复习
1,分页
# 利用URL携带参数page,views.py中通过request.GET来获取page参数
# utils: 放常用工具
- 在工具包utils中自定义mypage,并用其完成分页显示(推荐使用)
book_list.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Book_list</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Book List</h1>
<div class="container">
<table class="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>Title</th>
<th>Publish Date</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for book in book_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ forloop.counter }}</td>
<td>{{ book.title }}</td>
<td>{{ book.publish_date|date:'Y-m-d' }}</td> # 格式化输出日期
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<nav aria-label="Page navigation" class="text-center">
<ul class="pagination">
{{ page_html|safe }} # 取消浏览器自动转译功能
</ul>
</nav>
<script src="/static/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from app01 import models
from utils import mypage
# 用工具包utils中的自定义mypage,完成分页显示
def book_list(request):
data = models.Book.objects.all()
total_num = data.count()
current_page = request.GET.get('page')
page_obj=mypage.Page(total_num, current_page, 'book_list',per_page=20)
book_list = data[page_obj.data_start:page_obj.data_end]
page_html = page_obj.page_html()
return render(request, "book_List.html", {'book_list':book_list, 'page_html':page_html})
utils -> mypage.py. (小工具,可反复使用)
class Page(object):
"""
这是一个自定义分页类
可以实现Django ORM数据的分页展示
使用说明:
from utils import mypage
page_obj = mypage.Page(total_num, current_page, 'publisher_list')
publisher_list = data[page_obj.data_start:page_obj.data_end]
page_html = page_obj.page_html()
为了显示效果,show_page_num最好使用奇数 #当前页面highlight,左右对称排列
"""
def __init__(self, total_num, current_page, url_prefix, per_page=10, show_page_num=11):
"""
:param total_num: 数据的总条数
:param current_page: 当前访问的页码
:param url_prefix: 分页代码里a标签的前缀
:param per_page: 每一页显示多少条数据
:param show_page_num: 页面上最多显示多少个页码
"""
self.total_num = total_num
self.url_prefix = url_prefix
self.per_page = per_page
self.show_page_num = show_page_num
self.half_show_page_num = self.show_page_num // 2
total_page, more = divmod(self.total_num, self.per_page) # divmod()得到商和余数的小元组
if more:
total_page += 1
self.total_page = total_page
try:
current_page = int(current_page) # GET得到的current_page是字符串,必须要转成int才能进行后续运算操作
except Exception as e:
current_page = 1
if current_page > self.total_page:
current_page = self.total_page
if current_page < 1:
current_page = 1
self.current_page = current_page
if self.current_page - self.half_show_page_num <= 1:
page_start = 1
page_end = self.show_page_num
elif self.current_page + self.half_show_page_num >= self.total_page:
page_end = self.total_page
page_start = self.total_page - self.show_page_num + 1
else:
page_start = self.current_page - self.half_show_page_num
page_end = self.current_page + self.half_show_page_num
self.page_start = page_start
self.page_end = page_end
@property # 将方法装饰成数据属性
def data_start(self):
return (self.current_page-1)*self.per_page
@property
def data_end(self):
return (self.current_page)*self.per_page
def page_html(self):
li_list = []
li_list.append('<li><a href="/{}/?page=1">首页</a></li>'.format(self.url_prefix))
if self.current_page <= 1:
prev_html = '<li class="disabled"><a aria-label="Previous"><span aria-hidden="true">«</span></a></li>' # disabled,当在第一页时不能选前一页
else:
prev_html = '<li><a href="/{}/?page={}" aria_label="Previous"><span aria-hidden="true">«</span></a></li>'.format(
self.url_prefix,self.current_page - 1)
li_list.append(prev_html)
for i in range(self.page_start, self.page_end + 1):
if i == self.current_page:
tmp = '<li class="active"><a href="/{0}/?page={1}">{1}</a></li>'.format(self.url_prefix,i) # active,当前页highlight
else:
tmp = '<li><a href="/{0}/?page={1}">{1}</a></li>'.format(self.url_prefix,i)
li_list.append(tmp)
if self.current_page >= self.total_page:
next_html = '<li class="disabled"><a aria-label="Previous"><span aria-hidden="true">»</span></a></li>'
else:
next_html = '<li><a href="/{}/?page={}" aria_label="Previous"><span aria-hidden="true">»</span></a></li>'.format(
self.url_prefix, self.current_page + 1)
li_list.append(next_html)
li_list.append('<li><a href="/{}/?page={}">尾页</a></li>'.format(self.url_prefix,self.total_page))
page_html = "".join(li_list) # 连成一个大的字符串,传至前段,方便后续操作
return page_html
- 用Django中的分页,完成显示
views.py
# 用django中的工具,完成分页显示;功能单薄,一般不用
from django.core.paginator import Paginator,EmptyPage,PageNotAnInteger
def publisher_list(request):
data = models.Publisher.objects.all()
current_page = request.GET.get('page')
page_obj = Paginator(data,10)
try:
publisher_list = page_obj.page(current_page)
# has_next 是否有下一页
# next_page_number 下一页页码
# has_previous 是否有上一页
# previous_page_number 上一页页码
# object_list 分页之后的数据列表
# number 当前页
# paginator paginator对象
except PageNotAnInteger:
publisher_list= page_obj.page(1)
except EmptyPage:
publisher_list = page_obj.page(page_obj.num_pages)
return render(request,'publisher_list.html',{'publisher_list':publisher_list})
publisher_list.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Publisher_list</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Publisher List</h1>
<div class="container">
<table class="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>Publish Name</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for publisher in publisher_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ forloop.counter }}</td>
<td>{{ publisher.name }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
<nav aria-label="Page navigation">
<ul class="pagination">
{% if publisher_list.has_previous %}
<li>
<a href="/publisher_list/?page={{ publisher_list.previous_page_number }}" aria-label="Previous">
<span aria-hidden="true">«</span>
</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="disabled">
<a aria-label="Previous">
<span aria-hidden="true">«</span>
</a>
</li>
{% endif %}
<li class="active"><a href="#">{{ publisher_list.number }}</a></li>
{% if publisher_list.has_next %}
<li>
<a href="/publisher_list/?page={{ publisher_list.next_page_number }}" aria-label="Next">
<span aria-hidden="true">»</span>
</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="disabled">
<a aria-label="Next">
<span aria-hidden="true">»</span>
</a>
</li>
{% endif %}
</ul>
</nav>
</div>
<script src="/static/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
-
Cookie
HTTP无状态 -> Cookie
Cookie:服务端在返回响应的时候设置的,保存在浏览器上的键值对。
复习:
print(request.path_info) # 获得路径
print(request.get_full_path()) # 获得路径+参数
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="{{ request.get_full_path }}" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<p>Username: <input type="text" name = "username"></p>
<p>Password: <input type="password" name="pwd"></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="Login"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse,render,redirect
from app01 import models
from utils import mypage
# 定义一个检测是否登陆的装饰器
def check_login(func):
def wrapper(request,*args,**kwargs):
login_flag = request.get_signed_cookie("login",default="",salt="shanghais1hao") # 获取Cookie,加盐版的盐要一致
# login_flag = request.COOKIES.get("login", "")
#获取Cookie,非加盐版
# default: 默认值
# salt: 加密盐
# max_age: 后台控制过期时间
if login_flag.upper() == 'OK':
return func(request,*args,**kwargs)
else:
url = request.path_info # 获取跳转源路径
return redirect("/login/?next={}".format(url)) # 如果是从其他页面跳转来,记录下该页面,完成验证后跳转回去
return wrapper
# 用工具包utils中的自定义mypage,完成分页显示
@check_login
def book_list(request):
data = models.Book.objects.all()
total_num = data.count()
current_page = request.GET.get('page')
page_obj=mypage.Page(total_num, current_page, 'book_list',per_page=20)
book_list = data[page_obj.data_start:page_obj.data_end]
page_html = page_obj.page_html()
return render(request, "book_List.html", {'book_list':book_list, 'page_html':page_html})
def login(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request.POST.get('pwd')
if username == 'alex' and pwd =='alex':
url = request.GET.get('next') # 如果是从其他页面跳转来,跳转至该页面
if not url:
url = '/publisher_list/' # 若非从其他页面跳转来的,跳转到默认页面
rep = redirect(url)
rep.set_signed_cookie("login","ok",salt="shanghais1hao")
# 给响应设置Cookie,加密盐版
# rep.set_cookie("login", "ok")
# 给响应设置Cookie
# key, 键
# value = '', 值
# max_age = None, 超时时间
# expires = None, 超时时间(IE requires expires, so set it if hasn't been already.)
# path = '/', Cookie生效的路径, / 表示根路径,特殊的:根路径的cookie可以被任何url的页面访问
# domain = None, Cookie生效的域名
# secure = False, https传输
# httponly = False 只能http协议传输,无法被JavaScript获取(不是绝对,底层抓包可以获取到也可以被覆盖)
return rep
return render(request,"login.html")
def logout(request):
rep = redirect('/login/')
rep.delete_cookie('login') # 删除用户浏览器上之前设置的cookie值
return rep
Session
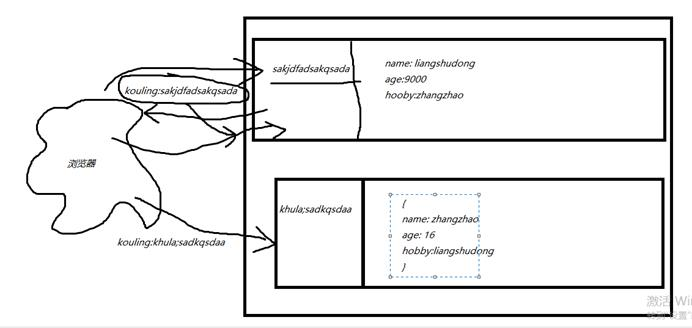
Cookie虽然在一定程度上解决了“保持状态”的需求,但是由于Cookie本身最大支持4096字节,以及Cookie本身保存在客户端,可能被拦截或窃取,因此就需要有一种新的东西,它能支持更多的字节,并且他保存在服务器,有较高的安全性。这就是Session。依赖cookie
# 用session前要现有一个数据库
1. 浏览器请求来了之后,服务端给你分配一个序号(口令)(程序级别完成)
2. 浏览器收到响应之后,把得到的口令保存在 cookie (浏览器自带)
3. 浏览器携带着刚才得到的口令,再次发送请求 (浏览器自带)
4. 服务端拿到口令,去后端根据口令找对应的数据(大字典)(程序级别完成)
views.py
def login(request):
err_msg = ""
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request.POST.get('pwd')
is_exist = models.User.objects.filter(name=username,pwd=pwd)
if is_exist:
# 登陆成功
# 1. 生成随机字符串(口令),给浏览器返回
# 2. 在服务端开辟一块空间,用来保存对应的session数据(大字典)
# 3. 在服务端开辟的空间中保存需要保存的键值对数据
request.session['login'] = 'OK'
request.session['user'] = username # 可以插入不只一条数据
request.session.set_expiry(60*60*24*14) # 两周,python支持上述写法
return redirect('/index/')
else:
err_msg = 'invalid username or password'
return render(request,'login.html',{'err_msg':err_msg})
def index(request):
# 1. 判断请求中是否携带了我下发的随机字符串(口令)
# 2. 拿着口令去后端找对应的session数据
# 3. 根据固定的key去取固定的值
login_flag = request.session.get('login')
if login_flag == 'OK':
return render(request,'index.html')
else:
return redirect('/login/')
def logout(request):
request.session.flush() # 删除当前的会话数据并删除会话的Cookie
return redirect('/login/')
总结:
# 获取、设置、删除Session中数据
request.session['k1']
request.session.get('k1',None)
request.session['k1'] = 123
request.session.setdefault('k1',123) # 存在则不设置
del request.session['k1']
# 所有 键、值、键值对
request.session.keys()
request.session.values()
request.session.items()
request.session.iterkeys()
request.session.itervalues()
request.session.iteritems()
# 会话session的key
request.session.session_key
# 将所有Session失效日期小于当前日期的数据删除
request.session.clear_expired() # session数据库中的数据不会自动清除,需手动删除
# 检查会话session的key在数据库中是否存在
request.session.exists("session_key")
# 删除当前会话的所有Session数据
request.session.delete()
# 删除当前的会话数据并删除会话的Cookie。
request.session.flush() # 推荐使用
这用于确保前面的会话数据不可以再次被用户的浏览器访问
例如,django.contrib.auth.logout() 函数中就会调用它。
# 设置会话Session和Cookie的超时时间
request.session.set_expiry(value)
* 如果value是个整数,session会在些秒数后失效。
* 如果value是个datatime或timedelta,session就会在这个时间后失效。
* 如果value是0,用户关闭浏览器session就会失效。
* 如果value是None,session会依赖全局session失效策略。
- CBV中加装饰器(Django内置的把函数装饰器转换成方法装饰器)
方式一:加载CBV视图的get或post方法上
views.py
from django import views
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
class Home(views.View):
@method_decorator(check_login)
def get(self, request):
return render(request, "home.html")
def post(self):
pass
urls.py
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^home/',views.Home.as_view()),
]
方式二:加载dispatch方法上
# 因为CBV中首先执行的就是dispatch方法,所以这么写相当于给get和post方法都加上了登录校验。
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
class HomeView(View):
@method_decorator(check_login)
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return super(HomeView, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
def get(self, request):
return render(request, "home.html")
def post(self, request):
print("Home View POST method...")
return redirect("/index/")
方式三:直接加在视图类上,但method_decorator必须传 name 关键字参数
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
@method_decorator(check_login, name="get")
@method_decorator(check_login, name="post")
class HomeView(View):
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return super(HomeView, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
def get(self, request):
return render(request, "home.html")
def post(self, request):
print("Home View POST method...")
return redirect("/index/")
CSRF Token相关装饰器(csrf_exempt,csrf_protect)
CSRF Token相关装饰器在CBV只能加到dispatch方法上
csrf_protect:为当前函数强制设置防跨站请求伪造功能,即便settings没设置全局中间件。
csrf_exempt,取消当前函数防跨站请求伪造功能,即便settings中设置了全局中间件。
views.py
from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt, csrf_protect
@csrf_exempt
def login(request):
err_msg = ""
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request.POST.get('pwd')
is_exist = models.User.objects.filter(name=username,pwd=pwd)
if is_exist:
# 登陆成功
# 1. 生成随机字符串(口令),给浏览器返回
# 2. 在服务端开辟一块空间,用来保存对应的session数据(大字典)
# 3. 在服务端开辟的空间中保存需要保存的键值对数据
request.session['login'] = 'OK'
request.session['user'] = username # 可以插入不只一条数据
request.session.set_expiry(60*60*24*14) # 两周,python支持上述写法
return redirect('/index/')
else:
err_msg = 'invalid username or password'
return render(request,'login.html',{'err_msg':err_msg})
logins.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="{{ request.get_full_path }}" method="post">
{# {% csrf_token %}#}
<p>Username: <input type="text" name = "username"></p>
<p>Password: <input type="password" name="pwd"></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="Login"></p>
<p style="color:red">{{ err_msg }}</p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
其他
有时间这片重新写 有点乱
[链接]2018年不容错过的Django全栈项目YaDjangoBlog
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33903527
https://www.cnblogs.com/liwenzhou/p/8343243.html
- 补充