Shell脚本编程,严格上说是BASH编程
工具:
Vim和Emacs(主流选择),图形化的gedit和kate也是不错的选择。
vim是vi编辑器的加强升级版, 有三种模式:命令模式,末行模式,编辑模式
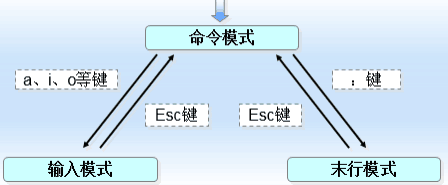
vim命令模式常用快捷键
dd:删除(剪切)光标所在整行
5dd:删除从光标开始的5行
yy:复制光标所在的整行
nyy:复制光标开始的n行
p:将之前删除(dd)或者复制(yy)过来的数据粘贴在光标后。
/字符串 :在文本中从上至下搜索该字符串。
?字符串:在文本中从下至上搜索
n:显示搜索定位到的下一个字符
N:显示搜索定位到的上一个字符
u:撤销上一步操作
vim末行模式的常用快捷键
:w 保存
:q 退出
:wq 保存退出
:q! 强制退出不保存
:wq!强制保存退出
:set nu 显示行号
:set nonu 不显示行号
:命令 执行该命令
:整数 调到该行
第一个程序:hello world
[songshichao@song dir1]$ vim helloworld #! /bin/bash ## “#!”,指定运行环境,脚本声明。 #display a line ## “#”开头是注释,
echo "Hello World" ## echo命令把其参数传递给标准输出,如果是字符串,应该用双引号把它包含起来。 [songshichao@song dir1]$ chmod +x helloworld ##为脚本加上执行权限 [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./helloworld ##执行脚本
Hello World
变量与运算符:
1.变量与赋值
[songshichao@song dir1]$ vim varible #! /bin/bash log='monday' ##“=”左右两边没有空格 echo "The value of logfile is :" echo $log ##Shell遇到$,自动替换为变量的值 [songshichao@song dir1]$ chmod +x varible [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./varible The value of logfile is : monday
变量只在其所在的脚本有效。使用source命令可以强行让脚本影响父shell环境,可以往log变量在当前Shell可见。
[songshichao@song dir1]$ echo $log [songshichao@song dir1]$ source varible The value of logfile is : monday [songshichao@song dir1]$ echo $log monday
export命令可以让脚本影响其子Shell环境。
[songshichao@song dir1]$ export count=5 ##输出变量count [songshichao@song dir1]$ bash ##启动子Shell [songshichao@song dir1]$ echo $count ##在子Shell中显示变量的值 5 [songshichao@song dir1]$ exit ##回到原先的Shell exit
unset命令手动注销一个变量
[songshichao@song dir1]$ unset log [songshichao@song dir1]$ echo $log [songshichao@song dir1]$ echo $count 5 [songshichao@song dir1]$ unset count [songshichao@song dir1]$ echo $count
2.变量替换
“$”用来解析变量,如果要输出这个符号使用转义字符“”,Shell会忽略特殊字符意义
[songshichao@song dir1]$ log='monday' [songshichao@song dir1]$ echo "The value of $log is $log" The value of $log is monday
Shell提供了“{}”来限定一个变量的开始和结束。在紧跟字母后缀的时候必须使用它
[songshichao@song dir1]$ word="big" [songshichao@song dir1]$ echo "The valus is ${word}ger" The valus is bigger
3.位置变量
Shell脚本中使用位置参数来保存参数。是一种特殊的位置变量,用于从命令行向Shell脚本传递参数 $1表示第一个参数,$2表示第二个参数,$3表示第三个以此类推,从${10}开始,参数需要用花括号括起来。${10}....${100}...。
特殊位置变量:
$0:这个变量用来存放脚本自己的名字。
$*和$@ 表示从$1开始的所有参数
$#表示包含参数的个数。
$!:上一个后台命令对应的进程号。
$?:表示最近一条命令执行后的退出状态(返回值),为10进制数,一般命令执行成功返回值为0
ongshichao@song dir1]$ vim display #! /bin/bash echo "one:$1" echo "one:$2" echo "one:$3" echo "one:$4" echo "one:$5" echo "one:$6" echo "one:$7" echo "one:$8" echo "one:$9" echo "all_one:$*" echo "all_one_num:$#" echo "$0:$0" [songshichao@song dir1]$ chmod +x display [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./display 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 one:1 one:2 one:3 one:4 one:5 one:6 one:7 one: ##因为传递了7个参数,所以$8为空 one: all_one:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 all_one_num:7 $0:./display
4.BASH引号规则
Shell脚本中的引号有三种:
双引号:阻止Shell对于大多数特殊字符(如#)进行解释,但 “ $ ” , “ ` ” , “ " ” 仍然有效。
单引号:阻止Shell对于所有的字符进行解释
倒引号:位于esc键下方,当用倒引号括起来一个Shell命令时,这个命令会被执行,执行结果作为这个表达式的值。倒引号中的特殊字符一般都解释。
[songshichao@song dir1]$ vim exam #! /bin/bash log=Saturday echo "Today is $log" echo 'Today is $log' echo "Today is `date` [songshichao@song dir1]$ chmod +x exam [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam Today is Saturday Today is $log Today is 2018年 04月 14日 星期六 15:33:02 CST
5.运算符,按优先级排列
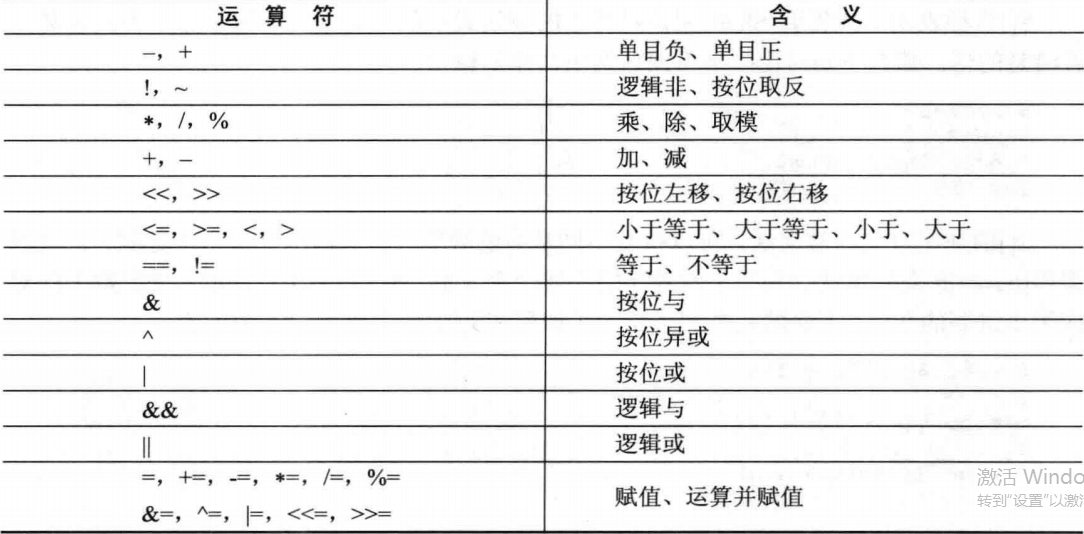
6.表达式求值,由于Shell脚本语言是一种弱类型的语言,并不能自身判断是非是数值或者字符串,所以采用$[]这种形式告诉Shell应该对其中的表达式求值。
[songshichao@song ~]$ num1=1 [songshichao@song ~]$ num=$num1+1 [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $num 1+1 [songshichao@song ~]$ num=$[ $num1 + 1 ] [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $num 2 [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $[ $num1 + 1 ] 2 [songshichao@song ~]$ num3=$[ 5 % 2 ] [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $num3 1 [songshichao@song ~]$ num3=$[ 5 - 2 ] [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $num3 3 [songshichao@song ~]$ num3=$[ 15 / 2 ] [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $num3 7
expr命令也可以执行求值操作。
[songshichao@song ~]$ expr 1 + 2 ##之间要有空格,否则按照字符串处理 3 [songshichao@song ~]$ expr 1+2 1+2
let命令用于计算整数表达式的值
[songshichao@song ~]$ num1=1 [songshichao@song ~]$ let num=$num1+1 [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $num 2
7.测试语句格式
[ 条件表达式 ],表达式两边都有空格隔开。
测试语句有文件测试、逻辑测试、整数值比较,字符串比较
文件测试:[ 操作符 文件或者目录名 ]
-d :测试是否为目录
-e:测试文件或者目录是否存在
-f :判断是否是文件
-r :测试当前用户是否有权限读取
-w:测试当前用户是否有权限写入
-x:测试当前用户是否有权限执行
[songshichao@song ~]$ [ -d ./dir1 ] [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $? 0 [songshichao@song ~]$ [ -f ./file1 ] [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $? 0 [songshichao@song ~]$ [ -e ./dir2 ] [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $? 1 ## 条件成立返回0 ,否则返回其他数值 [songshichao@song ~]$ [ -w ./file1 ] [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $? 0
逻辑测试:[ 表达式1 ] 操作符 [ 表达式2 ]
&& : 逻辑的与,而且的意思
|| : 逻辑的或,或者的意思
! : 逻辑的否
[songshichao@song ~]$ echo $USER songshichao [songshichao@song ~]$ [ $USER != root ]&&echo "not root" not root [songshichao@song ~]$ [ $USER != songshichao ]&&echo "user"||echo "root" ## 前面&&不成立,||后面才会执行 root
整数值比较:[ num1 操作符 num2 ]
-eq :判断是否等于
-ne : 判断是否不等
-gt : 判断是否大于
-lt : 判断是否小于
-le : 判断是否等于或者小于
-ge :判断是否大于或者等于
字符串比较:[ string1 操作符 string2 ]
= : 比较字符串是否相同
!= :比较字符串是否不同
-z:判断是否为空
[songshichao@song ~]$ [ -z $String ] [songshichao@song ~]$ echo $? 0 [songshichao@song ~]$ [ $LANG != en_US.UTF-8 ]&&echo "not en" not en
脚本执行语句命令和控制语句
1、if选择结构
if条件语句分为单分支结构,双分支结构和多分支结构
单分支仅由if、then、fi关键词组成,只有条件成立后执行
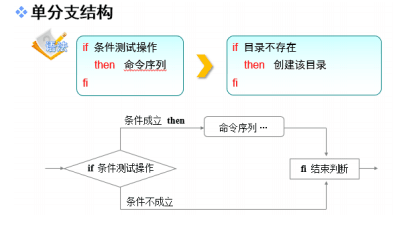
##判断目录是否存在不存在就创建 [songshichao@song ~]$ vim exam1 #!/bin/bash DIR=./dir1/dir1_2 if [ ! -e $DIR ] then mkdir -p $DIR fi [songshichao@song ~]$ cd ./dir1 [songshichao@song dir1]$ ls dir1_2 dir2
双分支是由if、then、else、fi关键词组成,做条件成立或者条件不成立的判断。

##判断指定主机能否ping通 [songshichao@song dir1]$ vim exam2 #!/bin/bash ping -c 3 -i 0.2 -W 3 $1 &> ./file_2 if [ $? -eq 0 ] then echo "host is up" else echo "host is down" fi [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam2 202.108.22.5 host is up [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam2 119.75.217.109 host is down
多分支是由if、then、elif、else、fi关键词组成,根据多种不同条件可能性执行不同分支
read命令用于将用户的输入参数赋值给指定变量,格式为:read -p [提示语句] 变量名
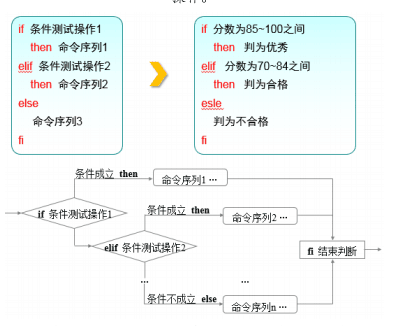
## 判断用户分数在哪个区间,判定优秀,通过,或失败
[songshichao@song dir1]$ vim exam3 #!/bin/bash read -p "Enter your score(0~100):" S if [ $S -ge 85 ]&&[ $S -le 100 ];then echo "$S is Excellent" elif [ $S -ge 70 ]&&[ $S -le 84 ];then echo "$S is Pass" else echo "Fail" fi [songshichao@song dir1]$ chmod +x exam3 [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam3 Enter your score(0~100):14 Fail [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam3 Enter your score(0~100):89 89 is Excellent [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam3 Enter your score(0~100):74 74 is Pass
2.for 条件语句
for条件语句会先读取多个不同的变量值,逐一执行同一组命令。

#从列表中获取主机地址,逐个测试是否在线
[songshichao@song dir1]$ vim exam_list 192.168.0.1 202.108.22.5 192.168.1.1 192.168.10.10 [songshichao@song dir1]$ vim exam4 #!/bin/bash HLIST=$(cat ./exam_list) for IP in $HLIST do ping -c 3 -i 0.2 -W 3 $IP &> ./file_3 if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "Host $IP is up" else echo "Host $IP is down" fi done [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam4 Host 192.168.0.1 is down Host 202.108.22.5 is up Host 192.168.1.1 is down Host 192.168.10.10 is down
3.while条件语句
用于重复测试某个条件,当条件成立的时候继续重复执行。

## 随机生成一个0~999的整数,判断用户输入的值过高或过低,正确后退出。
[songshichao@song dir1]$ vim exam5 #!/bin/bash PRICE=$(expr $RANDOM % 1000) TIMES=0 echo "Guess the price" while true do read -p "Enter the price:" INT let TIMES++ if [ $INT -eq $PRICE ];then echo "you get it" echo "use $TIMES " exit 0 elif [ $INT -gt $PRICE ];then echo "too high" else echo "too low" fi done [songshichao@song dir1]$ chmod +x exam5 [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam5 Guess the price Enter the price:78 too low Enter the price:896 too high ... Enter the price:256 too low Enter the price:258 you get it use 14
4.case条件语句
可以根据变量的不同取值,分别执行不同的命令条件。

## 输入一个字符,判断是字母,数字或者特殊字符 [songshichao@song dir1]$ vim exam6 #!/bin/bash read -p "Entry someone:" KEY case $KEY in [a-z]|[A-Z]) echo "letter" ;; [0-9]) echo "number" ;; *) echo "char" esac [songshichao@song dir1]$ chmod +x exam6 [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam6 Entry someone:8 number [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam6 Entry someone:i letter [songshichao@song dir1]$ ./exam6 Entry someone:? char
脚本执行命令
exit命令 退出脚本并且返回一个特定的值。
trap命令 用来捕获一个信号
cut命令,用来从输入的行中提取指定的部分
diff命令 用来确定两个版本的源文件之间存在哪些修改
sort命令 接受输入航并按张字母顺序进行排列
uniq命令 可以从已经排好序的输入中删除重复的行
tr命令 按照用户指定的方式对字符进行替换,并将替换后的结果在标准输出上显示(不改变源文件 )
wc命令 用来统计文件中字节,单词以及行的数量
substr命令 从字符串中提取一部分。
seq命令 用于产生一个整数数列。