前两节讨论了那么多,这节就是两个议题,讨论了新增的日期的api,再说一说我的Java8的一些心得体会了。
首先,我们必须要搞清楚Java 8 为什么要增加新的日期的api,这是由于老的日期api非常的繁琐,使用起来非常不方便,Java作者奉行这变者通不变者死的原则,于是增加了这些api。下面,我们总点介绍这几个类——LocalDate类、LocalTime类、LocalDateTime类、DateTimeFormatter类,zoneDate类。一个个来看:
Ⅰ、LocalDate类——返回日期类。
LocalDate表示不带时区的日期,比如2000-1-1.此类的常见方法是:
getYear——返回相应的年份,
getMonth——返回相应的月份,
getDayOfMonth——返回相应的月份的某一天,
of——传递整型格式化日期。
例如我们用此类将当前日期格式化xxxx年xx月xx日,并且与相应的tostring方法就行对比。例如,请看代码:
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now(); int year = localDate.getYear(); int month = localDate.getMonthValue(); int day=localDate.getDayOfMonth(); DecimalFormat decimalFormat=new DecimalFormat("00"); System.out.println(year+"年"+decimalFormat.format(month)+"月"+decimalFormat.format(day)+"日"); System.out.println(localDate.toString());
运行结果如下:

我们看到Localdate不想calendar类中的月份的值自动少一了。
ⅡLocalTime类——返回时间类。
LocalTime表示不带时区的时间,比如04:44:50.12。常见的方法有:
getHour——返回当前所对应的小时数,
getMinute——返回当前所对应的分钟数,
getSecond——返回当前所对应的秒数,
ofxxxx——返回所对应某(小时,分钟,秒)数.
例如我们用此类将当前时间格式化xx时xx分xx秒,并且与相应的tostring方法就行对比。例如,请看代码:
LocalTime time=LocalTime.now(); DecimalFormat decimalFormat=new DecimalFormat("00"); int hour= time.getHour(); int minute=time.getMinute(); int second=time.getSecond(); System.out.println(decimalFormat.format(hour)+"时"+decimalFormat.format(minute)+"分"+decimalFormat.format(second)); System.out.println(time.toString());
运行结果如下:

从而看出LocalTime能够抛弃时区的影响。
ⅢLocalDateTime类——返回时间日期类。
他是日期日期时间中一个最重要的类,它是LocalDate和LocalTime的组合体,表示的是不带时区的日期及时间。看上去,LocalDateTime和Instant很象,但记得的是“Instant中是不带时区的即时时间点。可能有人说,即时的时间点不就是日期+时间么?看上去是这样的,但还是有所区别,比如LocalDateTime对于用户来说,可能就只是一个简单的日期和时间的概念,考虑如下的例子:两个人都在2013年7月2日11点出生,第一个人是在英国出生,而第二个是在中国北京,如果我们问他们是在什么时候出生的话,则他们看上去都是在同样的时间出生(就是LocalDateTime所表达的),但如果我们根据时间线(如格林威治时间线)去仔细考察,则会发现在出生的人会比在英国出生的人稍微早8个小时(这就是Instant所表达的概念,并且要将其转换为UTC格式的时间)。常见的方法有:
getYear——返回相应的年份,
getMonth——返回相应的月份,
getDayOfMonth——返回相应的月份的某一天,
getHour——返回当前所对应的小时数,
getMinute——返回当前所对应的分钟数,
getSecond——返回当前所对应的秒数。
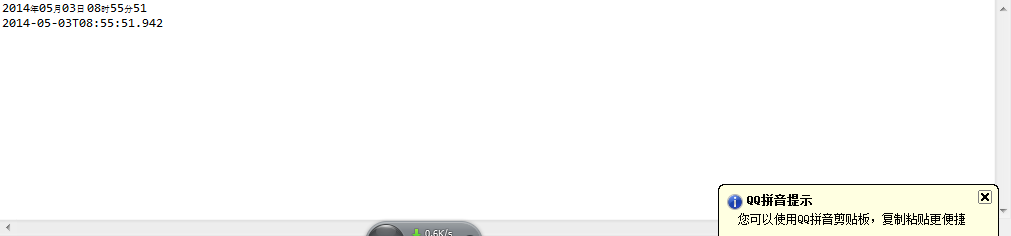
例如我们用此类将当前时间格式化xxxx年xx月xx日 xx时xx分xx秒,并且与相应的tostring方法就行对比。例如,请看代码:
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now(); int year = localDateTime.getYear(); int month = localDateTime.getMonthValue(); int day = localDateTime.getDayOfMonth(); DecimalFormat decimalFormat = new DecimalFormat("00"); int hour = localDateTime.getHour(); int minute = localDateTime.getMinute(); int second = localDateTime.getSecond(); System.out.println(year + "年" + decimalFormat.format(month) + "月" + decimalFormat.format(day) + "日" + " " + decimalFormat.format(hour) + "时" + decimalFormat.format(minute) + "分" + decimalFormat.format(second)); System.out.println(localDateTime.toString());
运行结果如下:
ⅣDateTimeFormatter类——返回日期时间格式化类。
java.text.NumberFormat不一样的是DateTimeFormatter是不可变的并且是类型安全的。常见的方法有:
format方法——将其格式化成相应的字符串。请看源代码:
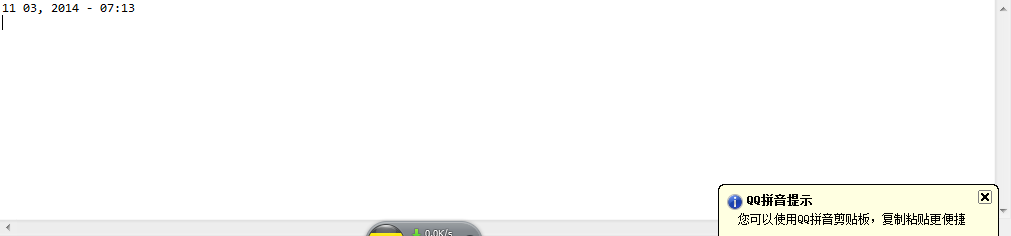
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter=DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("MM dd, yyyy - HH:mm");
LocalDateTime parsed = LocalDateTime.parse("11 03, 2014 - 07:13", dateTimeFormatter);
String string = dateTimeFormatter.format(parsed);
System.out.println(string);
运行结果如下:
这样格式化字符串更加的方便
ⅤZonedDateTime类——获取相应的时区时间,妈妈再也不用为我的时区问题发愁了。
ZonedDateTime, ZoneId -时区很重要的时候使用.
我们看个实例,获取相应时区时间:
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime= ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println(zonedDateTime.toString());
运行结果如下:

看到没有了,能够获取相应时区。十分的方便。
总之,Java8 日期的api十分方便。
java8最终总结,一些边边角角的知识拾人牙慧
反射和注解的变化
通过类型注解,我们能够在更多的地方使用注解,例如像List<@Nullable String>这样的泛型参数中。这增强了通过静态分析工具发现错误的能力,它将增强并重定义Java内置的类型系统。
Nashorn JavaScript引擎
Nashorn是一个集成到JDK中的新的、轻量级、高性能的JavaScript实现。Nashorn是Rhino的继任者,它提升了性能和内存使用情况。它将会支持javax.script API,但是它并不会支持DOM/CSS,也不会包含浏览器插件API。
java.lang、java.util等其他地方的新增功能
Java 8还向很多其他的包中添加了大量其他的功能,在本文中我们并没有提及。下面是一些值得注意的内容。可以使用ThreadLocal.withInitial(Supplier)更加简洁的声明本地线程变量。长期未兑现的StringJoiner和String.join(...)现在已经是Java 8的一部分了。比较器提供了一些新的方法能够用于链接和基于域的比较。默认的字符串池映射大小更大了,大约在25—50K。