1、vue响应式原理流程图概览
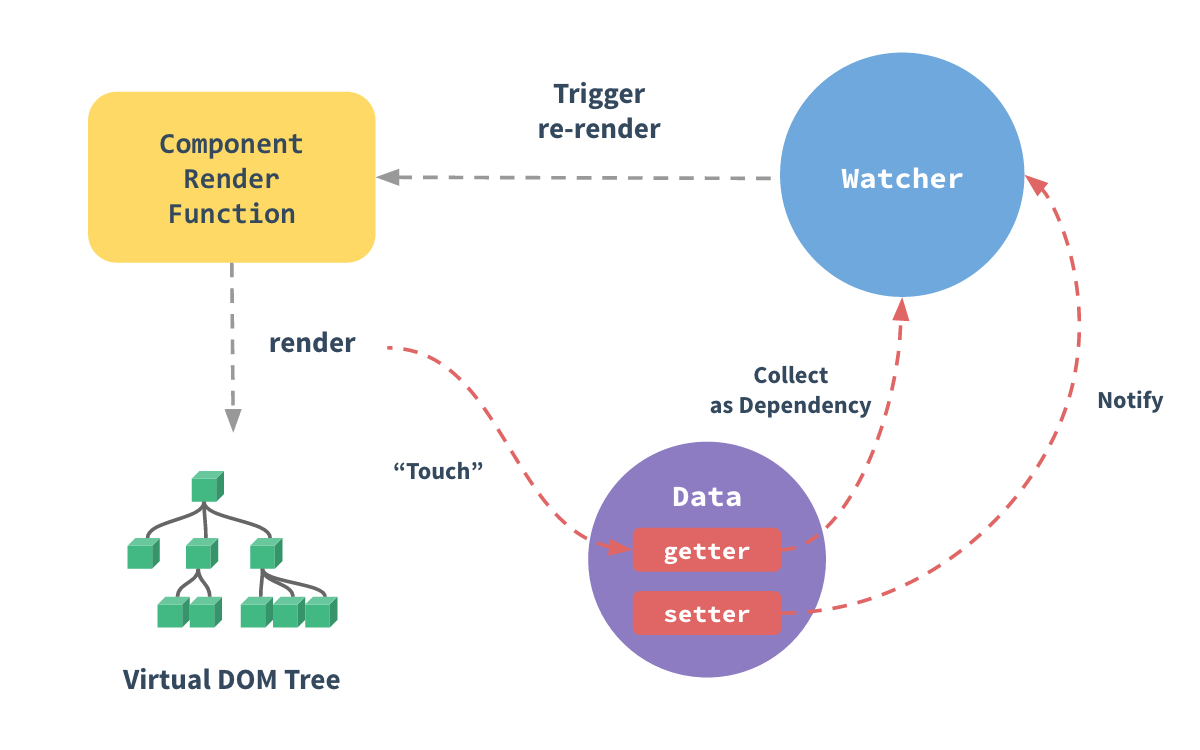
2、具体流程
(1)vue示例初始化(源码位于instance/index.js)
import { initMixin } from './init'
import { stateMixin } from './state'
import { renderMixin } from './render'
import { eventsMixin } from './events'
import { lifecycleMixin } from './lifecycle'
import { warn } from '../util/index'
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
响应式相关的是“stateMixin”。
(2)、state.js(源码位于instance/state.js)
与响应式有关的是:
function initData (vm: Component) {
let data = vm.$options.data
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {}
if (!isPlainObject(data)) {
data = {}
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'data functions should return an object:
' +
'https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#data-Must-Be-a-Function',
vm
)
}
// proxy data on instance
const keys = Object.keys(data)
const props = vm.$options.props
const methods = vm.$options.methods
let i = keys.length
while (i--) {
const key = keys[i]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (methods && hasOwn(methods, key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a data property.`,
vm
)
}
}
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`The data property "${key}" is already declared as a prop. ` +
`Use prop default value instead.`,
vm
)
} else if (!isReserved(key)) {
proxy(vm, `_data`, key)
}
}
// observe data
observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
}
在initData中实现了2个功能:
(2).1 将data中的对象代理(proxy)到_data上
说明proxy函数也是使用的Object.defineProperty,
export function proxy (target: Object, sourceKey: string, key: string) {
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = function proxyGetter () {
return this[sourceKey][key]
}
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function proxySetter (val) {
this[sourceKey][key] = val
}
Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition)
}
也就是说vm._data.变量都是响应式数据(即vm.变量)。
(2).2 将data中的数据变为响应式数据,即
// observe data
observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
(3)observe类
第(2)步的observe函数:
export function observe (value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
let ob: Observer | void
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__
} else if (
shouldObserve &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
ob = new Observer(value)
}
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++
}
return ob
}
调用了Observer类:
现在看Observer的构造函数和walk方法:
constructor (value: any) {
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep()
this.vmCount = 0
def(value, '__ob__', this)
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
const augment = hasProto
? protoAugment
: copyAugment
augment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
this.observeArray(value)
} else {
this.walk(value)
}
}
/**
* Walk through each property and convert them into
* getter/setters. This method should only be called when
* value type is Object.
*/
walk (obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i])
}
}
需要说明的是,并不是data中的所有数据都会变成响应式的。
请看例子:
new Vue({
template:
`<div>
<span>text1:</span> {{text1}}
<span>text2:</span> {{text2}}
<div>`,
data: {
text1: 'text1',
text2: 'text2',
text3: 'text3'
}
});
data中text3并没有被模板实际用到,为了提高代码执行效率,我们没有必要对其进行响应式处理,因此,依赖收集简单点理解就是收集只在实际页面中用到的data数据,即text1和text2。
2019.3.8 修正

Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify()
}
defineReactive函数中会用到Dep类来收集依赖(dep.depend())以及当数据变化时触发更新(dep.notify())。
(4)Dep类
export default class Dep {
static target: ?Watcher;
id: number;
subs: Array<Watcher>;
constructor () {
this.id = uid++
this.subs = []
}
addSub (sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
removeSub (sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub)
}
depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
notify () {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
const subs = this.subs.slice()
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
// subs aren't sorted in scheduler if not running async
// we need to sort them now to make sure they fire in correct
// order
subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id)
}
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update()
}
}
}
Dep类的构造函数中的subs是Watcher(观察者)类。vue实例中data的一个值,可以添加多个Watcher,同时这个值变化的时候也是触发这多个Watcher的更新。
(5)Watcher类
Watcher类主要用来收集依赖和触发更新。
Watcher类也是实现了$watch(),即:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#watch
(6)Observer、Dep和Watcher类关系

Observer类是书店(vue实例的data对象),里面有好多书(Dep类),每本书可以被订阅(Watcher类)。
当某一本书更新时,订阅的Watcher类会收到通知,进而更新书店内容(vue实例的data对象)。
Dep类是Observer类和Watcher类链接的桥梁。