引言
在OpenGL中有三种类型的光:方向光(directional)、点光(point)、聚光(spotlight)。本教程将从方向光讲起,首先我们将使用GLSL来模仿OpenGL中的光。
我们将向shader中逐渐添加环境光、散射光和高光效果。
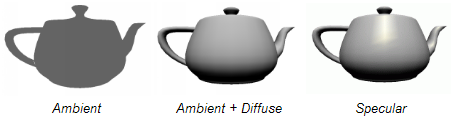
后面的教程中我们将使用逐像素光照以获得更好的效果。

接下来我们将实现逐像素的点光和聚光。这些内容与方向光很相近,大部分代码都是通用的。
在卡通着色的教程中我们接触过在GLSL中如何访问OpenGL状态中关于光源的部分,这些数据描述了每个光源的参数。
- struct gl_LightSourceParameters
- {
- vec4 ambient;
- vec4 diffuse;
- vec4 specular;
- vec4 position;
- vec4 halfVector;
- vec3 spotDirection;
- float spotExponent;
- float spotCutoff; // (range: [0.0,90.0], 180.0)
- float spotCosCutoff; // (range: [1.0,0.0],-1.0)
- float constantAttenuation;
- float linearAttenuation;
- float quadraticAttenuation;
- };
- uniform gl_LightSourceParameters gl_LightSource[gl_MaxLights];
- struct gl_LightModelParameters
- {
- vec4 ambient;
- };
- uniform gl_LightModelParameters gl_LightModel;
在GLSL中也同样可以访问材质参数:
- struct gl_MaterialParameters
- {
- vec4 emission;
- vec4 ambient;
- vec4 diffuse;
- vec4 specular;
- float shininess;
- };
- uniform gl_MaterialParameters gl_FrontMaterial;
- uniform gl_MaterialParameters gl_BackMaterial;
在OpenGL程序中,这些参数中的大部分,不论属于光源还是材质,用起来都是相似的。我们将使用这些参数实现自己的方向光。
方向光I
本节的公式来自《OpenGL编程指南》中“和光照有关的数学知识”这一章。
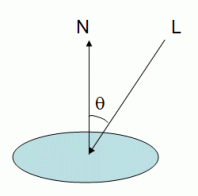
我们从散射光开始讨论。在OpenGL中假定,不管观察者的角度如何,得到的散射光强度总是相同的。散射光的强度与光源中散射光成分以及材质中散射光反射系数相关,此外也和入射光角度与物体表面法线的夹角相关。
OpenGL用下面的公式计算散射光成分:

I是反射光的强度,Ld是光源的散射成分(gl_LightSource[0].diffuse),Md是材质的散射系数(gl_FrontMaterial.diffuse)。
这个公式就是Lambert漫反射模型。Lambert余弦定律描述了平面散射光的亮度,正比于平面法线与入射光线夹角的余弦,这一理论提出已经超过200年了。
在顶点shader中要实现这个公式,需要用到光源参数中的方向、散射成分强度,还要用到材质中的散射成分值。因此使用此shader时,在OpenGL中需要像在平时一样设置好光源。注意:由于没有使用固定功能流水线,所以不需要对光源调用glEnable。
要计算余弦值,首先要确保光线方向向量(gl_LightSource[0].position)与法线向量都是归一化的,然后就可以使用点积得到余弦值。注意:对方向光,OpenGL中保存的方向是从顶点指向光源,与上面图中画的相反。
OpenGL将光源的方向保存在视点空间坐标系内,因此我们需要把法线也变换到视点空间。完成这个变换可以用预先定义的一致变量gl_NormalMatrix。这个矩阵是模型视图变换矩阵的左上3×3子矩阵的逆矩阵的转置。
以下就是上述内容的顶点shader代码:
- void main()
- {
- vec3 normal, lightDir;
- vec4 diffuse;
- float NdotL;
- /* first transform the normal into eye space and normalize the result */
- normal = normalize(gl_NormalMatrix * gl_Normal);
- /* now normalize the light's direction. Note that according to the
- OpenGL specification, the light is stored in eye space. Also since
- we're talking about a directional light, the position field is actually
- direction */
- lightDir = normalize(vec3(gl_LightSource[0].position));
- /* compute the cos of the angle between the normal and lights direction.
- The light is directional so the direction is constant for every vertex.
- Since these two are normalized the cosine is the dot product. We also
- need to clamp the result to the [0,1] range. */
- NdotL = max(dot(normal, lightDir), 0.0);
- /* Compute the diffuse term */
- diffuse = gl_FrontMaterial.diffuse * gl_LightSource[0].diffuse;
- gl_FrontColor = NdotL * diffuse;
- gl_Position = ftransform();
- }
在片断shader中要做的就是使用易变变量gl_Color设置颜色。
- void main()
- {
- gl_FragColor = gl_Color;
- }
下图显示了应用此shader的茶壶效果。注意茶壶的底部非常黑,这是因为还没有使用环境光的缘故。

加入环境光非常容易,只需要使用一个全局的环境光参数以及光源的环境光参数即可,公式如下所示:
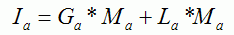
前面的顶点shader中需要加入几条语句完成环境光的计算:
- void main()
- {
- vec3 normal, lightDir;
- vec4 diffuse, ambient, globalAmbient;
- float NdotL;
- normal = normalize(gl_NormalMatrix * gl_Normal);
- lightDir = normalize(vec3(gl_LightSource[0].position));
- NdotL = max(dot(normal, lightDir), 0.0);
- diffuse = gl_FrontMaterial.diffuse * gl_LightSource[0].diffuse;
- /* Compute the ambient and globalAmbient terms */
- ambient = gl_FrontMaterial.ambient * gl_LightSource[0].ambient;
- globalAmbient = gl_FrontMaterial.ambient * gl_LightModel.ambient;
- gl_FrontColor = NdotL * diffuse + globalAmbient + ambient;
- gl_Position = ftransform();
- }
下图显示了最终效果。加入环境光后整个画面都变亮了,不过相对于应用了反射光效果的全局光照模型(global illumination model),这种计算环境光的方式只能算廉价的解决方案。

方向光II
下面介绍OpenGL方向光中的镜面反射部分。我们使用称为Blin-Phong模型的光照模型,这是Phong模型的简化版。在这之前,我们有必要先看看Phong模型,以便于更好地理解Blin-Phong模型。
在Phong模型中,镜面反射成分和反射光线与视线夹角的余弦相关,如下图:
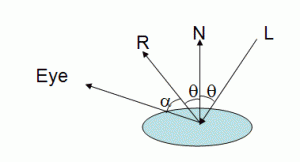
L表示入射光,N表示法线,Eye表示从顶点指向观察点的视线,R是L经镜面反射后的结果,镜面反射成分与α角的余弦相关。
如果视线正好和反射光重合,我们将接收到最大的反射强度。当视线与反射光相分离时,反射强度将随之下降,下降速率可以由一个称为shininess的因子
控制,shininess的值越大,下降速率越快。也就是说,shininess越大的话,镜面反射产生的亮点就越小。在OpenGL中这个值的范围是0
到128。

计算反射光向量的公式:
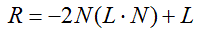
OpenGL中使用Phong模型计算镜面反射成分的公式:
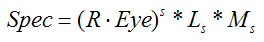
式中指数s就是shininess因子,Ls是光源中镜面反射强度,Ms是材质中的镜面反射系数。
Blinn提出了一种简化的模型,也就是Blinn-Phong模型。它基于半向量(half-vector),也就是方向处在观察向量以及光线向量之间的一个向量:
现在可以利用半向量和法线之间夹角的余弦来计算镜面反射成分。OpenGL所使用的Blinn-Phong模型计算镜面反射的公式如下:

这个方法与显卡的固定流水线中使用的方法相同。因为我们要模拟OpenGL中的方向光,所以在shader中也使用此公式。幸运的是:OpenGL会帮我们算半向量,我们只需要使用下面的代码:
- /* compute the specular term if NdotL is larger than zero */
- if (NdotL > 0.0)
- {
- // normalize the half-vector, and then compute the
- // cosine (dot product) with the normal
- NdotHV = max(dot(normal, gl_LightSource[0].halfVector.xyz),0.0);
- specular = gl_FrontMaterial.specular * gl_LightSource[0].specular *
- pow(NdotHV,gl_FrontMaterial.shininess);
- }
完整的Shader Designer工程下载:
http://lighthouse3d.com/wptest/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/ogldirsd.zip