今天要介绍的是List接口中最常用的实现类——ArrayList,本篇的源码分析基于JDK8,如果有不一致的地方,可先切换到JDK8后再进行操作。
本篇的内容主要包括这几块:
1.源码结构介绍
2.源代码展示
3.要点说明
4.优缺点说明
一、源码结构介绍
ArrayList的源码跟之前的接口源码比起来,那可就不能同日而语了,一千多行代码,如果直接看的话确实有些费劲,但仔细看看就会发现,其实大致结构是这样的:
其中包含了好四个内部类:
ArrayListSpliterator:ArrayList可分割的迭代器,基于二分法的可分割迭代器,是为了并行遍历元素而设计的一种迭代器,jdk1.8 中的集合框架中的数据结构都默认实现了 spliterator。
Itr:实现Iterator接口的迭代器,为ArrayList进行优化。
ListItr:实现ListIterator接口的迭代器,为ArrayList进行优化。
SubList:实现了AbstractList和RandomAccess接口的子列表。
这四个内部类就占了将近一半的篇幅,足可见其重要性。这四个类中前三个都是跟迭代器有关,最后一个是为了处理局部列表而设计的子列表类。
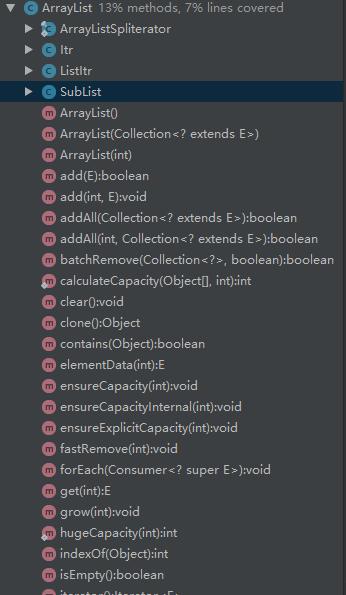
二、源代码展示:
下面是蹩脚翻译讲解版的源码:
/** * ArrayList 是List接口的动态数组实现,实现了List的所有可选操作,并且允许所有元素,包括null。 * ArrayList 跟Vector差不多,但它不是线程安全的。 * ArrayList 的容量会根据列表大小自动调整。在添加大量元素之前,可以使用ensureCapacity 方法来保证列表有足够空间存放元素。 * ArrayList 不是线程安全的,所以如果多条线程将要对其进行结构性改变时(如添加删除元素),需要使用synchronized 进行同步。 * 如果不存在这样的对象,则需要使用其同步包装类 Collections.synchronizedList * List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...)); * * iterator() 方法将会返回一个listIterator,其中的方法是“fail-fast(快速失败的)”,如果在创建了迭代器之后,在用迭代器遍历一个列表时, * 如果遍历过程中对集合对象的内容进行了修改(增加、删除、修改),则会抛出Concurrent Modification Exception。 * 但fail-fast 的行为是无法得到保证的,不可能对是否出现不同步并发修改做出任何硬性保证。 * 快速失败迭代器会尽最大努力抛出 ConcurrentModificationException。 * 因此,为提高这类迭代器的正确性而编写一个依赖于此异常的程序是错误的做法:迭代器的快速失败行为应该仅用于检测 bug。 */ public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; /** * 默认容量 */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; /** * 空实例共享的空数组 * todo 为什么要区分 EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 与 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA */ private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * 默认大小的空实例共享的空数组 */ private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * ArrayList的元素存储在其中的数组缓冲区。ArrayList的容量是这个数组缓冲区的长度。 * 当添加第一个元素时,任何为 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 的空ArrayList的容量 * 将扩充到默认大小DEFAULT_CAPACITY(10)。 * 设置为非private 是为了方便内部类进行访问 * * todo 内部动态数组的维护 */ transient Object[] elementData; /** * 列表中实际存储的元素个数 * * todo size 与 capacity */ private int size; /** * 构造一个指定初始容量的空列表 */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } /** * 构造一个默认容量的空列表 */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } /** * 构造一个包含集合C中所有元素的列表,存储顺序为集合C迭代器遍历的顺序 */ public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // replace with empty array. this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } } /** * 调整容量大小到列表当前元素个数,以节约存储空间 */ public void trimToSize() { //todo modCount的作用 modCount++; if (size < elementData.length) { elementData = (size == 0) ? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA : Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } } /** * 增加列表容量以确保它至少能容纳指定数量的元素 * * todo 扩容方式 */ public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { //最小扩容量 //如果elementData是空数组则最小扩容量为0,否则最小扩容量为10 int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) ? 0 : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; //如果指定的容量比最小扩容量大,则进行扩容操作 if (minCapacity > minExpand) { ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } } private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // overflow-conscious code if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } /** * 数组容量最大值(- 8 是因为部分 JVM 需要在数组中存入部分头信息) */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /** * 扩容函数,扩容1.5 倍,扩容后的列表大小在minCapacity与1.5 倍原大小之间取最大值 */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // >> 是右移运算符,作用结果是将原数值的二进制数右移指定位数,转换成十进制的效果 // 就是除以2的指定次方,这里右移一位即除以2 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } /** * 元素个数 */ public int size() { return size; } /** * 是否为空 */ public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } /** * 是否包含某个元素 */ public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; } /** * 查找元素第一次出现的位置 */ public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } /** * 查找元素最后一次出现的位置 */ public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } /** * 返回一个深克隆对象 */ public Object clone() { try { // Object 的克隆方法,复制本对象及其内所有基本类型成员和 String 类型成员 // 但不会复制引用对象 ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone(); v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); v.modCount = 0; return v; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable throw new InternalError(e); } } /** * 转化成对象数组 */ public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } /** * 将列表转存到数组a中,如果a的空间足够则直接存放,否则会新建一个数组进行存储 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { if (a.length < size) // Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents: return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass()); System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size); if (a.length > size) a[size] = null; return a; } // 位置访问操作 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E elementData(int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; } /** * 取序号为index的元素 */ public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } /** * 替换指定位置的元素,并返回原来的元素 */ public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } /** * 添加元素 */ public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } /** * 插入元素 */ public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } /** * 移除指定序号的元素 */ public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; } /** * 移除某个元素 */ public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } /* * 快速移除 */ private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) //调用System.arraycopy 进行数组拷贝 //四个参数分别是:待拷贝的数组,原数组的拷贝起始位置,拷贝到的目标数组,目标数组的起始位置 //这里相当于把原数组的一部分拷贝到另一部分,将数组从index+1以后的部分整体往前移一个单位 //将index那个元素覆盖掉 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); //然后将最后一个元素置为null elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work } /** * 移除所有元素(将所有元素置为null,容量不变) */ public void clear() { modCount++; // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0; } /** * 将集合C中的所有元素添加到列表中 */ public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { //先将c转换为数组,然后再复制过来 Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } /** * 将集合C中的元素插入指定位置 */ public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } /** * 范围性移除,移除列表里序号从fromIndex到toIndex的所有元素,包含fromIndex,不包含toIndex */ protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - toIndex; System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex, numMoved); // 将其余位置置为null int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex); for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) { elementData[i] = null; } size = newSize; } /** * 检测index是否超过边界 */ private void rangeCheck(int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } /** * 插入时边界检测 */ private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } /** * 生成 IndexOutOfBoundsException 的详细信息 */ private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size; } /** * 移除列表中所有存在于集合c中的元素 */ public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, false); } /** * 仅保留所有在集合C中的元素 */ public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, true); } private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; int r = 0, w = 0; boolean modified = false; try { for (; r < size; r++) if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; } finally { if (r != size) { System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r); w += size - r; } if (w != size) { // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = w; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; modCount += size - w; size = w; modified = true; } } return modified; } /** * 将列表实例保存到输出流(即序列化) */ private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException{ int expectedModCount = modCount; s.defaultWriteObject(); s.writeInt(size); for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { s.writeObject(elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } /** * 从输入流中读取列表实例 */ private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; s.defaultReadObject(); s.readInt(); // ignored if (size > 0) { int capacity = calculateCapacity(elementData, size); SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity); ensureCapacityInternal(size); Object[] a = elementData; // Read in all elements in the proper order. for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { a[i] = s.readObject(); } } } /** * 返回一个从指定序号元素开始的ListIterator */ public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { if (index < 0 || index > size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index); return new ListItr(index); } /** * 返回一个ListIterator */ public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { return new ListItr(0); } /** * 返回一个Iterator */ public Iterator<E> iterator() { return new Itr(); } /** * 优化版本的Iterator * todo 迭代器中modCount的作用 */ private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; // index of next element to return int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such int expectedModCount = modCount; Itr() {} public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) { Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); final int size = ArrayList.this.size; int i = cursor; if (i >= size) { return; } final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]); } // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic cursor = i; lastRet = i - 1; checkForComodification(); } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } /** * 优化版的ListIterator */ private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> { ListItr(int index) { super(); cursor = index; } public boolean hasPrevious() { return cursor != 0; } public int nextIndex() { return cursor; } public int previousIndex() { return cursor - 1; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E previous() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor - 1; if (i < 0) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } public void set(E e) { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e); } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } public void add(E e) { checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor; ArrayList.this.add(i, e); cursor = i + 1; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } } /** * 获取从 fromIndex 到 toIndex 之间的子集合 * 如果fromIndex == toIndex,则返回的空集合。对该子集合的操作,会影响原有集合。 */ public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex); } /** * 检查传入索引的合法性 */ static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) { if (fromIndex < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex); if (toIndex > size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex); if (fromIndex > toIndex) throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")"); } /** * 内部类——子列表 */ private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess { private final AbstractList<E> parent; private final int parentOffset; private final int offset; int size; SubList(AbstractList<E> parent, int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) { this.parent = parent; this.parentOffset = fromIndex; this.offset = offset + fromIndex; this.size = toIndex - fromIndex; this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; } public E set(int index, E e) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index); ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e; return oldValue; } public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index); } public int size() { checkForComodification(); return this.size; } public void add(int index, E e) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); checkForComodification(); parent.add(parentOffset + index, e); this.modCount = parent.modCount; this.size++; } public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index); this.modCount = parent.modCount; this.size--; return result; } protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { checkForComodification(); parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex, parentOffset + toIndex); this.modCount = parent.modCount; this.size -= toIndex - fromIndex; } public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(this.size, c); } public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); int cSize = c.size(); if (cSize==0) return false; checkForComodification(); parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c); this.modCount = parent.modCount; this.size += cSize; return true; } public Iterator<E> iterator() { return listIterator(); } public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) { checkForComodification(); rangeCheckForAdd(index); final int offset = this.offset; return new ListIterator<E>() { int cursor = index; int lastRet = -1; int expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != ArrayList.SubList.this.size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= ArrayList.SubList.this.size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (offset + i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)]; } public boolean hasPrevious() { return cursor != 0; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E previous() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor - 1; if (i < 0) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (offset + i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i; return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)]; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) { Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); final int size = ArrayList.SubList.this.size; int i = cursor; if (i >= size) { return; } final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (offset + i >= elementData.length) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { consumer.accept((E) elementData[offset + (i++)]); } // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic lastRet = cursor = i; checkForComodification(); } public int nextIndex() { return cursor; } public int previousIndex() { return cursor - 1; } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.SubList.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } public void set(E e) { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this.set(offset + lastRet, e); } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } public void add(E e) { checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor; ArrayList.SubList.this.add(i, e); cursor = i + 1; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } final void checkForComodification() { if (expectedModCount != ArrayList.this.modCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }; } public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); return new ArrayList.SubList(this, offset, fromIndex, toIndex); } private void rangeCheck(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { if (index < 0 || index > this.size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size; } private void checkForComodification() { if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.modCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } public Spliterator<E> spliterator() { checkForComodification(); return new ArrayList.ArrayListSpliterator<E>(ArrayList.this, offset, offset + this.size, this.modCount); } } /** * 遍历 */ @Override public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); final int expectedModCount = modCount; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData; final int size = this.size; for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { action.accept(elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } /** * 创建一个分割器 */ @Override public Spliterator<E> spliterator() { return new ArrayList.ArrayListSpliterator<>(this, 0, -1, 0); } /** 基于索引的、二分的、懒加载的分割器*/ static final class ArrayListSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> { //用于存放ArrayList对象 private final ArrayList<E> list; //起始位置(包含),advance/split操作时会修改 private int index; //结束位置(不包含),-1 表示到最后一个元素 private int fence; //用于存放list的modCount,当fence被设值后初始化 private int expectedModCount; /** 创建一个范围性的分割器 */ ArrayListSpliterator(ArrayList<E> list, int origin, int fence, int expectedModCount) { this.list = list; // OK if null unless traversed this.index = origin; this.fence = fence; this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount; } //在第一次使用时实例化结束位置 private int getFence() { int hi; ArrayList<E> lst; if ((hi = fence) < 0) { if ((lst = list) == null) hi = fence = 0; else { expectedModCount = lst.modCount; hi = fence = lst.size; } } return hi; } /** * 分割list,返回一个新分割出的spliterator实例,相当于二分法,这个方法会递归 * 1.ArrayListSpliterator本质上还是对原list进行操作,只是通过index和fence来控制每次处理范围 * 2.ArrayListSpliterator在遍历元素时,不能对list进行结构变更操作,否则抛错。 */ public ArrayList.ArrayListSpliterator<E> trySplit() { int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1; return (lo >= mid) ? null : // divide range in half unless too small new ArrayList.ArrayListSpliterator<E>(list, lo, index = mid, expectedModCount); } /** * 返回true 时,只表示可能还有元素未处理 * 返回false 时,没有剩余元素需要处理 */ public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) { if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hi = getFence(), i = index; if (i < hi) { index = i + 1; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)list.elementData[i]; action.accept(e); if (list.modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); return true; } return false; } /** * 顺序遍历处理所有剩下的元素 */ public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop ArrayList<E> lst; Object[] a; if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); if ((lst = list) != null && (a = lst.elementData) != null) { if ((hi = fence) < 0) { mc = lst.modCount; hi = lst.size; } else mc = expectedModCount; if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) { for (; i < hi; ++i) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i]; action.accept(e); } if (lst.modCount == mc) return; } } throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } /** * 估算大小 */ public long estimateSize() { return (long) (getFence() - index); } /** * 获取特征值 */ public int characteristics() { return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED; } } /** * 条件过滤 */ @Override public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) { Objects.requireNonNull(filter); // figure out which elements are to be removed // any exception thrown from the filter predicate at this stage // will leave the collection unmodified int removeCount = 0; final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size); final int expectedModCount = modCount; final int size = this.size; for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final E element = (E) elementData[i]; if (filter.test(element)) { removeSet.set(i); removeCount++; } } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } // shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0; if (anyToRemove) { final int newSize = size - removeCount; for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) { i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i); elementData[j] = elementData[i]; } for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) { elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work } this.size = newSize; if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } modCount++; } return anyToRemove; } /** * 全部替换 */ @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) { Objects.requireNonNull(operator); final int expectedModCount = modCount; final int size = this.size; for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { elementData[i] = operator.apply((E) elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } modCount++; } /** * 用外部比较器来排序 */ @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) { final int expectedModCount = modCount; Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c); if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } modCount++; } }
讲真,我已经尽力了。
三、要点说明
这部分主要根据上面的源码进行说明,如果有不太清楚的地方,可以返回上面的源码进行查看。
1.ArrayList 其实只是内部维护了一个数组,通过暴露出方便操作的接口来简化操作。
2.ArrayList中,size和capacity是两码事,size表示列表中实际存储的元素个数,一般小于内部数组长度,而capacity表示容量,即内部数组的长度。
3.ArrayList中,默认的大小是10,当你使用new ArrayList();时并不会立即为数组分配大小为10的空间,而是等插入第一个元素时才会真正分配,这样做是为了节约内存空间。
4.由于上述目的的存在,为了区分默认列表和空列表,设置了两个空数组常量,EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA和DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,这样在扩容时就能进行不同的处理。
5.维护内部数组时,使用的是Arrays.copyOf()方法和System.arraycopy()方法。
6.里面有多处使用modCount,这个变量其实是继承自父类AbstractList,用来标识列表内部数组大小被修改的次数(如add,trimToSize等操作可能会触发),元素的替换并不会改变它的值,迭代器的“fail-fast”机制跟这个modCount变量紧密相关,一般会在操作前赋值一次 expectedModCount = modCount; 在操作执行完之后再进行一次检测,如果仍相等,说明结构未改变,否则将抛出异常,这也就是为什么上一篇中ArrayList修改过之后,操作迭代器会抛出异常的原因。
7.在扩容时,默认的扩容因子是1.5,每次需要扩容时,会将原数组大小的1.5倍和实际需要的数组空间进行比较,从中取最大值作为数组大小。然后新建一个数组,把原数组中的所有元素复制到新数组中去。所以扩容其实是最耗费时间的操作,不仅仅需要重新分配空间,而且需要重新赋值。
8.因为ArrayList的方法操作的都是同一个内部数组,而所有方法都没有加锁,没有同步机制,所以它是线程不安全的。
9.ArrayList中可以存放null值,可以在源码中看到,在比较时对null值都进行了处理。
四、优缺点说明
因为列表其实是内部维护管理着一个数组,所以数组的优点它都具备。当然,数组的缺点它同样也存在。
数组是将元素在内存中连续存放,由于每个元素占用内存相同,可以通过下标迅速访问数组中任何元素。但是如果要在数组中增加一个元素,需要移动大量元素,在内存中空出一个元素的空间,然后将要增加的元素放在其中。同样的道理,如果想删除一个元素,同样需要移动大量元素去填掉被移动的元素。
但是列表在维护这个内部数组时,还是花了一点心思的,比如使用capacity的概念来减少数组结构改变的次数,所以并不会每次add操作都导致结构改变。将扩容因子选为1.5而不是2,也是为了在满足需求的前提下尽可能的节约空间,但如果事先就知道元素的大概个数时,最好先在构造器中设置好列表的容量,这样就可以省掉不少扩容时的开销。
呼。这篇准备了两天才搞定,希望能够帮助到大家,如果有什么遗漏或者讲的不够清晰的地方,欢迎指出,如果有说错的知识点,也请不要吝啬,欢迎指正。
看在我这样辛勤耕作的份上,动动小手点个赞吧,也欢迎关注我的博客,后续还会持续更新。