Mophues
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 327670/327670 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1922 Accepted Submission(s): 791
Problem Description
As we know, any positive integer C ( C >= 2 ) can be written as the multiply of some prime numbers:
C = p1×p2× p3× ... × pk
which p1, p2 ... pk are all prime numbers.For example, if C = 24, then:
24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3
here, p1 = p2 = p3 = 2, p4 = 3, k = 4
Given two integers P and C. if k<=P( k is the number of C's prime factors), we call C a lucky number of P.
Now, XXX needs to count the number of pairs (a, b), which 1<=a<=n , 1<=b<=m, and gcd(a,b) is a lucky number of a given P ( "gcd" means "greatest common divisor").
Please note that we define 1 as lucky number of any non-negative integers because 1 has no prime factor.
C = p1×p2× p3× ... × pk
which p1, p2 ... pk are all prime numbers.For example, if C = 24, then:
24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3
here, p1 = p2 = p3 = 2, p4 = 3, k = 4
Given two integers P and C. if k<=P( k is the number of C's prime factors), we call C a lucky number of P.
Now, XXX needs to count the number of pairs (a, b), which 1<=a<=n , 1<=b<=m, and gcd(a,b) is a lucky number of a given P ( "gcd" means "greatest common divisor").
Please note that we define 1 as lucky number of any non-negative integers because 1 has no prime factor.
Input
The first line of input is an integer Q meaning that there are Q test cases.
Then Q lines follow, each line is a test case and each test case contains three non-negative numbers: n, m and P (n, m, P <= 5×105. Q <=5000).
Then Q lines follow, each line is a test case and each test case contains three non-negative numbers: n, m and P (n, m, P <= 5×105. Q <=5000).
Output
For each test case, print the number of pairs (a, b), which 1<=a<=n , 1<=b<=m, and gcd(a,b) is a lucky number of P.
Sample Input
2
10 10 0
10 10 1
Sample Output
63
93
http://blog.csdn.net/wh2124335/article/details/11846661 转载自此
记录一下自己的思路
未简化过的代码核心应该是这样的
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)//枚举每个因子 if(d[i]<=k)//如果因子的素数质因子小于等于k for(int j=i;j<=n;j+=i) ans+=u(j/i)*(n/i)*(m/i)//枚举F(i);
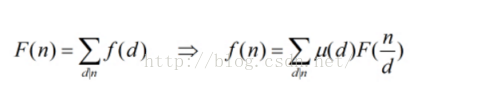
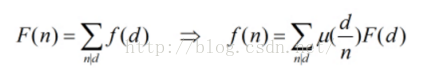
利用的是第二个,然后可以发现,对于每个数字i,他的倍数j的系数都要加上u[j/i],可以与处理出来U(N),其中U(i)就是u[i/第一个因子]+u[i/第二个因子]+....(这里的U先不考虑素因子个数限制)
那么上述式子就可以化简成为
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) ans+=U(i)*(n/i)*(m/i);//直接枚举
然后U(i)考虑素因子个数限制的话,那么显然预处理也是可以搞出来的,详细见代码,代码里的cnt[N][19]就是U考虑限制的。
然后就是普通的分块操作,为了简化时间,因为W=(n/i)*(m/i),i倘若在一定范围内,这个W是不变的,所以可以加速。
所以最后就是这样了
for(int i=1,last=i;i<=n;i=last+1){ last=min(n/(n/i),m/(m/i)); ans+=(ll)(cnt[last][k]-cnt[i-1][k])*(n/i)*(m/i); }
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; const int maxn = 500100; typedef long long ll; int mu[maxn],sum[maxn],num[maxn]; ll cnt[maxn][19]; bool flag[maxn]; vector<int>prime; void init(){ mu[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<maxn;i++){ if(!flag[i]){ prime.push_back(i); mu[i]=-1; num[i]=1; } for(int j=0;j<prime.size()&&i*prime[j]<maxn;j++){ flag[i*prime[j]]=true; num[i*prime[j]]=num[i]+1; if(i%prime[j])mu[i*prime[j]]=-mu[i]; else {mu[i*prime[j]]=0;break;} } } for(int i=1;i<maxn;i++){ for(int j=i;j<maxn;j+=i){ cnt[j][num[i]]+=mu[j/i]; } } for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++){ for(int j=1;j<19;j++){ cnt[i][j]+=cnt[i][j-1]; } } for(int i=1;i<maxn;i++){ for(int j=0;j<19;j++){ cnt[i][j]+=cnt[i-1][j]; } } } int main(){ init(); int q; scanf("%d",&q); while(q--){ int n,m,k; scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k); k=min(k,18); ll ans=0; if(n>m)swap(n,m); for(int i=1,last=i;i<=n;i=last+1){ last=min(n/(n/i),m/(m/i)); ans+=(ll)(cnt[last][k]-cnt[i-1][k])*(n/i)*(m/i); } //printf("%lld ",ans); printf("%I64d ",ans); } }