55 //最后增加当前栈容量 56 S->stacksize += STACKINCREMENT; 57 } 58 //再把入栈的数据存放好 59 (S->Top)->x = x; 60 (S->Top)->y = y; 61 S->Top++; 62 63 //在地图上将该点标为2 64 Maze[x][y] = 2; 65 return 1; 66 } 67 68 //将该点丢弃 69 int Pop(STACK *S) 70 { 71 if (S->Bottom == S->Top) 72 { 73 printf("Empty Stack!Can not pop! "); 74 return 0; 75 } 76 //top指针先减1再取值 77 --S->Top; 78 return 1; 79 }
寻路的逻辑放在了main函数里,迷宫地图的定义也在这里
main.c
二维数组Maze存放了迷宫的信息,你也可以自己改改*。
1 #include"Stack.h" 2 3 #define Up 1 4 #define Right 2 5 #define Down 3 6 #define Left 4 7 //代表已无路可走 8 //End of Road 9 #define EOR 5 10 11 //迷宫的地图 12 //墙壁表示为1,可走的地方表示为0,走过的地方表示为2 13 //入口为(4,0),出口为(0,8) 14 //可自行更改,但请确保有通路 15 16 Maze[10][10] = { 17 //0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 18 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1, //0 19 1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1, //1 20 1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,1, //2 21 1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1, //3 22 0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1, //4 23 1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1, //5 24 1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,1, //6 25 1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1, //7 26 1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1, //8 27 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 }; //9 28 29 //打印结果 30 int Print() 31 { 32 int lop, lop2; 33 for (lop = 0; lop < 10; lop++) 34 { 35 for (lop2 = 0; lop2 < 10; lop2++) 36 { 37 if (Maze[lop][lop2] == 2) 38 { 39 printf("1"); 40 } 41 else 42 { 43 printf(" "); 44 } 45 } 46 printf(" "); 47 } 48 return 1; 49 } 50 51 int GameOver(STACK s, XY *loc,XY End) 52 { 53 GetTop(s, &(loc->x), &(loc->y)); 54 if (loc->x == End.x && loc->y == End.y) 55 { 56 return 1; 57 } 58 else 59 { 60 return 0; 61 } 62 } 63 64 //1 up.2 right.3 down.4 left 65 //看看当前位置的上下左右还有没有能走的地方 66 int SearchPath(STACK s, XY loc) 67 { 68 int x, y; 69 x = loc.x; 70 y = loc.y; 71 72 //Up Available? 73 if (x != 0) 74 { 75 if (!Maze[x - 1][y]) 76 { 77 return Up; 78 } 79 } 80 //Right ? 81 if (y != 9) 82 { 83 if (!Maze[x][y + 1]) 84 { 85 return Right; 86 } 87 } 88 //Down? 89 if (x != 9) 90 { 91 if (!Maze[x + 1][y]) 92 { 93 return Down; 94 } 95 } 96 //Left? 97 if (y != 0) 98 { 99 if (!Maze[x][y - 1]) 100 { 101 return Left; 102 } 103 } 104 return EOR; 105 } 106 107 int main() 108 { 109 //储存走出迷宫的路径 110 STACK Path; 111 //储存当前位置 112 XY loc; 113 //起点终点的位置 114 XY Start = { 4,0 }, End = { 0,8 }; 115 116 InitStack(&Path); 117 //将起点入栈 118 Push(&Path, Start.x, Start.y); 119 120 //开始 121 while (!GameOver(Path, &loc, End)) 122 { 123 switch (SearchPath(Path, loc)) 124 { 125 case Up: 126 Push(&Path, loc.x - 1, loc.y); 127 break; 128 case Right: 129 Push(&Path, loc.x, loc.y + 1); 130 break; 131 case Down: 132 Push(&Path, loc.x + 1, loc.y); 133 break; 134 case Left: 135 Push(&Path, loc.x, loc.y - 1); 136 break; 137 case EOR: 138 Pop(&Path); 139 break; 140 default: 141 printf("Shit Happened! Check your code! "); 142 break; 143 } 144 } 145 Print(); 146 DestroyStack(&Path); 147 return 0; 148 }
最后运行结果如图
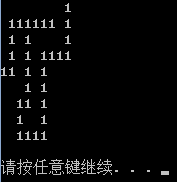
有一行多出来的1,因为打印的是走过的路径。
*如果你想自己更改迷宫地图的话,请务必记得更改相应的起点和终点(114行)