曾经在公司内部做的一起关于koa源码的分享,希望对你有帮助;
koa2 源码分析整理
koa2(2.4.1版本)源码主要包含四个js,包括application.js, context.js, request.js, response.js;
一、application.js
1、介绍:入口文件,暴露Application类
module.exports =
class Application extends Emitter { // 继承Emitter类(原生events模块), 实例对象上可使用on,emit等方法进行事件监听,如抛出异常等;
/**
* Initialize a new `Application`.
*
* @api public
*/
constructor () {
super() // 继承了Emitter, 需调用super
this.proxy = false // 是否获取真正的客户端ip地址,
this.middleware = []
this.subdomainOffset = 2 // 子域名偏移设置, test.api.baidu.com, 如果设置subdomainOffset为2, 那么返回的数组值为 [“api”, “test”]
this.env = process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development'
this.context = Object.create(context) // 初始化koa自身封装的context等三个对象
this.request = Object.create(request)
this.response = Object.create(response)
}
接下来从头往下介绍几个侧重点:
(1)监听
listen (...args) {
debug('listen')
const server = http.createServer(this.callback()) // 类似原生监听,也是通过http模块创建server,不过回调函数是koa封装的callback
return server.listen(...args)
}
(2)callback
/**
* Return a request handler callback
* for node's native http server.
*
* @return {Function}
* @api public
*/
callback () {
const fn = compose(this.middleware) // 通过第三方依赖,建立中间件机制
if (!this.listeners('error').length) this.on('error', this.onerror) // 如果没有对error事件进行监听, 那么绑定error事件监听处理
const handleRequest = (req, res) => {
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res) // 将原生request和response对象进行处理,搭建(挂载)koa的全局对象,生成新的context
return this.handleRequest(ctx, fn) // 处理请求,执行中间件
}
return handleRequest
}
(3)koa-compose
- 通过compose函数(依赖三方库koa-compose)
合并app.middleware中的所有中间件处理返回一个函数
'use strict'
/**
* Expose compositor.
*/
module.exports = compose
/**
* Compose `middleware` returning
* a fully valid middleware comprised
* of all those which are passed.
*
* @param {Array} middleware
* @return {Function}
* @api public
*/
function compose (middleware) {
if (!Array.isArray(middleware)) throw new TypeError('Middleware stack must be an array!')
for (const fn of middleware) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') throw new TypeError('Middleware must be composed of functions!')
}
/**
* @param {Object} context
* @return {Promise}
* @api public
*/
return function (context, next) { // 接受koa的ctx和next作为参数,处理中间件
// last called middleware #
let index = -1 // 防止next多次调用
return dispatch(0)
function dispatch (i) {
if (i <= index) return Promise.reject(new Error('next() called multiple times'))
// 每个中间件都有属于自己的一个闭包作用域,同一个中间件的 i 是不变的,而 index 是在闭包作用域外面的, 当同一个中间件调用第二个next时,
// 此时index = 2, index > 1, 如果不加这种验证,则会执行dispatch(2)等,执行不到下一个中间件
index = i
let fn = middleware[i]
if (i === middleware.length) fn = next // 最后一个中间件执行完后,自动调取next返回一个没有任何操作的resolve,结束流程
if (!fn) return Promise.resolve()
try {
return Promise.resolve(fn(context, function next () { // 用Promise包裹中间件,方便await调用
return dispatch(i + 1) // 通过递归的方式不断的运行中间件(跳到下一个中间件进行do something),从而形成洋葱中间件模式
}))
} catch (err) {
return Promise.reject(err)
}
}
}
}
(4)createContext
- 将原生request和response对象进行处理,搭建(挂载)koa的全局对象,生成新的context
/**
* Initialize a new context.
*
* @api private
*/
createContext (req, res) {
const context = Object.create(this.context)
const request = context.request = Object.create(this.request) // ctx.request继承自原生request, 如 ctx.url = ctx.request.url,下同
const response = context.response = Object.create(this.response)
context.app = request.app = response.app = this
context.req = request.req = response.req = req
context.res = request.res = response.res = res
request.ctx = response.ctx = context
request.response = response
response.request = request
context.originalUrl = request.originalUrl = req.url
context.cookies = new Cookies(req, res, {
keys: this.keys,
secure: request.secure
})
request.ip = request.ips[0] || req.socket.remoteAddress || ''
context.accept = request.accept = accepts(req)
context.state = {}
return context // 挂载信息到koa上
}
(5)handleRequest
- 处理请求,执行中间件
/**
* Handle request in callback.
*
* @api private
*/
handleRequest (ctx, fnMiddleware) {
const res = ctx.res
res.statusCode = 404
const onerror = err => ctx.onerror(err) // koa默认的错误处理函数,处理异常结束
const handleResponse = () => respond(ctx) // 输出处理,如:http code为空如何输出,http method是head如何输出,body返回是流或json时如何输出等
onFinished(res, onerror) // 监听http response的结束事件,执行回调
return fnMiddleware(ctx).then(handleResponse).catch(onerror) // 执行中间件并监听,返回结果
}
(6)use使用中间件
use (fn) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') throw new TypeError('middleware must be a function!')
if (isGeneratorFunction(fn)) { // 依赖包is-generator-function拓展方法,验证fn是否为generator函数
deprecate('Support for generators will be removed in v3. ' +
'See the documentation for examples of how to convert old middleware ' +
'https://github.com/koajs/koa/blob/master/docs/migration.md')
fn = convert(fn) // 将koa1中的生成器函数转为Promise函数
}
debug('use %s', fn._name || fn.name || '-')
this.middleware.push(fn) // 添加中间件函数进入中间件数组
return this
}
(7) next():中间件和洋葱模型
- 洋葱模型是中间件的一种串行机制,
并且是支持异步,
第一个中间件函数中如果执行了next(),
则下一个中间件会被执行,
运行原理是基于以上提到的compose;
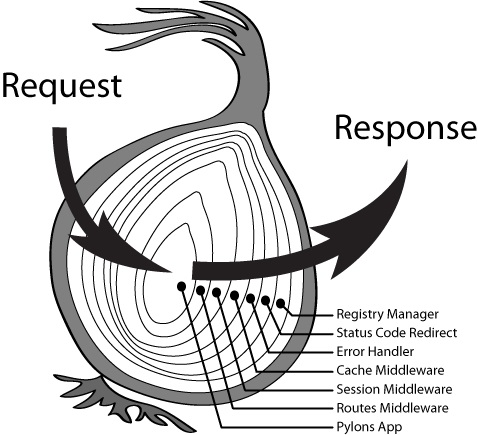
(8) 中间件特点:
- 洋葱模型
- 每个中间件都会执行两次
二、request.js、response.js
- 对原生的 http 模块的 requets 对象进行封装,提供请求相关的数据与操作,使用es6的get和set方法,重新定义并暴露api;
- request:包含了一些操作Node原生请求对象的方法,如: 获取query数据,获取请求url等;
- response: 包含了一些用于设置状态码,主体数据,header等一些用于操作响应请求的方法。
/**
* Prototype.
*/
module.exports = {
/**
* Return request header.
*
* @return {Object}
* @api public
*/
get header() {
return this.req.headers;
},
/**
* Set request header.
*
* @api public
*/
set header(val) {
this.req.headers = val;
},
三、context.js
Context中有两部分,
- 一部分是自身属性(prop),主要是应用于框架内
部使用;
/**
* Context prototype.
*/
const proto = module.exports = {
/**
* util.inspect() implementation, which
* just returns the JSON output.
*
* @return {Object}
* @api public
*/
inspect() {
if (this === proto) return this; //
return this.toJSON();
},
- 另一部分是Request和Response委托的操作方法,主要为提供给我们更方便从Request获取想要的参数和设置Response内容,它用到的是delegates三方库,他把request, response 对象上的属性方法代理到context 对象上;如: this.ctx.headersSent === this.response.headersSent
/**
* Response delegation.
*/
delegate(proto, 'response') // proto: 指向原型,即context对象
.method('attachment')
.method('redirect')
.method('remove')
.method('vary')
.method('set')
.method('append')
.method('flushHeaders')
.access('status')
.access('message')
.access('body')
.access('length')
.access('type')
.access('lastModified')
.access('etag')
.getter('headerSent')
.getter('writable');
/**
* Request delegation.
*/
delegate(proto, 'request')
.method('acceptsLanguages')
.method('acceptsEncodings')
.method('acceptsCharsets')
.method('accepts')
.method('get')
.method('is')
.access('querystring')
.access('idempotent')
.access('socket')
.access('search')
.access('method')
.access('query')
.access('path')
.access('url')
.getter('origin')
.getter('href')
.getter('subdomains')
.getter('protocol')
.getter('host')
.getter('hostname')
.getter('URL')
.getter('header')
.getter('headers')
.getter('secure')
.getter('stale')
.getter('fresh')
.getter('ips')
.getter('ip');
/**
* Delegate method `name`.
*
* @param {String} name
* @return {Delegator} self
* @api public
*/
Delegator.prototype.method = function(name){
var proto = this.proto;
var target = this.target;
this.methods.push(name);
proto[name] = function(){
return this[target][name].apply(this[target], arguments); // 绑定response方法,如context.headersSent === this.response.headersSent
};
return this;
};
/**
* Delegator getter `name`.
*
* @param {String} name
* @return {Delegator} self
* @api public
*/
Delegator.prototype.getter = function(name){
var proto = this.proto; // context
var target = this.target; // 'response'
this.getters.push(name); // 推到getters数组
proto.__defineGetter__(name, function(){
return this[target][name];
// 调用原生的__defineGetter__方法进行getter代理,那么proto[name]就相当于proto[target][name]
// context.response === response
});
四、错误处理
1、 application.js中的onerror :
绑定在 koa 实例对象上的,它监听的是整个对象的 error 事件,用来处理出错函数的堆栈打印, 方便我们进行问题定位。
onerror(err) {
// 判断 err 是否是 Error 实例
assert(err instanceof Error, `non-error thrown: ${err}`);
// 忽略 404 错误
if (404 == err.status || err.expose) return;
// 如果有静默设置, 则忽略
if (this.silent) return;
// 打印出出错堆栈
const msg = err.stack || err.toString();
console.error();
console.error(msg.replace(/^/gm, ' '));
console.error();
}
2、context.js中的onerror:
在中间函数数组生成的 Promise 的 catch 中与 res 对象的 onFinished 函数的回调应用到, 为了处理请求或响应中出现的 error 事件
onerror(err) {
// don't do anything if there is no error.
// this allows you to pass `this.onerror`
// to node-style callbacks.
// 没有错误则忽略, 不执行下面的逻辑
if (null == err) return;
// 将错误转化为 Error 实例
if (!(err instanceof Error)) err = new Error(util.format('non-error thrown: %j', err));
let headerSent = false;
if (this.headerSent || !this.writable) {
headerSent = err.headerSent = true;
}
// delegate
// 触发 koa 实例对象的 error 事件, application 上的 onerror 函数会执行
this.app.emit('error', err, this);
// nothing we can do here other
// than delegate to the app-level
// handler and log.
// 如果响应头部已经发送(或者 socket 不可写), 那么退出函数
if (headerSent) {
return;
}
// 获取 http 原生 res 对象
const { res } = this;
if (typeof res.getHeaderNames === 'function') {
res.getHeaderNames().forEach(name => res.removeHeader(name));
} else {
res._headers = {};
}
// then set those specified
this.set(err.headers);
// force text/plain
// 出错后响应类型为 text/plain
this.type = 'text';
// ENOENT support
// 对 ENOENT 错误进行处理, ENOENT 的错误 message 是文件或者路径不存在, 所以状态码应该是 404
if ('ENOENT' == err.code) err.status = 404;
// default to 500
// 默认设置状态码为 500
if ('number' != typeof err.status || !statuses[err.status]) err.status = 500;
// respond
const code = statuses[err.status];
const msg = err.expose ? err.message : code;
// 设置响应状态码
this.status = err.status;
// 设置响应 body 长度
this.length = Buffer.byteLength(msg);
// 返回 message
this.res.end(msg);
}