1 MySQL相关概念介绍
MySQL为关系型数据库(Relational Database Management System), 这种所谓的"关系型"可以理解为"表格"的概念, 一个关系型数据库由一个或数个表格组成, 如图所示的一个表格:
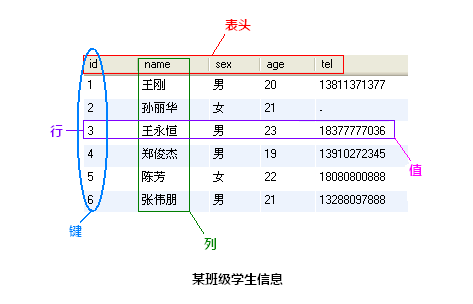
- 表头(header): 每一列的名称;
- 列(row): 具有相同数据类型的数据的集合;
- 行(col): 每一行用来描述某个人/物的具体信息;
- 值(value): 行的具体信息, 每个值必须与该列的数据类型相同;
- 键(key): 表中用来识别某个特定的人物的方法, 键的值在当前列中具有唯一性。
2 MySQL的安装配置以及服务的启停
|
windows下MySQL安装以及配置 即字符编码设置:default-character-set = gbk |
3 MySQL脚本以及数据类型
3.1 MySQL脚本
与常规的脚本语言类似, MySQL也具有一套对字符、单词以及特殊符号的使用规定, MySQL通过执行SQL语句来完成对数据库的操作, 该脚本由一条或多条MySQL语句(SQL语句 + 扩展语句)组成, 保存时脚本文件后缀名一般为.sql。在控制台下, MySQL客户端也可以对语句进行单句的执行而不用保存为.sql文件。
语句——MySQL语句是组成MySQL脚本的基本单位, 每条语句能完成特定的操作, 他是由SQL标准语句 + MySQL扩展语句组成。
函数——MySQL函数用来实现数据库操作的一些高级功能, 这些函数大致分为以下几类:字符串函数、数学函数、日期时间函数、搜索函数、加密函数、信息函数。
3.2 MySQL数据类型
MySQL有三大类数据类型, 分别为数字、日期/时间、字符串, 这三大类中又更细致的划分了许多子类型:
数字类型
整数: tinyint、smallint、mediumint、int、bigint
浮点数: float、double、real、decimal
日期和时间: date、time、datetime、timestamp、year
字符串类型:
字符串: char、varchar
文本: tinytext、text、mediumtext、longtext
二进制(可用来存储图片、音乐等): tinyblob、blob、mediumblob、longblob
4 MySQL基本操作
(1)启动、登陆数据库
启动:net start mysql(/etc/init.d/mysql start)
登陆:mysql -h 地址 -P 端口 -u 用户名 -p 密码
登陆本机:mysql -u'主机名或ip地址' -p
跳过权限验证登录:mysqld --skip-grant-tables
(2)库基本操作
查看:show databases;
使用:use [databasename];
创建:create database [name];
(3)表基本操作
查看:show tables;
创建:
create table students
(
id int not null auto_increment primary key,
name char(8) not null,
sex char(4) not null,
age tinyint unsigned not null,
tel char(13) null default "-"
);
(4)数据操作
插入:insert into students(name,sex,age,tel) values('alex','man',18,'151515151')
删除:delete from students where id =2;
修改:update students set name = 'sb' where id =1;
查询:select * from students

1 #创建数据库jumpserver,设置字符编码为utf8 2 create database jumpserver character set = utf8; 3 #使用数据库 4 use jumpserver 5 6 #创建数据表host_group(主机组表) 7 create table host_group 8 ( 9 group_id int auto_increment primary key, 10 name char(20) not null, 11 description text 12 ); 13 14 #创建数据表user_info(用户表) 15 create table user_info 16 ( 17 user_id int auto_increment primary key, 18 user_name char(20) not null, 19 user_group_id int not null, 20 foreign key(user_group_id) references host_group(group_id) 21 ); 22 23 #创建数据表host_info(主机表) 24 create table host_info 25 ( 26 host_id int auto_increment primary key, 27 host_name char(50) not null, 28 host_type char(50) not null, 29 address char(15) not null, 30 cpu_count smallint, 31 cpu_type char(20), 32 disk_count smallint, 33 size_perdisk int, 34 host_description text 35 ); 36 37 #创建数据表host_group_relation(主机与主机组关系表) 38 create table host_group_relation 39 ( 40 id int, 41 host_id int not null, 42 group_id int not null, 43 foreign key(host_id) references host_info(host_id), 44 foreign key(group_id) references host_group(group_id), 45 primary key(host_id,group_id) 46 ); 47 48 #向表host_group中插入3条数据 49 insert into host_group values 50 (1,'admin','管理员,可操作所有机器,执行任何操作'), 51 (2,'developer','程序开发人员,只能操作应用服务器'), 52 (3,'dba','数据库管理员,只能操作数据库服务器'); 53 54 #向表user_info中插入3条数据 55 insert into user_info values 56 (1,'alex',1),(2,'eric',2),(3,'tony',3); 57 58 #向表host_info中插入3条数据 59 insert into host_info (host_id,host_name,host_type,address) values 60 (1,'host1','web','192.168.1.171'), 61 (2,'host2','application','192.168.1.172'), 62 (3,'host3','db','192.168.1.173'); 63 64 #向表host_group_relation中插入5条数据 65 insert into host_group_relation values 66 (1,1,1), 67 (2,2,1), 68 (3,3,1), 69 (4,2,2), 70 (5,3,3);
更多请参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/shockerli/p/1000-plus-line-mysql-notes.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/yunf/archive/2011/04/12/2013448.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/hoojo/archive/2011/06/20/2085390.html
5 Python MySQL API
5.1 Python 操作 Mysql 模块的安装
linux:
yum install MySQL-python
window:
http://files.cnblogs.com/files/wupeiqi/py-mysql-win.zip
|
5.2 数据库操作

1 #导入Python操作MySQL的模块
2 import MySQLdb
3 #创建连接对象
4 conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='111111',db='mydb')
5 #创建游标
6 cur = conn.cursor()
7 #执行sql语句,返回影响数据库的条数(语句最后传入的是元组)
8 reCount = cur.execute('insert into UserInfo(Name,Address) values(%s,%s)',('tim','china'))
9 #同上(语句最后传入的是字典)
10 # reCount = cur.execute('insert into UserInfo(Name,Address) values(%(id)s, %(name)s)',{'id':12345,'name':'alex'})
11 #把修改提交到数据库
12 conn.commit()
13 #关闭游标
14 cur.close()
15 #关闭数据库连接
16 conn.close()

1 #导入Python操作MySQL的模块 2 import MySQLdb 3 #创建连接对象 4 conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='111111',db='mydb') 5 #创建游标 6 cur = conn.cursor() 7 #插入的数据列表 8 li =[ 9 ('name1','address1'), 10 ('name2','address2'), 11 ] 12 #执行批量插入语句 13 reCount = cur.executemany('insert into UserInfo(Name,Address) values(%s,%s)',li) 14 #把修改提交到数据库 15 conn.commit() 16 #关闭游标 17 cur.close() 18 #关闭数据库连接 19 conn.close() 20 #打印影响的数据库条数 21 print reCount

1 #导入Python操作MySQL的模块 2 import MySQLdb 3 #创建连接对象 4 conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='111111',db='mydb') 5 #创建游标 6 cur = conn.cursor() 7 #执行sql语句,返回影响数据库的条数 8 reCount = cur.execute('delete from UserInfo') 9 #把修改提交到数据库 10 conn.commit() 11 #关闭游标 12 cur.close() 13 #关闭数据库连接 14 conn.close() 15 #打印影响数据库的条数 16 print reCount

1 #导入Python操作MySQL的模块 2 import MySQLdb 3 #创建连接对象 4 conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='111111',db='mydb') 5 #创建游标 6 cur = conn.cursor() 7 #执行sql语句,返回影响数据库的条数 8 reCount = cur.execute('update UserInfo set Name = %s',('alin',)) 9 #把修改提交到数据库 10 conn.commit() 11 #关闭游标 12 cur.close() 13 #关闭数据库连接 14 conn.close() 15 #打印影响数据库的条数 16 print reCount

1 # ##########fetchone/fetchmany(num) ############## 2 #导入模块 3 import MySQLdb 4 #创建连接 5 conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='111111',db='mydb') 6 #创建游标 7 cur = conn.cursor() 8 #执行sql语句 9 reCount = cur.execute('select * from UserInfo') 10 #打印查询到得结果,fetchone每次只取一条,类似文件操作,当前指针指向下一条 11 print cur.fetchone() 12 print cur.fetchone() 13 #类似于文件操作的文件指针移动,相对移动 14 cur.scroll(-1,mode='relative') 15 print cur.fetchone() 16 print cur.fetchone() 17 #绝对移动 18 cur.scroll(0,mode='absolute') 19 print cur.fetchone() 20 print cur.fetchone() 21 #关闭游标、连接 22 cur.close() 23 conn.close() 24 #打印影响数据条数 25 print reCount 26 27 # ############ fetchall ############# 28 #导入模块 29 import MySQLdb 30 #创建连接 31 conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='111111',db='mydb') 32 #创建字典操作游标,查询返回的数据为字典形式 33 #cur = conn.cursor(cursorclass = MySQLdb.cursors.DictCursor) 34 #默认返回数据为序列形式 35 cur = conn.cursor() 36 #执行sql语句 37 reCount = cur.execute('select Name,Address from UserInfo') 38 #一次性把查询数据从内存中取出 39 nRet = cur.fetchall() 40 #关闭游标、连接 41 cur.close() 42 conn.close() 43 #打印 44 print reCount 45 print nRet 46 for i in nRet: 47 print i[0],i[1]
参考资料:
http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5095821.html
